Custom Validator in Angular
January 14, 2024
On this page, we will learn to create custom validators for reactive form and template-driven form in our Angular application.
1. For reactive form, we create a validator function that returns either
ValidatorFn or AsyncValidatorFn. The ValidatorFn is used for sync validator function and AsyncValidatorFn is used for async validator function.
2. For template-driven form, we create a validator class directive by implementing either
Validator interface or AsyncValidator interface. The Validator interface is used for sync validator and AsyncValidator interface is used for async validator.
3. The sync validator takes a control instance and returns either a set of validation errors or null. The sync validators validate user input immediately. Sync validator functions are passed as second argument of
FormControl for reactive form. Sync validator directives are used as attribute of HTML input elements or as property binding to pass any value in template-driven form.
4. The async validator takes a control instance and returns
Observable or Promise that later emits either a set of validation errors or null. Async validator functions are passed as third argument of FormControl. Async validator directives are used as attribute of HTML input elements or as property binding to pass any value. Find the link dedicated to asynchronous validation.
Angular Custom Async Validator Example
On this page we will discuss creating sync validators for reactive form as well as template-driven form with complete code step-by-step.
Contents
1. For Reactive Form
To create custom validator for Reactive form, we need to create a validator function that will returnValidatorFn or AsyncValidatorFn.
a. The
ValidatorFn is a function that receives a control and returns a map of validation errors as ValidationErrors if present, otherwise null.
b. The
AsyncValidatorFn is a function that receives a control and returns an Observable or Promise that emits validation errors as ValidationErrors if present, otherwise null.
Creating validators using
ValidatorFn:Let us create our first validator using
ValidatorFn. We know that ValidatorFn is used to create sync validator function. Suppose we need to validate a number to be only even entered by user. It means user should not enter odd number. If user enters odd number, error message needs to be displayed. Let us create our validator to perform this validation.
Step-1: Find the validator function.
oddnum-validator.ts
import { ValidatorFn, AbstractControl } from '@angular/forms';
import { ValidationErrors } from '@angular/forms';
export function oddNumValidator(): ValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): ValidationErrors | null => {
const v = control.value;
return (v % 2 === 1) ? { "oddNum": true } : null;
};
}
oddNum error using which we can display error message.
Step-2: We will use
oddNumValidator() with FormControl. To use sync validator with FormControl, we need to pass our sync validators as second argument of the FormControl.
numOfPerson = new FormControl('', oddNumValidator());
numOfPerson = new FormControl('', [Validators.required, oddNumValidator()]);
FormGroup with FormBuilder, the sync validators can be used as following.
teamForm = this.formBuilder.group({
numOfPerson: ['', [Validators.required, oddNumValidator()]],
------
});
<input formControlName="numOfPerson">
<div *ngIf="teamForm.get('numOfPerson').hasError('oddNum')">
Odd number not allowed.
</div>
2. For Template-driven Form
To create custom validator for template-driven form, we need to create aDirective by implementing Validator interface for sync validation and implement AsyncValidator interface for asynchronous validation.
a. The
Validator is an interface that is implemented by classes to perform synchronous validation. The class needs to override its validate() method that returns ValidationErrors or null.
b. The
AsyncValidator is an interface that is implemented by classes to perform asynchronous validation. The class needs to override its validate() method that returns Promise<ValidationErrors | null> or Observable<ValidationErrors | null>.
Creating sync validators using
Validator interface:We will create a validator
Directive to validate a number to be even. We will create a class by implementing Validator interface and overriding its validate() method. The class will be decorated with Directive() decorator. The validate() method will return error object if number is odd and return null if number is even. Find the class.
oddnum-validator.directive.ts
import { Directive } from '@angular/core';
import { NG_VALIDATORS, ValidationErrors, Validator, FormControl } from '@angular/forms';
@Directive({
selector: '[oddNum]',
standalone: true,
providers: [{ provide: NG_VALIDATORS, useExisting: OddNumValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class OddNumValidatorDirective implements Validator {
validate(control: FormControl): ValidationErrors | null {
const v = control.value;
return (v % 2 === 1) ? { "oddNum": true } : null;
}
}
NG_VALIDATORS adds the custom validator to the existing collection of validators and it requires multi: true options.
To use the validator in our code, the directive needs to be imported in standalone component or application module.
For application module.
import { OddNumValidatorDirective } from './validators/oddnum-validator.directive';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
------
OddNumValidatorDirective
],
------
})
export class AppModule { }
@Component({
selector: 'app-template',
standalone: true,
imports: [OddNumValidatorDirective],
templateUrl: './team-template-driven-form.component.html'
})
export class TeamTemplateDrivenFormComponent implements OnInit {
------
}
Find the HTML template code to use our custom validator with
ngModel.
<input name="numOfPerson" ngModel oddNum #numOfPerson="ngModel"> <div *ngIf="numOfPerson.errors?.['oddNum']"> Odd number not allowed. </div>
3. With Parameters
Here we will create synchronous validators with parameter. We need to pass an argument to our validator function that will be used in validation. For validator directive, we will perform property binding to pass the value.Custom validator for reactive form:
Here we will create a validator function that will validate a string that must have a given prefix. Find the validator function for reactive form.
export function teamNameValidator(teamNamePrefix): ValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): ValidationErrors | null => {
const v = control.value;
return (v!== null && v !== '' && !v.startsWith(teamNamePrefix)) ? { "teamNamePrefix": true } : null;
};
}
teamNameValidator. Find the code snippet to use it with FormGroup.
teamNamePrefix = 'CP';
teamForm = this.formBuilder.group({
teamName: ['', [teamNameValidator(this.teamNamePrefix)]],
------
});
<input formControlName="teamName">
<div *ngIf="teamForm.get('teamName').hasError('teamNamePrefix')">
Start team name with {{teamNamePrefix}}.
</div>
Custom validator for template-driven form:
We will create here a
Directive() to create a custom validator. We can pass value to validator using property binding and that value will be received by class using @Input() decorator.
Find the validator class that will validate user input that must have the given prefix passed as property binding.
@Directive({
selector: '[teamNamePrefix]',
standalone: true,
providers: [{ provide: NG_VALIDATORS, useExisting: TeamNameValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class TeamNameValidatorDirective implements Validator {
@Input()
teamNamePrefix: string;
validate(control: FormControl): ValidationErrors | null {
const v = control.value;
return (v!== null && v !== '' && !v.startsWith(this.teamNamePrefix)) ? { "teamNamePrefix": true } : null;
}
}
<input name="teamName" ngModel [teamNamePrefix]="teamNamePrefix" #teamName="ngModel">
<div *ngIf="teamName.errors?.['teamNamePrefix']" ngClass="error">
Start team name with {{teamNamePrefix}}.
</div>
We can reuse the validator function code in validator directive. Find the code.
teamname-validator.directive.ts
import { Directive, Input } from '@angular/core';
import { NG_VALIDATORS, Validator, FormControl } from '@angular/forms';
import { ValidatorFn, ValidationErrors, AbstractControl } from '@angular/forms';
export function teamNameValidator(teamNamePrefix): ValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): ValidationErrors | null => {
const v = control.value;
return (v!== null && v !== '' && !v.startsWith(teamNamePrefix)) ? { "teamNamePrefix": true } : null;
};
}
@Directive({
selector: '[teamNamePrefix]',
providers: [{ provide: NG_VALIDATORS, useExisting: TeamNameValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class TeamNameValidatorDirective implements Validator {
@Input()
teamNamePrefix: string;
validate(control: FormControl): ValidationErrors | null {
return teamNameValidator(this.teamNamePrefix)(control);
}
}
4. Complete Example
Here we will provide complete code of our demo application. We have two validators that have been explained above in the article. For the validator code, look into the following files given above in the article. These files are as given below.oddnum-validator.ts
oddnum-validator.directive.ts
teamname-validator.directive.ts
Now find the code of other files used in our application.
A. Find the code for reactive form.
team-reactive-form.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormBuilder, Validators, ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { TeamService } from './team-service';
import { oddNumValidator } from './validators/oddnum-validator';
import { teamNameValidator } from './validators/teamname-validator.directive';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
@Component({
selector: 'app-reactive',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule, ReactiveFormsModule],
templateUrl: './team-reactive-form.component.html'
})
export class TeamReactiveFormComponent implements OnInit {
teamNamePrefix = 'CP';
constructor(private formBuilder: FormBuilder, private teamService: TeamService) {
}
ngOnInit() {
}
teamForm = this.formBuilder.group({
teamName: ['', [Validators.required, teamNameValidator(this.teamNamePrefix)]],
numOfPerson: ['', [Validators.required, oddNumValidator()]]
});
onFormSubmit() {
if (this.teamForm.valid) {
this.teamService.createUser(this.teamForm.value);
this.teamForm.reset();
}
}
}
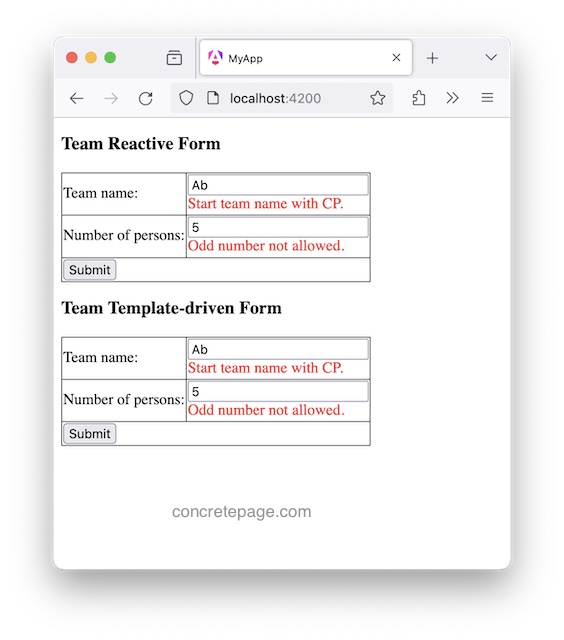
<h3>Team Reactive Form</h3>
<form [formGroup]="teamForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Team name: </td>
<td>
<input formControlName="teamName">
<div *ngIf="teamForm.get('teamName')?.hasError('required')" ngClass="error">
Enter team name.
</div>
<div *ngIf="teamForm.get('teamName')?.hasError('teamNamePrefix')" ngClass="error">
Start team name with {{teamNamePrefix}}.
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Number of persons: </td>
<td>
<input formControlName="numOfPerson">
<div *ngIf="teamForm.get('numOfPerson')?.hasError('required')" ngClass="error">
Enter person numbers.
</div>
<div *ngIf="teamForm.get('numOfPerson')?.hasError('oddNum')" ngClass="error">
Odd number not allowed.
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<button>Submit</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
B. Find the code for template-driven form.
team-template-driven-form.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule, NgForm } from '@angular/forms';
import { TeamService } from './team-service';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { TeamNameValidatorDirective } from './validators/teamname-validator.directive';
import { OddNumValidatorDirective } from './validators/oddnum-validator.directive';
@Component({
selector: 'app-template',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule, FormsModule, TeamNameValidatorDirective, OddNumValidatorDirective],
templateUrl: './team-template-driven-form.component.html'
})
export class TeamTemplateDrivenFormComponent implements OnInit {
teamNamePrefix = 'CP';
constructor(private teamService: TeamService) {
}
ngOnInit() {
}
onFormSubmit(form: NgForm) {
if (form.valid) {
this.teamService.createUser(form.value);
form.resetForm();
}
}
}
<h3>Team Template-driven Form</h3>
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Team name:</td>
<td>
<input name="teamName" ngModel required [teamNamePrefix]="teamNamePrefix" #teamName="ngModel">
<div *ngIf="teamName.errors?.['required']" ngClass="error">
Enter team name.
</div>
<div *ngIf="teamName.errors?.['teamNamePrefix']" ngClass="error">
Start team name with {{teamNamePrefix}}.
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Number of persons:</td>
<td>
<input name="numOfPerson" ngModel required oddNum #numOfPerson="ngModel">
<div *ngIf="numOfPerson.errors?.['required']" ngClass="error">
Enter person numbers.
</div>
<div *ngIf="numOfPerson.errors?.['oddNum']" ngClass="error">
Odd number not allowed.
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<button>Submit</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class TeamService {
createUser(team: any) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(team));
}
}
Find the print-screen of the output.
5. References
ValidatorFnValidator


