Angular Custom Async Validator Example
September 04, 2021
This page will walk through Angular custom async validator example. Angular provides AsyncValidatorFn, AsyncValidator interfaces and NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS provider for asynchronous validation. The AsyncValidatorFn and the method ofAsyncValidator returns Promise<ValidationErrors | null> or Observable<ValidationErrors | null>. If validation fails, they contain ValidationErrors otherwise null. Using AsyncValidatorFn, we create asynchronous validator functions that are used with FormControl, FormGroup and FormArray in reactive form. Using AsyncValidator, we create async validator directive. The NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS is used as provider with multi: true in our async validator directive. Async validator directive is used in HTML template in reactive form or with ngModel in template-driven from. Async validator is used to validate data against the data located at remote server. To avoid frequent hit to server, we should also use synchronous validators such as required, email, minlength and maxlength etc. Async validators can also use debounce time to minimize the number of hit.
Here on this page we will create custom async validators using
AsyncValidatorFn and AsyncValidator interfaces to check existing username, email, mobile number. We will provide complete example to create and use custom async validators with reactive form as well as template-driven form.
Contents
1. Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Angular 12.1.0
2. Node.js 12.14.1
3. NPM 7.20.3
4. Angular-in-memory-web-api 0.11.0
2. AsyncValidatorFn Interface
Angular providesAsyncValidatorFn interface to create custom async validator function that will be used by FormControl in reactive form. Find the structure of AsyncValidatorFn interface from Angular doc.
interface AsyncValidatorFn {
(c: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null>
}
AsyncValidatorFn has a method declaration that has argument as AbstractControl and it will contain latest value of the form control. This method will return either Promise<ValidationErrors | null> or Observable<ValidationErrors | null>. To create an async validator function using AsyncValidatorFn, we need to create a function whose return type must be AsyncValidatorFn.
Suppose we want to validate existing mobile number, we will create an async validator function as given below.
import { AsyncValidatorFn, AbstractControl, ValidationErrors } from '@angular/forms';
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
import { map } from "rxjs/operators";
export function existingMobileNumberValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
return userService.getUserByMobileNumber(control.value).pipe(map(
(users: User[]) => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "mobNumExists": true } : null;
}
));
};
}
UserService as an argument. UserService is being used to fetch data over HTTP.
If validation is successful then
null will be returned by our async validator and if there is validation error then value of type ValidationErrors i.e. {"mobNumExists": true} will be returned. To display error message we can access the value of mobNumExists using errors object as errors.mobNumExists . In our example it will return true if there is validation error.
2.1 Async Validator with FormControl, FormGroup and FormBuilder
To use async validator withFormControl we need to understand its constructor arguments. Find the constructor of FormControl from Angular doc.
constructor(formState: any = null,
validatorOrOpts?: ValidatorFn | ValidatorFn[] | AbstractControlOptions | null,
asyncValidator?: AsyncValidatorFn | AsyncValidatorFn[] | null)
Argument 1: Value of form control.
Argument 2: Synchronous validator or array of Synchronous validators
Argument 3: Asynchronous validator or array of Asynchronous validators
If we do not have synchronous validators, we need to pass
null to that place. Now find the sample code to use validators.
a. Using FormControl
Suppose we have two async validator functions.
existingMobileNumberValidator blackListedMobileNumberValidator
FormControl .
mobileNumber = new FormControl('',
[ Validators.required, Validators.maxLength(10) ], //sync validators
[ existingMobileNumberValidator(this.userService),
blackListedMobileNumberValidator(this.userService) ] //async validators
);
mobileNumber = new FormControl('',
null,
[ existingMobileNumberValidator(this.userService),
blackListedMobileNumberValidator(this.userService) ] //async validators
);
null for synchronous validators.
b. Using FormGroup
userForm = new FormGroup({
mobileNumber: new FormControl('',
[ Validators.required, Validators.maxLength(10) ], //sync validators
[ existingMobileNumberValidator(this.userService),
blackListedMobileNumberValidator(this.userService) ]), //async validators
---------
});
null as second argument of FormControl.
c. Using FormBuilder
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
mobileNumber: ['',
[ Validators.required, Validators.maxLength(10) ], //sync validators
[ existingMobileNumberValidator(this.userService),
blackListedMobileNumberValidator(this.userService) ] //async validators
],
---------
});
null to their place.
Now find the HTML template code snippet.
<input formControlName="mobileNumber">
<div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.errors" class = "error">
<div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.errors?.required">
Mobile number required.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.errors?.maxlength">
Mobile number must be 10 digit max.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.errors?.mobNumExists">
Mobile number already exists.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.errors?.blackListedMobNum">
Black listed mobile number.
</div>
</div>
3. AsyncValidator Interface
Angular providesAsyncValidator interface using which we create custom async validator directive. This async validator directive can be used with formControlName, formControl and ngModel. Find the structure of AsyncValidator interface from Angular doc.
interface AsyncValidator extends Validator {
validate(c: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null>
}
AsyncValidator has a method validate that has argument AbstractControl and it will contain latest value of the form control. The validate method will return either Promise<ValidationErrors | null> or Observable<ValidationErrors | null>.
Suppose we want to validate existing mobile number, we will create an async validator directive as given below.
import { Directive } from '@angular/core';
import { AsyncValidator, NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, AbstractControl, ValidationErrors } from '@angular/forms';
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
import { map } from "rxjs/operators";
@Directive({
selector: '[mobNumExists][formControlName],[mobNumExists][formControl],[mobNumExists][ngModel]',
providers: [{ provide: NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, useExisting: ExistingMobileNumberValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class ExistingMobileNumberValidatorDirective implements AsyncValidator {
constructor(private userService: UserService) { }
validate(control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> {
return this.userService.getUserByMobileNumber(control.value).pipe(
map(
users => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "mobNumExists": true } : null;
}
));
}
}
NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS is a provider for asynchronous validators and it is used with multi: true. The directive needs to be configured in application module in declarations part of @NgModule decorator.
We can inject dependency using constructor if required. In the above example we are injecting
UserService dependency to fetch data over HTTP.
Our async validator directive will give
null if validation successful and if there is validation error then value of type ValidationErrors i.e. {"mobNumExists": true} will be returned. To display error message we can fetch mobNumExists using errors object as errors.mobNumExists.
In our async validator directive, we have following selector.
[mobNumExists][formControlName] [mobNumExists][formControl] [mobNumExists][ngModel]
AsyncValidatorFn and AsyncValidator both, we can utilize the method definition of AsyncValidatorFn into the validate method of AsyncValidator as following.
import { Directive } from '@angular/core';
import { AsyncValidatorFn, AsyncValidator, NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, AbstractControl, ValidationErrors } from '@angular/forms';
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
import { map } from "rxjs/operators";
import { UserService } from '../user-service';
import { User } from '../user';
export function existingMobileNumberValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
return userService.getUserByMobileNumber(control.value).pipe(map(
(users: User[]) => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "mobNumExists": true } : null;
}
));
};
}
@Directive({
selector: '[mobNumExists][formControlName],[mobNumExists][formControl],[mobNumExists][ngModel]',
providers: [{ provide: NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, useExisting: ExistingMobileNumberValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class ExistingMobileNumberValidatorDirective implements AsyncValidator {
constructor(private userService: UserService) { }
validate(control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> {
return existingMobileNumberValidator(this.userService)(control);
}
}
validate method, we have utilized existingMobileNumberValidator function.
3.1 Async Validator with ngModel, formControlName and formControl
Async validator directive usingAsyncValidator interface can be used with ngModel, formControlName and formControl in HTML template.
a. Using ngModel
Suppose we have two async validator directives with selector
mobNumExists and blackListedMobNum. We will use them with ngModel in template-driven form as following.
<input name="mobileNumber" required maxlength="10"
mobNumExists blackListedMobNum ngModel #mnumber="ngModel">
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors" class = "error">
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors.required">
Mobile number required.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors.maxlength">
Mobile number must be 10 digit max.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors.required">
Mobile number required.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors.mobNumExists">
Mobile number already exists.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors.blackListedMobNum">
Black listed mobile number.
</div>
</div>
We can use our asynchronous validators with
formControlName as following.
<input formControlName="mobileNumber" mobNumExists blackListedMobNum >
Find the code snippet to use asynchronous validators with
formControl .
<input [formControl]="mobileNumber" mobNumExists blackListedMobNum >
4. Debounce with RxJS timer()
We can debounce async validators using RxJStimer(). Find the sample code.
export function existingUsernameValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
let debounceTime = 1000; //milliseconds
return timer(debounceTime).pipe(
switchMap(() => userService.getUserByUsername(control.value)),
map((users: User[]) => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "usernameExists": true } : null;
})
);
};
}
5. Async Validator using Observable
We can create async validators usingObservable as well as Promise. Above in the article we have used Observable yet. Find one more example for Observable. Suppose we have a method in UserService that returns Observable as following.
getBlackListedMobNumMobileNumberDetail(mobileNumber: string): Observable<User[]> {
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.urlblackListedMNums + '?mobileNumber=' + mobileNumber);
}
export function blackListedMobileNumberValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
return userService.getBlackListedMobNumMobileNumberDetail(control.value).pipe(map(
(users: User[]) => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "blackListedMobNum": true } : null;
}
));
};
}
6. Async Validator using Promise
Here we will create async validator usingPromise. Find a method in UserService that returns Promise as following.
getUserByEmail(userEmail: string): Promise<User[]> {
userEmail = userEmail.trim().replace('@', '%40');
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.url + '?email=' + userEmail).toPromise();
}
export function existingEmailValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
return userService.getUserByEmail(control.value).then(
users => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "emailExists": true } : null;
}
);
};
}
7. Angular In-Memory Web API
Angular provides In-Memory Web API to perform HTTP request in test environment. Find the steps to use it.Step-1: To install angular-in-memory-web-api, run below command from root folder of the project.
npm i angular-in-memory-web-api@0.11.0 --save
InMemoryDbService interface. In our example we are creating an in-memory DB for users.
test-data.ts
import { InMemoryDbService } from 'angular-in-memory-web-api';
export class TestData implements InMemoryDbService {
createDb() {
let userDetails = [
{id: 1, username: 'mahesh', email: 'mahesh11@gmail.com', mobileNumber: '2323232323'},
{id: 2, username: 'krishna', email: 'krishna11@gmail.com', mobileNumber: '1212121212'}
];
let blackListedMobileNumbers = [
{id: 111, mobileNumber: '1111111111'},
{id: 222, mobileNumber: '2222222222'}
];
return { users: userDetails, blackListedMNums: blackListedMobileNumbers };
}
}
/api/users /api/blackListedMNums
imports part of @NgModule as following.
import { InMemoryWebApiModule } from 'angular-in-memory-web-api';
import { TestData } from './test-data';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
InMemoryWebApiModule.forRoot(TestData)
------
]
------
})
8. Complete Example
Now we will provide complete example to create and use async validators with reactive form as well as template-driven form. Find the project structure.my-app | |--src | | | |--app | | | | | |--custom-validators | | | | | | | |--existing-username-validator.ts | | | |--existing-email-validator.ts | | | |--existing-mobilenumber-validator.ts | | | |--blacklisted-mobilenumber-validator.ts | | | | | |--reactive-form.component.ts | | |--reactive-form.component.html | | |--template-driven-form.component.ts | | |--template-driven-form.component.html | | |--user.ts | | |--user-service.ts | | | | | |--app.component.ts | | |--app.module.ts | | |--test-data.ts | | | |--main.ts | |--index.html | |--styles.css | |--node_modules |--package.json
8.1 Custom Async Validators
Find the custom async validators that we have created in our application.existing-mobilenumber-validator.ts
import { Directive } from '@angular/core';
import { AsyncValidatorFn, AsyncValidator, NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, AbstractControl, ValidationErrors } from '@angular/forms';
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
import { map } from "rxjs/operators";
import { UserService } from '../user-service';
import { User } from '../user';
export function existingMobileNumberValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
return userService.getUserByMobileNumber(control.value).pipe(map(
(users: User[]) => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "mobNumExists": true } : null;
}
));
};
}
@Directive({
selector: '[mobNumExists][formControlName],[mobNumExists][formControl],[mobNumExists][ngModel]',
providers: [{ provide: NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, useExisting: ExistingMobileNumberValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class ExistingMobileNumberValidatorDirective implements AsyncValidator {
constructor(private userService: UserService) { }
validate(control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> {
return existingMobileNumberValidator(this.userService)(control);
}
}
import { Directive } from '@angular/core';
import { AsyncValidatorFn, AsyncValidator, NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, AbstractControl, ValidationErrors } from '@angular/forms';
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
import { map } from "rxjs/operators";
import { UserService } from '../user-service';
import { User } from '../user';
export function blackListedMobileNumberValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
return userService.getBlackListedMobNumMobileNumberDetail(control.value).pipe(map(
(users: User[]) => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "blackListedMobNum": true } : null;
}
));
};
}
@Directive({
selector: '[blackListedMobNum][formControlName],[blackListedMobNum][formControl],[blackListedMobNum][ngModel]',
providers: [{ provide: NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, useExisting: BlackListedMobileNumberValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class BlackListedMobileNumberValidatorDirective implements AsyncValidator {
constructor(private userService: UserService) { }
validate(control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> {
return blackListedMobileNumberValidator(this.userService)(control);
}
}
import { Directive } from '@angular/core';
import { AsyncValidatorFn, AsyncValidator, NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, AbstractControl, ValidationErrors } from '@angular/forms';
import { Observable, timer } from "rxjs";
import { map, switchMap } from "rxjs/operators";
import { UserService } from '../user-service';
import { User } from '../user';
export function existingUsernameValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
let debounceTime = 1000; //milliseconds
return timer(debounceTime).pipe(
switchMap(() => userService.getUserByUsername(control.value)),
map((users: User[]) => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "usernameExists": true } : null;
})
);
};
}
@Directive({
selector: '[usernameExists][formControlName],[usernameExists][formControl],[usernameExists][ngModel]',
providers: [{ provide: NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, useExisting: ExistingUsernameValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class ExistingUsernameValidatorDirective implements AsyncValidator {
constructor(private userService: UserService) { }
validate(control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> {
return existingUsernameValidator(this.userService)(control);
}
}
import { Directive } from '@angular/core';
import { AsyncValidatorFn, AsyncValidator, NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, AbstractControl, ValidationErrors } from '@angular/forms';
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
import { UserService } from '../user-service';
export function existingEmailValidator(userService: UserService): AsyncValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> => {
return userService.getUserByEmail(control.value).then(
users => {
return (users && users.length > 0) ? { "emailExists": true } : null;
}
);
};
}
@Directive({
selector: '[emailExists][formControlName],[emailExists][formControl],[emailExists][ngModel]',
providers: [{ provide: NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS, useExisting: ExistingEmailValidatorDirective, multi: true }]
})
export class ExistingEmailValidatorDirective implements AsyncValidator {
constructor(private userService: UserService) { }
validate(control: AbstractControl): Promise<ValidationErrors | null> | Observable<ValidationErrors | null> {
return existingEmailValidator(this.userService)(control);
}
}
8.2 Async Validation using Reactive Form
reactive-form.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormBuilder, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
import { UserService } from './user-service';
import { User } from './user';
import { existingUsernameValidator } from './custom-validators/existing-username-validator';
import { existingEmailValidator } from './custom-validators/existing-email-validator';
import { existingMobileNumberValidator } from './custom-validators/existing-mobilenumber-validator';
import { blackListedMobileNumberValidator } from './custom-validators/blacklisted-mobilenumber-validator';
@Component({
selector: 'app-reactive',
templateUrl: './reactive-form.component.html'
})
export class ReactiveFormComponent implements OnInit {
dataSaved = false;
userForm = {} as FormGroup;
constructor(private formBuilder: FormBuilder, private userService: UserService) {
}
ngOnInit() {
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
username: ['',
[Validators.required], //sync validators
[existingUsernameValidator(this.userService)] //async validators
],
email: ['',
[Validators.required, Validators.email], //sync validators
[existingEmailValidator(this.userService)] //async validators
],
mobileNumber: ['',
[Validators.required], //sync validators
[existingMobileNumberValidator(this.userService),
blackListedMobileNumberValidator(this.userService)] //async validators
]
});
}
onFormSubmit() {
this.dataSaved = false;
let user = this.userForm.value;
this.userService.getAllUsers().subscribe((users: User[]) => {
let maxIndex = users.length - 1;
let maxIndexItem = users[maxIndex];
user.id = maxIndexItem.id + 1;
this.userService.createUser(user).subscribe(
() => {
this.dataSaved = true;
}
);
});
this.userForm.reset();
}
get username() {
return this.userForm.get('username');
}
get email() {
return this.userForm.get('email');
}
get mobileNumber() {
return this.userForm.get('mobileNumber');
}
}
<h3>Reactive Form</h3> <p *ngIf="dataSaved && userForm.pristine" ngClass="success"> User saved successfully. </p> <form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()"> <table> <tr> <td>Username: </td> <td> <input formControlName="username"> <div *ngIf="username?.dirty && username?.errors" class="error"> <div *ngIf="username?.errors?.required"> Username required. </div> <div *ngIf="username?.errors?.usernameExists"> Username already exists. </div> </div> </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Email: </td> <td> <input formControlName="email"> <div *ngIf="email?.dirty && email?.errors" class="error"> <div *ngIf="email?.errors?.required"> Email required. </div> <div *ngIf="email?.errors?.email"> Email not valid. </div> <div *ngIf="email?.errors?.emailExists"> Email already exists. </div> </div> </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Mobile Number: </td> <td> <input formControlName="mobileNumber"> <div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.dirty && mobileNumber?.errors" class="error"> <div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.errors?.required"> Mobile number required. </div> <div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.errors?.mobNumExists"> Mobile number already exists. </div> <div *ngIf="mobileNumber?.errors?.blackListedMobNum"> Black listed mobile number. </div> </div> </td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="2"> <button [disabled]="userForm.invalid">Submit</button> </td> </tr> </table> </form>
export interface User {
id: string;
username: string;
email: string;
mobileNumber: string;
}
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { User } from './user';
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
url = "/api/users";
urlblackListedMNums = "/api/blackListedMNums";
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
getUserByUsername(username: string): Observable<User[]> {
username = '^' + username.trim() + '$'; //For exact match testing in Angular In-Memory Web API
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.url + '?username=' + username);
}
getUserByEmail(userEmail: string): Promise<User[]> {
userEmail = userEmail.trim().replace('@', '%40'); //Convert @ into Percent-encoding
userEmail = '^' + userEmail + '$'; //For exact match testing in Angular In-Memory Web API
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.url + '?email=' + userEmail).toPromise();
}
getUserByMobileNumber(mobileNumber: string): Observable<User[]> {
mobileNumber = '^' + mobileNumber.trim() + '$'; //For exact match testing in Angular In-Memory Web API
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.url + '?mobileNumber=' + mobileNumber);
}
getBlackListedMobNumMobileNumberDetail(mobileNumber: string): Observable<User[]> {
mobileNumber = '^' + mobileNumber.trim() + '$'; //For exact match testing in Angular In-Memory Web API
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.urlblackListedMNums + '?mobileNumber=' + mobileNumber);
}
getAllUsers(): Observable<User[]> {
return this.http.get<User[]>(this.url);
}
createUser(user: User): Observable<User> {
return this.http.post<User>(this.url, user);
}
getAllBlackListedMobileNumbers(): Observable<any> {
return this.http.get(this.urlblackListedMNums);
}
}
8.3 Async Validation using Template-driven Form
template-driven-form.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { NgForm } from '@angular/forms';
import { UserService } from './user-service';
import { User } from './user';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-template',
templateUrl: './template-driven-form.component.html'
})
export class TemplateDrivenFormComponent implements OnInit {
dataSaved = false;
allUsers$: Observable<User[]>;
allBlackListedMnums$: Observable<any>;
constructor(private userService: UserService) {
this.allUsers$ = this.userService.getAllUsers();
this.allBlackListedMnums$ = this.userService.getAllBlackListedMobileNumbers();
}
ngOnInit() {
}
onFormSubmit(form: NgForm) {
this.dataSaved = false;
let user: User = form.value;
this.userService.getAllUsers().subscribe((users: User[]) => {
let maxIndex = users.length - 1;
let maxIndexItem = users[maxIndex];
user.id = maxIndexItem.id + 1;
this.userService.createUser(user).subscribe(
() => {
this.dataSaved = true;
}
);
});
form.resetForm();
}
loadAllUsers() {
this.allUsers$ = this.userService.getAllUsers();
}
}
<h3>Template-driven Form</h3>
<p *ngIf="dataSaved && userForm.pristine" class="success">
User saved successfully.
</p>
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Username:</td>
<td>
<input name="username" required usernameExists ngModel #uname="ngModel">
<div *ngIf="uname.dirty && uname.errors" class="error">
<div *ngIf="uname.errors.required">
Username required.
</div>
<div *ngIf="uname.errors.usernameExists">
Username already exists.
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Email:</td>
<td>
<input name="email" required email emailExists ngModel #uemail="ngModel">
<div *ngIf="uemail.dirty && uemail.errors" class="error">
<div *ngIf="uemail.errors.required">
Email required.
</div>
<div *ngIf="uemail.errors.email">
Email not valid.
</div>
<div *ngIf="uemail.errors.emailExists">
Email already exists.
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Mobile Number:</td>
<td>
<input name="mobileNumber" required mobNumExists blackListedMobNum ngModel #mnumber="ngModel">
<div *ngIf="mnumber.dirty && mnumber.errors" class="error">
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors.required">
Mobile number required.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors.mobNumExists">
Mobile number already exists.
</div>
<div *ngIf="mnumber.errors.blackListedMobNum">
Black listed mobile number.
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<button [disabled]="userForm.invalid">Submit</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<h3>User Details: <button (click)="loadAllUsers()">Reload All Users</button></h3>
<p *ngFor="let user of allUsers$ | async">
Id: <b>{{user.id}}</b> | User: <b>{{user.username}}</b> |
Email: <b>{{user.email}}</b> | Mobile: <b>{{user.mobileNumber}}</b>
</p>
<h3>Black Listed Mobile Numbers</h3>
<p *ngFor="let item of allBlackListedMnums$ | async">
{{item['mobileNumber']}}
</p>
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<app-reactive></app-reactive>
<app-template></app-template>
`
})
export class AppComponent {
}
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { FormsModule, ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { ReactiveFormComponent } from './reactive-form.component';
import { TemplateDrivenFormComponent } from './template-driven-form.component';
import { UserService } from './user-service';
import { ExistingUsernameValidatorDirective } from './custom-validators/existing-username-validator';
import { ExistingEmailValidatorDirective } from './custom-validators/existing-email-validator';
import { ExistingMobileNumberValidatorDirective } from './custom-validators/existing-mobilenumber-validator';
import { BlackListedMobileNumberValidatorDirective } from './custom-validators/blacklisted-mobilenumber-validator';
//For InMemory testing
import { InMemoryWebApiModule } from 'angular-in-memory-web-api';
import { TestData } from './test-data';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
ReactiveFormsModule,
HttpClientModule,
InMemoryWebApiModule.forRoot(TestData)
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
ReactiveFormComponent,
TemplateDrivenFormComponent,
ExistingUsernameValidatorDirective,
ExistingEmailValidatorDirective,
ExistingMobileNumberValidatorDirective,
BlackListedMobileNumberValidatorDirective
],
providers: [
UserService
],
bootstrap: [
AppComponent
]
})
export class AppModule { }
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
.error {
color: red;
}
.success {
color: green;
}
9. Run Application
To run the application, find following steps.1. Download source code using download link given below on this page.
2. Use downloaded src in your Angular CLI application. To install Angular CLI, find the link.
3. Install angular-in-memory-web-api@0.11.0
4. Run ng serve using command prompt.
5. Now access the URL http://localhost:4200
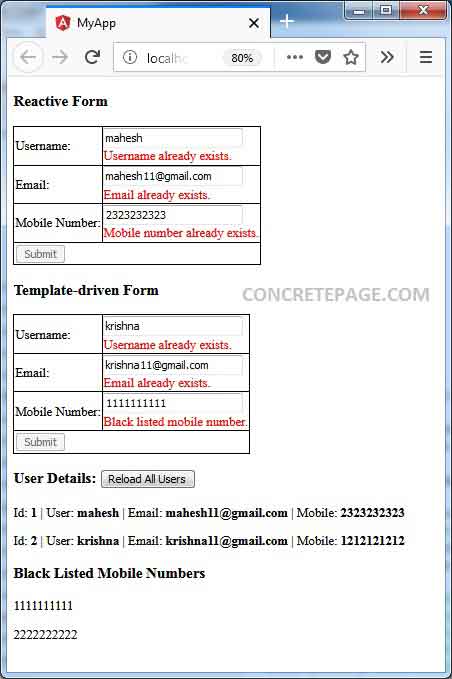
When we fill existing data, we will get validation errors. Find the print screen.
10. References
AsyncValidatorFnAsyncValidator
NG_ASYNC_VALIDATORS


