Angular Test Inject Service
April 04, 2022
This page will walk through Angular test inject service example. Angular test provides TestBed that configures and initializes environment for unit testing. The TestBed provides methods for creating components and services in unit tests. The TestBed methods are inject(), configureTestingModule() etc. To inject a service, we use TestBed.inject() method.
Find the
TestBed.inject() doc.
inject<T>(token: ProviderToken<T>,
notFoundValue?: T,
flags?: InjectFlags): T
empService = TestBed.inject(EmployeeService);
In our example we will inject a simple service as well as a service with
HttpClient dependency.
Contents
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Angular 13.1.0
2. Node.js 12.20.0
Inject Service
Suppose we have a service class.
@Injectable()
export class EmployeeService {
------
}
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
providers: [
EmployeeService
]
});
empService = TestBed.inject(EmployeeService);
Inject Service with HttpClient
Suppose we have a service to handle HTTP requests. This service has theHttpClient dependency. The HttpClient is used to perform HTTP requests.
@Injectable()
export class EmployeeService {
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
------
}
HttpClientTestingModule that is used to expect and flush requests in our tests.
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [HttpClientTestingModule],
providers: [
EmployeeService
]
});
HttpClient, HttpTestingController and our service EmployeeService.
httpClient = TestBed.inject(HttpClient); httpTestingController = TestBed.inject(HttpTestingController); empService = TestBed.inject(EmployeeService);
HttpTestingController is injected into tests that allows for mocking and flushing of requests.
Complete Example
employee.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient, HttpHeaders, HttpErrorResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
import { map, catchError, tap } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { Employee } from './employee';
const httpOptions = {
headers: new HttpHeaders({
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': 'my-auth-token'
})
};
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class EmployeeService {
empUrl = "/api/employees";
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
addEmployee(emp: Employee): Observable<Employee> {
return this.http.post<Employee>(this.empUrl, emp, httpOptions)
.pipe(
tap(employee => console.log("employee: " + JSON.stringify(employee))),
catchError(this.handleError(emp))
);
}
getAllEmployees(): Observable<Employee[]> {
return this.http.get<Employee[]>(this.empUrl).pipe(
tap(employees => console.log("employees: " + JSON.stringify(employees))),
catchError(this.handleError<Employee[]>([]))
);
}
private handleError<T>(result = {} as T) {
return (error: HttpErrorResponse): Observable<T> => {
console.error(error);
return of(result);
};
}
}
import { HttpClientTestingModule, HttpTestingController } from '@angular/common/http/testing';
import { TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { HttpClient, HttpResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Employee } from './employee';
import { EmployeeService } from './employee.service';
//Testing of EmployeeService
describe('#EmployeeService.addEmploye()', () => {
let httpClient: HttpClient;
let httpTestingController: HttpTestingController;
let empService: EmployeeService;
beforeEach(() => {
//Configures testing app module
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [HttpClientTestingModule],
providers: [
EmployeeService
]
});
//Instantiates HttpClient, HttpTestingController and EmployeeService
httpClient = TestBed.inject(HttpClient);
httpTestingController = TestBed.inject(HttpTestingController);
empService = TestBed.inject(EmployeeService);
});
afterEach(() => {
httpTestingController.verify(); //Verifies that no requests are outstanding.
});
//Test case for GET
it('should return expected employees by calling once', () => {
const expectedEmps = [
{ name: 'Krishna', age: 101 },
{ name: 'Arjun', age: 102 }
] as Employee[];
empService.getAllEmployees().subscribe({
next: emps => expect(emps).toEqual(expectedEmps),
error: fail
});
const req = httpTestingController.expectOne(empService.empUrl);
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('GET');
req.flush(expectedEmps); //Return expectedEmps
});
//Test case for POST
it('should add an employee and return it', () => {
const newEmp: Employee = { name: 'Mahesh', age: 25 };
empService.addEmployee(newEmp).subscribe({
next: data => expect(data).toEqual(newEmp),
error: fail
});
// addEmploye should have made one request to POST employee
const req = httpTestingController.expectOne(empService.empUrl);
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('POST');
expect(req.request.body).toEqual(newEmp);
// Expect server to return the employee after POST
const expectedResponse = new HttpResponse({ status: 201, statusText: 'Created', body: newEmp });
req.event(expectedResponse);
});
});
Run Test Cases
To run the test cases, find the steps.1. Install Angular CLI using link.
2. Download source code using download link given below on this page.
3. Use downloaded src in your Angular CLI application.
4. Run ng test using command prompt. Test result can be seen on command prompt as well as on browser.
5. A browser for test result will open automatically or we can also use the URL http://localhost:9876/
Find the print screen of test result.
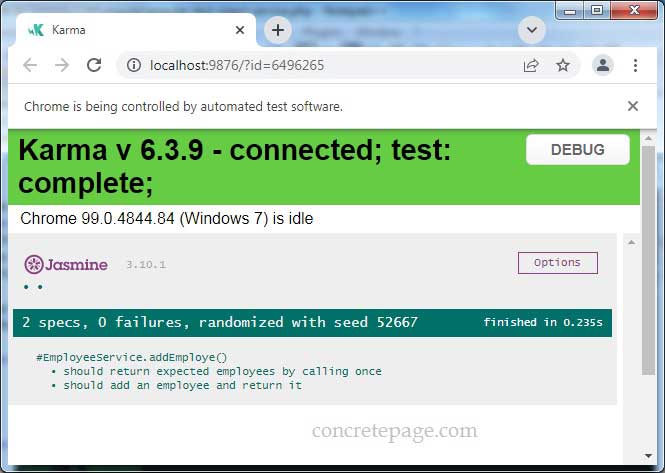
References
TestBedSubscribe Arguments


