Angular Custom Preloading Strategy
September 02, 2021
This page will walk through Angular custom preloading strategy example. Preloading is loading modules in background just after application starts. In preloading, modules are loaded asynchronously. Angular provides built-in PreloadAllModules strategy that loads all feature modules as quickly as possible configured with loadChildren in application routing module.
Custom preloading strategies allow to preload selective modules. We can also customize to preload modules after a certain delay after application starts. To create a custom preloading strategy, Angular provides
PreloadingStrategy class with a preload method. We need to create a service by implementing PreloadingStrategy and overriding its preload method. To enable custom preloading strategies, we need to configure our preloading strategy service with RouterModule.forRoot using preloadingStrategy property.
On this page we will discuss to create custom preloading strategy in detail step-by-step.
Contents
- Technologies Used
- Preloading
- Custom Preloading Strategy
- Custom Preloading Strategy Example 1: Selective Module Preloading
- Custom Preloading Strategy Example 2: Selective Module Preloading with Delay
- Demo Project Structure
- Other Components, Services and Modules used in Demo
- Run Application
- References
- Download Source Code
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Angular 12.1.0
2. Node.js 12.14.1
3. NPM 7.20.3
Preloading
1. To load a feature module, we need to useloadChildren in application routing module i.e. AppRoutingModule. Find the code snippet.
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'country',
loadChildren: () => import('./country/country.module').then(mod => mod.CountryModule)
}
------
];
CountryModule in application module i.e. AppModule.
3. To configure preloading, angular provides
preloadingStrategy property which is used with RouterModule.forRoot in application routing module. Find the code snippet.
RouterModule.forRoot(routes,
{
preloadingStrategy: PreloadAllModules
})
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { PreloadAllModules } from '@angular/router';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'country',
loadChildren: () => import('./country/country.module').then(mod => mod.CountryModule)
},
------
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(routes,
{
preloadingStrategy: PreloadAllModules
})
],
exports: [
RouterModule
]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
PreloadAllModules and NoPreloading in-built strategies.
a. PreloadAllModules: Strategy that preloads all modules configured by
loadChildren in application routing module as quickly as possible. We use it as following.
RouterModule.forRoot(routes,
{
preloadingStrategy: PreloadAllModules
})
RouterModule.forRoot(routes,
{
preloadingStrategy: NoPreloading
})
Custom Preloading Strategy
Angular providesPreloadingStrategy class using which we can create custom preloading strategy. Find the structure of PreloadingStrategy from Angular Doc.
class PreloadingStrategy {
preload(route: Route, fn: () => Observable<any>): Observable<any>
}
PreloadingStrategy and override its preload method. Let us discuss step by step.
Step-1: Use
data property in route configuration. data is a property of Route interface. data provides additional data to component via ActivatedRoute. The data property can be used in route configuration as following.
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'country',
loadChildren: () => import('./country/country.module').then(mod => mod.CountryModule),
data: { preload: true }
},
------
];
data with any number of flags with any name as required.
Example 1:
data: { preload: true }
data: { preload: true, delay: true }
PreloadingStrategy class and override its preload method. Here we are creating a custom preloading strategy with name CustomPreloadingStrategy.
@Injectable()
export class CustomPreloadingStrategy implements PreloadingStrategy {
preload(route: Route, load: () => Observable<any>): Observable<any> {
if (route.data && route.data['preload']) {
return load();
} else {
return of(null);
}
}
}
preload method. This method will run for all modules configured with loadChildren in route configuration. When the preload method finds the value of route.data['preload'] as true for a module, load() is returned and that module is preloaded and if it finds false then we need to return Observable<null> and that module will not be preloaded.
Step-3: Suppose we have following route configuration.
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'person',
loadChildren: () => import('./person/person.module').then(mod => mod.PersonModule),
data: { preload: true }
},
{
path: 'address',
loadChildren: () => import('./address/address.module').then(mod => mod.AddressModule)
}
------
];
PersonModule and AddressModule have been configured. According to our CustomPreloadingStrategy implementation, PersonModule will be preloaded because it is using data property as preload: true. Another feature module AddressModule will not be preloaded.
Step-4: To enable our custom preloading strategy
CustomPreloadingStrategy, we need to assign it to preloadingStrategy property in RouterModule.forRoot method in application routing module. Find the code snippet.
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(routes,
{
preloadingStrategy: CustomPreloadingStrategy
})
],
------
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
CustomPreloadingStrategy with providers metadata in application routing module. Find the code snippet.
@NgModule({
providers: [ CustomPreloadingStrategy ],
------
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
Custom Preloading Strategy Example 1: Selective Module Preloading
Here we will create a custom preloading strategy using which only selective feature modules will be preloaded.custom-preloading-strategy.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { PreloadingStrategy, Route } from '@angular/router';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class CustomPreloadingStrategy implements PreloadingStrategy {
preload(route: Route, load: () => Observable<any>): Observable<any> {
if (route.data && route.data['preload']) {
console.log('Preload Path: ' + route.path);
return load();
} else {
return of(null);
}
}
}
app-routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { PageNotFoundComponent } from './page-not-found.component';
import { CustomPreloadingStrategy } from './custom-preloading-strategy';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'country',
loadChildren: () => import('./country/country.module').then(mod => mod.CountryModule),
data: { preload: true }
},
{
path: 'person',
loadChildren: () => import('./person/person.module').then(mod => mod.PersonModule),
data: { preload: true }
},
{
path: 'address',
loadChildren: () => import('./address/address.module').then(mod => mod.AddressModule),
},
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '',
pathMatch: 'full'
},
{
path: '**',
component: PageNotFoundComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(routes,
{
preloadingStrategy: CustomPreloadingStrategy
})
],
exports: [
RouterModule
],
providers: [ CustomPreloadingStrategy ]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
AppModule loaded. Angular is running in the development mode. Call enableProdMode() to enable the production mode. Preload Path: country Preload Path: person CountryModule loaded. PersonModule loaded.
AppModule is loaded and application started. After that feature modules CountryModule and PersonModule are loaded. AddressModule will be lazy loaded.
Custom Preloading Strategy Example 2: Selective Module Preloading with Delay
Here we will create a custom preloading strategy using which only selective feature modules will be preloaded with a certain delay.custom-preloading-with-delay-strategy.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { PreloadingStrategy, Route } from '@angular/router';
import { Observable, timer, of } from 'rxjs';
import { mergeMap } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Injectable()
export class CustomPreloadingWithDelayStrategy implements PreloadingStrategy {
preload(route: Route, load: () => Observable<any>): Observable<any> {
if (route.data && route.data['preload']) {
console.log('Preload Path: ' + route.path + ', delay:' + route.data['delay']);
if (route.data['delay']) {
return timer(5000).pipe(mergeMap(() => load()));
}
return load();
} else {
return of(null);
}
}
}
delay as true to data property in route configuration, then that module will be preloaded after 5 seconds once the application started. Find the application routing module.
app-routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { PageNotFoundComponent } from './page-not-found.component';
import { CustomPreloadingWithDelayStrategy } from './custom-preloading-with-delay-strategy';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'country',
loadChildren: () => import('./country/country.module').then(mod => mod.CountryModule),
data: { preload: true, delay: false }
},
{
path: 'person',
loadChildren: () => import('./person/person.module').then(mod => mod.PersonModule),
data: { preload: true, delay: true }
},
{
path: 'address',
loadChildren: () => import('./address/address.module').then(mod => mod.AddressModule),
},
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '',
pathMatch: 'full'
},
{
path: '**',
component: PageNotFoundComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(routes,
{
preloadingStrategy: CustomPreloadingWithDelayStrategy
})
],
exports: [
RouterModule
],
providers: [ CustomPreloadingWithDelayStrategy ]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
CountryModule will be preloaded as quickly as possible. PersonModule will start preloading after 5 seconds once the application starts. AddressModule will be lazy loaded.
Demo Project Structure
Find the project structure of our demo application.my-app | |--src | | | |--app | | | | | |--country | | | | | | | |--country.component.ts | | | |--country.ts | | | |--country.module.ts | | | |--country-routing.module.ts | | | | | | | |--country-list | | | | | | | | | |--country.list.component.html | | | | |--country.list.component.ts | | | | | | | |--services | | | | | | | | | |--country.service.ts | | | | | |--person | | | | | | | |--person.component.ts | | | |--person.ts | | | |--person-routing.module.ts | | | |--person.module.ts | | | | | | | |--person-list | | | | | | | | | |--person.list.component.html | | | | |--person.list.component.ts | | | | | | | | | | | | |--services | | | | | | | | | |--person.service.ts | | | | | |--address | | | | | | | |--address.component.ts | | | |--address-routing.module.ts | | | |--address.module.ts | | | | | |--custom-preloading-strategy.ts | | |--custom-preloading-with-delay-strategy.ts | | | | | |--page-not-found.component.ts | | |--app.component.ts | | |--app-routing.module.ts | | |--app.module.ts | | | |--main.ts | |--index.html | |--styles.css | |--node_modules |--package.json
Other Components, Services and Modules used in Demo
In our application we have three feature modules. Find the code feature wise.1. Code for country feature:
country.ts
export class Country {
constructor(public countryId:number, public countryName:string,
public capital:string, public currency:string) {
}
}
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
import { Country } from '../country';
const COUNTRIES = [
new Country(1, 'India', 'New Delhi', 'INR'),
new Country(2, 'China', 'Beijing', 'RMB')
];
let countryList$ = of(COUNTRIES);
@Injectable()
export class CountryService {
getCountries(): Observable<Country[]> {
return countryList$;
}
}
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { CountryService } from '../services/country.service';
import { Country } from '../country';
@Component({
templateUrl: './country.list.component.html'
})
export class CountryListComponent implements OnInit {
countries$: Observable<Country[]>;
constructor(private countryService: CountryService) {
this.countries$ = this.countryService.getCountries();
}
ngOnInit() {
}
}
<h3>Country List</h3>
<p *ngFor="let country of countries$ | async">
{{country.countryId}}. {{country.countryName}}
- {{country.capital}} - {{country.currency}}
</p>
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
template: `
<h2>Welcome to Country Home</h2>
<a [routerLink]="['country-list']" routerLinkActive="active">View Country List</a>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
`
})
export class CountryComponent {
}
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { CountryComponent } from './country.component';
import { CountryListComponent } from './country-list/country.list.component';
const countryRoutes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: CountryComponent,
children: [
{
path: 'country-list',
component: CountryListComponent
}
]
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [ RouterModule.forChild(countryRoutes) ],
exports: [ RouterModule ]
})
export class CountryRoutingModule { }
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { CountryComponent } from './country.component';
import { CountryListComponent } from './country-list/country.list.component';
import { CountryService } from './services/country.service';
import { CountryRoutingModule } from './country-routing.module';
@NgModule({
imports: [
CommonModule,
CountryRoutingModule
],
declarations: [
CountryComponent,
CountryListComponent
],
providers: [ CountryService ]
})
export class CountryModule {
constructor() {
console.log('CountryModule loaded.');
}
}
person.ts
export class Person {
constructor(public personId:number, public name:string, public city:string) {
}
}
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
import { Person } from '../person';
const PERSONS = [
new Person(1, 'Mahesh', 'Varanasi'),
new Person(2, 'Ram', 'Ayodhya'),
new Person(3, 'Kishna', 'Mathura')
];
let personList$ = of(PERSONS);
@Injectable()
export class PersonService {
getPersons(): Observable<Person[]> {
return personList$;
}
}
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { PersonService } from '../services/person.service';
import { Person } from '../person';
@Component({
templateUrl: './person.list.component.html'
})
export class PersonListComponent implements OnInit {
persons$: Observable<Person[]>;
constructor(private personService: PersonService) {
this.persons$ = this.personService.getPersons();
}
ngOnInit() {
}
}
<h3>Person List</h3>
<p *ngFor="let person of persons$ | async">
{{person.personId}}. {{person.name}} - {{person.city}}
</p>
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
template: `
<h2>Welcome to Person Home</h2>
<a [routerLink]="['person-list']" routerLinkActive="active">View Person List</a>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
`
})
export class PersonComponent {
}
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { PersonComponent } from './person.component';
import { PersonListComponent } from './person-list/person.list.component';
const personRoutes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: PersonComponent,
children: [
{
path: 'person-list',
component: PersonListComponent
}
]
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [ RouterModule.forChild(personRoutes) ],
exports: [ RouterModule ]
})
export class PersonRoutingModule { }
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { PersonComponent } from './person.component';
import { PersonListComponent } from './person-list/person.list.component';
import { PersonService } from './services/person.service';
import { PersonRoutingModule } from './person-routing.module';
@NgModule({
imports: [
CommonModule,
PersonRoutingModule
],
declarations: [
PersonComponent,
PersonListComponent
],
providers: [ PersonService ]
})
export class PersonModule {
constructor() {
console.log('PersonModule loaded.');
}
}
3. Code for address feature:
address.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
template: `
<h3>ADDRESS</h3>
<p><b> Article: Angular Custom Preloading Strategy </b></p>
<p><b> Category: Angular </b></p>
<p><b> Website: CONCRETEPAGE.COM </b></p>
<div>
<a [routerLink]="['/location']">Find Location</a>
</div>
`
})
export class AddressComponent {
}
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { AddressComponent } from './address.component';
const addressRoutes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: AddressComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [ RouterModule.forChild(addressRoutes) ],
exports: [ RouterModule ]
})
export class AddressRoutingModule { }
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { AddressRoutingModule } from './address-routing.module';
import { AddressComponent } from './address.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [
CommonModule,
AddressRoutingModule
],
declarations: [
AddressComponent
]
})
export class AddressModule {
constructor() {
console.log('AddressModule loaded.');
}
}
Now find other files used in the demo application.
page-not-found.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Location } from '@angular/common';
@Component({
template: `<h2>Page Not Found.</h2>
<div>
<button (click)="goBack()">Go Back</button>
</div>
`
})
export class PageNotFoundComponent {
constructor(private location: Location) { }
goBack(): void {
this.location.back();
}
}
.parent-menu ul {
list-style-type: none;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
overflow: hidden;
background-color: #333;
}
.parent-menu li {
float: left;
}
.parent-menu li a {
display: block;
color: white;
text-align: center;
padding: 15px 15px;
text-decoration: none;
}
.parent-menu li a:hover:not(.active) {
background-color: #111;
}
.parent-menu .active{
background-color: #4CAF50;
}
.parent-container {
padding-left: 10px;
}
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<nav [ngClass] = "'parent-menu'">
<ul>
<li><a routerLink="/country" routerLinkActive="active">Country</a></li>
<li><a routerLink="/person" routerLinkActive="active">Person</a></li>
<li><a routerLink="/address" routerLinkActive="active">Address</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<div [ngClass] = "'parent-container'">
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
`
})
export class AppComponent {
}
Run Application
To run the application, find the steps.1. Download source code using download link given below on this page.
2. Use downloaded src in your Angular CLI application. To install Angular CLI, find the link.
3. Run ng serve using command prompt.
4. Access the URL http://localhost:4200
Find the print screen of the output.
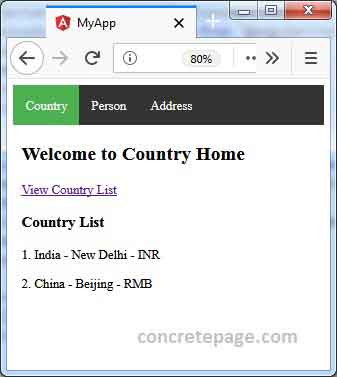
References
PreloadingStrategyCommon Routing Tasks
PreloadAllModules
NoPreloading
Angular Child Routes and Relative Navigation Example


