Angular Two-Way Data Binding + NgModel Example
February 10, 2024
This page will walk through Angular two-way data binding and NgModel with examples. Using two-way binding, we can display a data property as well as update that property when user does changes. We can achieve it in component element and HTML element both. Two-way binding uses the syntax as [()] or bindon- keyword. Two-way binding uses the syntax of property binding and event binding together. Property binding uses the syntax as bracket [] or bind- and event binding uses the syntax as parenthesis () or on- and these bindings are considered as one-way binding. Two-way binding works in both direction setting the value and fetching the value. Two-way binding uses a specific name pattern. Event name should be property adding Change keyword as suffix. So if we have a property xyz then event name should be xyzChange . In component property binding and custom event binding we create our own property name and event name as target in binding. So we can follow the naming pattern. But in HTML element there are in-built names as target in binding such as value in property binding and input in event binding. So here the role of NgModel directive comes into the picture to work as bridge that enables two-way binding to HTML elements. It provides the required name pattern of target as ngModel in property binding and ngModelChange in event binding. When two-way binding is between components at component element level and input property name is xyz and output property name is xyzChange then the target in two-way binding will be written as [(xyz)] . If two-way binding is taking place at HTML element level such as in input box or select box then we will use ngModel for target name as [(ngModel)] . Now find the complete example of two-way binding step-by-step.
Contents
- Two-Way Binding Syntax
- Create Component and Module
- Two-Way Binding between Components
- Two-Way Binding with NgModel in Input Text Box
- Two-Way Binding with Input and Output Property Aliasing
- Two-Way Binding between Components to Change Style
- Two-Way Binding with NgModel in Select Box
- Two-Way Binding between Components using Object Property
- Two-Way Binding with NgModel using Object Property
- Run Application
- Reference
- Download Source Code
Two-Way Binding Syntax
The syntax for two-way binding is as follows.1. [(target)] = "source" is two-way binding where [] is to set value from source to target and () is to set value from target to source. For example find the code snippet.
<msg-app [(cdMsg)] ="msg"> </msg-app>
2. bindon-target = "source" is also two-way binding syntax where bind sets value from source to target and on sets value from target to source. For example find the code snippet.
<msg-app bindon-cdMsg ="msg"> </msg-app>
3. Use Change keyword as suffix in input variable name to create output variable. Suppose input variable name is xyz then output variable name will be
xyzChange.
4. [(ngModel)] = "source" is a two-way binding using
NgModel directive. We will use [(ngModel)] in HTML element where we set a specific element property and listen for an element change event . We will use two-way binding with NgModel in text box and select box in our example. [(ngModel)] can set only data-bound property. To use NgModel we need to import FormsModule and add it to imports attribute of @NgModule in our module file. Now for the example of two-way data binding using NgModel find the code snippet.
<input [(ngModel)] ="myMsg"/>
Create Component and Module
In our example we have a parent component that will call many child components. Find the parent component and its HTML template.app.component.ts
import {Component} from '@angular/core';
import {Employee} from './employee';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html'
})
export class AppComponent {
//Property for MsgComponent and AliasComponent
msg = 'Hello World';
//Property for AliasComponent
city = 'Varanasi';
//Property for TextSizeComponent
textSize = 20;
//Property for SelectBoxComponent
colors = ['RED', 'GREEN', 'YELLOW'];
//Property for CaseComponent
emp = new Employee(1, 'Mohan Das');
}
<b>1. msg-app</b><br/><br/>
<div>
<msg-app [(cdMsg)] ="msg"> </msg-app>
<msg-app bindon-cdMsg ="msg"> </msg-app>
<msg-app [cdMsg] ="msg" (cdMsgChange) = "msg=$event" > </msg-app>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
</div>
<b>2. text-app</b><br/><br/>
<div>
<text-app> </text-app>
</div>
<br/><b>3. alias-app</b><br/><br/>
<div>
<alias-app [(myCity)] ="city"> </alias-app>
{{city}}
</div>
<br/><b>4. size-app</b><br/><br/>
<div>
<size-app [(cdTextSize)] ="textSize"> </size-app>
<p [style.font-size.px] = "textSize">Hello World!</p>
</div>
<b>5. select-app</b><br/><br/>
<div>
<select-app [cdColors] ="colors"> </select-app>
</div>
<b>6. case-app</b><br/><br/>
<div>
<case-app [(myName)] ="emp.name"> </case-app>
<p>{{emp.name}} </p>
</div>
<b>7. upper-case-app</b><br/><br/>
<div>
<upper-case-app> </upper-case-app>
</div>
app.module.ts
import {NgModule} from '@angular/core';
import {BrowserModule} from '@angular/platform-browser';
import {FormsModule} from '@angular/forms';
import {AppComponent} from './app.component';
import {MsgComponent} from './msg.component';
import {AliasComponent} from './alias.component';
import {TextBoxComponent} from './textbox.component';
import {TextSizeComponent} from './textsize.component';
import {SelectBoxComponent} from './selectbox.component';
import {CaseComponent} from './case.component';
import {UpperCaseComponent} from './uppercase.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [BrowserModule,
FormsModule],
declarations: [AppComponent,
MsgComponent,
AliasComponent,
TextBoxComponent,
TextSizeComponent,
SelectBoxComponent,
CaseComponent,
UpperCaseComponent],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
FormsModule and adding it to imports attribute of @NgModule so that we can use NgModel in our code.
Two-Way Binding between Components
Here we will provide example for two-way data binding between components. We will discuss a scenario in which a string property of parent component will be sent to child component. In child component that property will be updated using text box. Parent component will listen the changes. We will provide step by step two-way binding example between the two components.1. Create a string property in
app.component.ts.
msg = 'Hello World';
2. Create input and output property in
msg.component.ts.
@Input() cdMsg : string; @Output() cdMsgChange = new EventEmitter<string>();
3. In
msg.component.html we will update cdMsg using a text box.
<input [value] = "cdMsg" (input)="update($event.target.value)"/>
4. For any input in text box,
update() method will be called.
update(val : string) {
this.cdMsg = val;
this.cdMsgChange.emit(this.cdMsg);
}
emit() method.
5. In
app.component.html we are performing two-way binding.
<msg-app [(cdMsg)] ="msg"> </msg-app>
<msg-app bindon-cdMsg ="msg"> </msg-app>
<msg-app [cdMsg] ="msg" (cdMsgChange) = "msg=$event" > </msg-app>
Now find the files used in our example.
msg.component.ts
import {Component, EventEmitter, Input, Output} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'msg-app',
templateUrl: './msg.component.html'
})
export class MsgComponent {
@Input() cdMsg : string;
@Output() cdMsgChange = new EventEmitter<string>();
update(val : string) {
this.cdMsg = val;
this.cdMsgChange.emit(this.cdMsg);
}
}
<input [value] = "cdMsg" (input)="update($event.target.value)"/>
Two-Way Binding with NgModel in Input Text Box
We will perform here two-way binding in input text box. The scenario is that a text box will display data using component property and on the change of text box value, component property will also get changed. Find the steps for two-way binding usingNgModel
1. To work with
NgModel we need FormsModule . Ensure that in module file we have imported FormsModule and added it to imports attribute of @NgModule . In my example module file is module.ts.
2. Create a property in
textbox.component.ts.
myMsg = 'Hello World!';
3. Use
ngModel for two-way binding in textbox.component.html.
<input [(ngModel)] ="myMsg"/>
[(ngModel)] can set only data-bound property. When we run the code the text box will display the value of myMsg. When the user changes the value in text box then myMsg will also get changed. Using bindon- we can use ngModel as follows.
<input bindon-ngModel ="myMsg"/>
4. If we want to use
NgModel as property binding and event binding separately then we need to use ngModel and ngModelChange as follows.
<input [ngModel] ="myMsg" (ngModelChange) ="myMsg=$event"/>
ngModel, then we do as follows.
<input [value] ="myMsg" (input)="myMsg=$event.target.value"/>
Now find the files used in our example.
textbox.component.ts
import {Component} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'text-app',
templateUrl: './textbox.component.html'
})
export class TextBoxComponent {
myMsg = 'Hello World!';
}
<input [(ngModel)] ="myMsg"/>
<br/>
<input bindon-ngModel ="myMsg"/>
<br/>
<input [ngModel] ="myMsg" (ngModelChange) ="myMsg=$event"/>
<br/>
<input [value] ="myMsg" (input)="myMsg=$event.target.value"/>
<br/>
{{myMsg}}
app.component.html we will call textbox.component.ts.
<div>
<text-app> </text-app>
</div>
Two-Way Binding with Input and Output Property Aliasing
We will understand here how to use two-way binding between components when@Input and @Output decorators are using property name aliasing. The property name pattern will be followed in alias name for two-way binding.
Now find the code that are using
@Input and @Output decorators.
alias.component.ts
import {Component, EventEmitter, Input, Output} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'alias-app',
templateUrl: './alias.component.html'
})
export class AliasComponent {
@Input('myCity') strCity : string;
@Output('myCityChange') cityObj = new EventEmitter<string>();
emitCity() {
this.cityObj.emit(this.strCity);
}
}
strCity is myCity and the alias for output property cityObj is myCityChange. Here event name alias is input property name alias adding Change as suffix. So we can perform two-way binding with these aliases.
strCity is getting updated by two-way binding using [(ngModel)] in text box. On click of button, emitCity() will be called. Find the HTML template.
alias.component.html
<input [(ngModel)] ="strCity" /> <button (click)="emitCity()" >Update</button>
app.component.html.
<div>
<alias-app [(myCity)] ="city"> </alias-app>
{{city}}
</div>
In
app.component.ts we are initializing our city property.
city = 'Varanasi';
alias.component.html.
Two-Way Binding between Components to Change Style
For the demo of two-way binding, now we will provide an example in which we have two buttons as plus(+) and minus(-). On click of these buttons we will change the font size of a text. Here we are using component element two-way binding.app.component.ts will initialize a font size in textSize property and it will send it to textsize.component.ts. Using plus and minus button we will increase and decrease its value that will also get updated in app.component.ts.
To achieve it we have created the property for size with some initial value in
app.component.ts.
textSize = 20;
app.component.html we are calling textsize.component.ts by creating component element with two-way binding as follows.
<div>
<size-app [(cdTextSize)] ="textSize"> </size-app>
<p [style.font-size.px] = "textSize">Hello World!</p>
</div>
textsize.component.ts file and its HTML template file.
textsize.component.ts
import {Component, EventEmitter, Input, Output} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'size-app',
templateUrl: './textsize.component.html'
})
export class TextSizeComponent {
@Input() cdTextSize : number;
@Output() cdTextSizeChange = new EventEmitter<number>();
plus() {
this.cdTextSize = this.cdTextSize + 1;
this.emitSize();
}
minus() {
this.cdTextSize = this.cdTextSize - 1;
this.emitSize();
}
emitSize() {
this.cdTextSizeChange.emit(this.cdTextSize);
}
}
<button (click)="plus()"> + </button> <button (click)="minus()"> - </button>
Two-Way Binding with NgModel in Select Box
Here we will provide example for two-way binding in which we will show how to useNgModel with HTML select box. The scenario is that an array of colors will be populated by select box. A default color initialized by component property will be selected initially in select box and a sample text is using that color. On change of color in select box, the color of text will change.
selectbox.component.ts
import {Component, EventEmitter, Input} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'select-app',
templateUrl: './selectbox.component.html'
})
export class SelectBoxComponent {
@Input() cdColors : Array<string>;
myColor = 'GREEN';
}
<!--select [value] ="myColor" (change)="myColor=$event.target.value" -->
<select [(ngModel)] ="myColor">
<option *ngFor = "let color of cdColors" [value] = "color">
{{color}}
</option>
</select>
<p [style.color] = "myColor"> Hello World!</p>
NgModel for two-way binding. We will observe that myColor is initially providing a default color as selected in select box and on change of color selection the value of myColor is getting changed.
If we do not want to use
NgModel we will do as follows.
<select [value] ="myColor" (change)="myColor=$event.target.value" >
We are using
selectbox.component.ts in app.component.html as follows.
<div> <select-app [cdColors] ="colors"> </select-app> </div>
app.component.ts is defining the array property colors.
colors = ['RED', 'GREEN', 'YELLOW'];
Two-Way Binding between Components using Object Property
Here we will use an object property for two-way binding between components. We have a class as follows.employee.ts
export class Employee {
constructor(public id : number, public name : string) {
}
}
app.component.ts we are creating an object of Employee class. Using two-way binding we will send name property of Employee class to case.component.ts. In this component we change the text as lowercase and uppercase on the click of radio button and then send this changed data to name property of Employee class in app.component.ts . Now find the code to change lower and upper case.
case.component.ts
import {Component, EventEmitter, Input, Output} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'case-app',
templateUrl: './case.component.html'
})
export class CaseComponent {
@Input() myName : string;
@Output() myNameChange = new EventEmitter<string>();
changeCase(val:string) {
if (val == 'upper') {
this.myName = this.myName.toUpperCase();
} else {
this.myName = this.myName.toLowerCase();
}
this.myNameChange.emit(this.myName);
}
}
<input type="radio" name="case" (click) = "changeCase('upper')">Upper Case<br>
<input type="radio" name="case" (click) = "changeCase('lower')"> Lower Case<br>
app.component.html as follows.
<div>
<case-app [(myName)] ="emp.name"> </case-app>
<p>{{emp.name}} </p>
</div>
app.component.ts we are instantiating Employee class as follows.
emp = new Employee(1, 'Mohan Das');
Two-Way Binding with NgModel using Object Property
Here we will useNgModel for two-way binding with object property. Our scenario is that we will create text box which will display value of name property of Employee class and on change of text box value the name property of Employee class will also get updated.
uppercase.component.ts
import {Component} from '@angular/core';
import {Employee} from './employee';
@Component({
selector: 'upper-case-app',
templateUrl: './uppercase.component.html'
})
export class UpperCaseComponent {
employee = new Employee(100, 'Mahesh Sharma');
toUpper(val:string) {
this.employee.name = val.toUpperCase();
}
}
<input [(ngModel)] ="employee.name"/>{{employee.name}}
<br/><input [ngModel] ="employee.name" (ngModelChange) ="toUpper($event)"/>{{employee.name}}
ngModelChange for event binding then we can call our component method and can pass data to it. Now we will use uppercase.component.ts in app.component.ts as follows.
<div>
<upper-case-app> </upper-case-app>
</div>
Run Application
Download the source code and run the application. Find the print-screen of the output.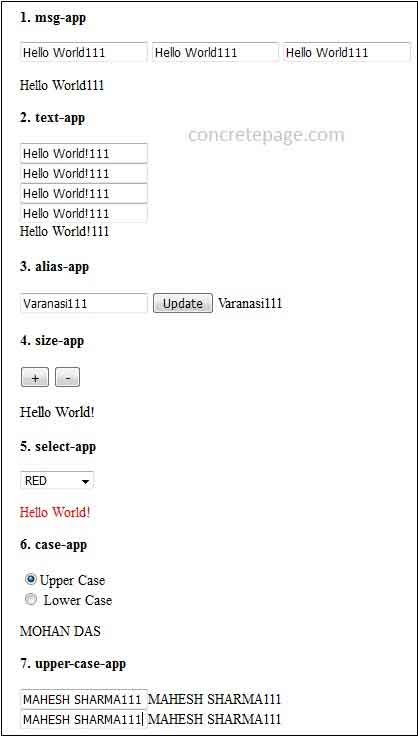
1. msg-app
When we change value in any text box then all text box value will get updated and at the same time text outside the text box will also get changed.
2. text-app
When we change value in any text box then all text box value will get updated and at the same time text outside the text box will also get changed.
3. alias-app
When we change value in text box and click on update button, the text will also get changed.
4. size-app
On click of button the size of text "Hello World!" will change. When we click plus (+), text size will increase and when we click minus (-) , text size will decrease.
5. select-app
When we select the color from select box then that color will also be applied on text color of "Hello World!".
6. case-app
When we click upper case radio button, the name will appear in upper case and when we click lower case radio button, the name will appear in lower case.
7. upper-case-app
In first text box when we change value, both the text box and text outside text box will get changed. When we change value in second text box, both the text box and text outside text box will get changed as well as they will be converted in upper case.
I am done now. Happy Angular learning!


