Angular NgForm with NgModel Directive Example
October 19, 2021
On this page we will provide Angular NgForm example with NgModel directive. To create HTML form using NgForm with NgModel is called template-driven form. The NgForm directive is used with HTML form tag that can be exported in local template variable to access form values and validation status and to pass entire form to our class on form submit. The NgModel is used in form fields and can be exported in local template variable to get its values and validation status in HTML template.
When we create HTML form, we have to use
name attribute in form fields. In the context of NgForm, the role of NgModel is to register the form field with form using name attribute. The NgModel is also used to bind the domain model of the class with view.
On this page we will provide how to use
NgForm in our Angular application. We will create some form fields within form and use NgModel with them. We will also provide using one-way and two-way binding with NgModel within the form tag. Let us understand complete example step-by-step.
Contents
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Angular 12.1.0
2. Node.js 12.14.1
3. NPM 7.20.3
NgForm Directive
NgForm directive is used with HTML <form> tag. To understand
NgForm, we should be aware with following classes.
FormControl : This class tracks the value and validation status of an individual form control.
FormGroup : This class tracks the value and validity state of a group of
FormControl.
Now let us understand
NgForm directive. NgForm is a directive that creates a top-level FormGroup instance and binds it to a form to track aggregate form value and validation status.
Find the steps to use
NgForm in our application.
1. Configure
FormsModule in imports metadata of @NgModule decorator in application module as given below.
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
@NgModule({
imports: [
FormsModule
------
],
------
})
export class AppModule { }
FormsModule, NgForm directive becomes active by default on all <form> tags. We can export NgForm into a local template variable. To import it we need to use NgForm as ngForm. Find the sample example.
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)"> ---------------- ---------------- <button>Submit</button> </form>
<button> whose type is submit by default for the entire modern browser.
Exporting
NgForm into local template variable is optional but useful. In the above code snippet, look into #userForm="ngForm". Here local template variable is userForm. Using local template variable we can access form in our HTML template as following.
userForm.value: It will return form value. It means we get an object containing the values of all the fields used within
<form> tag.
userForm.valid: It will return boolean value. When the value is true then form is valid. Form is said to be valid if all the fields returns validity true.
userForm.touched: It will return boolean value. If the value is true, it means user has entered value at least in one field.
userForm.submitted: It will return boolean value. If the value is true, it means form has been submitted.
We use local template variable to submit form data. Look into
(ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)"
onFormSubmit(userForm: NgForm) {
console.log(userForm.value);
console.log('Name:' + userForm.controls['name'].value);
console.log('Form Valid:' + userForm.valid);
console.log('Form Submitted:' + userForm.submitted);
}
controls[] of NgForm, we can access the form field value by field name in our class as following.
userForm.controls['name'].value; userForm.controls['city'].value; userForm.controls['state'].value
3. To reset form,
NgForm has resetForm() method that is called as follows.
resetUserForm(userForm: NgForm) {
userForm.resetForm();;
}
<button type="button" (click)="resetUserForm(userForm)">Reset</button>
resetUserForm(userForm: NgForm) {
userForm.resetForm({
name: 'Mahesh',
city: 'Noida'
});
}
NgModel Directive
NgModel directive creates a FormControl instance from a domain model created in class and binds it to a form control element. FormControl keeps the track of user interaction and validation status of the form control. NgModel can be used standalone as well as with the parent form. When it is used as standalone, we can use it as follows.
<input [(ngModel)]="name" required #userName="ngModel">
<p>Name value: {{ name }} </p>
<p>Name value: {{ userName.value }} </p>
<p>Name valid: {{ userName.valid }} </p>
#userName="ngModel". Here userName is local template variable that can be used to get form control value, valid, invalid, pending etc properties in HTML template.
NgModel can be used as one-way binding and two-way binding. In one way binding using [ ] sign, when value changes in domain model in the class then that is set to view also. In two-way binding using [( )] sign, the value changes in domain model is set to view and values changes in view is also set to domain model.
NgForm with NgModel
We will use hereNgForm with NgModel directive. When we use ngModel with <form> tag, we have also to supply a name attribute to register a control with parent form using that name.
When we are using parent form, we need not to use two-way binding to get form fields values in our class. We can pass
<form> local template variable such as userForm to our submit method such as onFormSubmit(userForm) as given below.
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)">
onFormSubmit(userForm: NgForm) {
console.log(userForm.value);
console.log('Name:' + userForm.controls['name'].value);
}
ngModel attribute in fields when using with parent form as given below.
<input name="message" ngModel>
ngModel attribute in fields such as
<input name="message" >
Let us understand case by case.
Case-1: Here we are using two-way binding in parent form.
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)"> <input name="message" [(ngModel)] = "msg"> <button>Submit</button> </form>
NgForm in our class. In case of parent form, most of the time, we need not to use two-way binding because we can access values in our class using NgForm itself. name attribute is required to register control with form.
Case-2: Here we are using one-way binding in parent form.
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)"> <input name="message" [ngModel] = "msg"> <button>Submit</button> </form>
name attribute is required to register control with form.
Case-3: Here we are using neither one-way nor two way binding.
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)"> <input name="message" ngModel> <button>Submit</button> </form>
ngModel as field attribute. If we are using neither one-way nor two way binding, still we need to use ngModel attribute so that the field can be registered with parent form otherwise the field value will not be passed on form submit. name attribute is required to register control with form.
Case-4: Here we are not using
ngModel in any way.
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)"> <input name="message"> <button>Submit</button> </form>
ngModel as field attribute. If we are not using ngModel as field attribute then that field will not be registered with parent form and hence the field value will not be passed on form submit to our class.
Complete Example
Find the complete example.app.component.html
<h3>Using NgForm with NgModel</h3>
<div>
<form #userForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit(userForm)">
<div>
Name: <input name="name" ngModel required #userName="ngModel">
</div>
<div>
City: <input name="city" ngModel #userCity="ngModel">
</div>
<div>
State: <input name="state" ngModel>
</div>
<div>
<button>Submit</button>
<button type="button" (click)="resetUserForm(userForm)">Reset</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div>
<p>Form value: <b> {{ userForm.value | json }} </b></p>
<p>Form valid: <b> {{ userForm.valid }} </b></p>
<p>Form touched: <b> {{ userForm.touched }} </b></p>
<p>Form submitted: <b> {{ userForm.submitted }} </b></p>
</div>
<div>
<p>Name value: <b> {{ userName.value }} </b></p>
<p>Name valid: <b> {{ userName.valid }} </b></p>
</div>
<div>
<p>City value: <b> {{ userCity.value }} </b></p>
<p>City valid: <b> {{ userCity.valid }} </b></p>
</div>
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { NgForm } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: 'app.component.html'
})
export class AppComponent {
onFormSubmit(userForm: NgForm) {
console.log(userForm.value);
console.log('Name:' + userForm.controls['name'].value);
console.log('Form Valid:' + userForm.valid);
console.log('Form Submitted:' + userForm.submitted);
}
resetUserForm(userForm: NgForm) {
userForm.resetForm();;
}
}
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
],
bootstrap: [
AppComponent
]
})
export class AppModule { }
Run Application
To run the application, find the following steps.1. Download source code using download link given below on this page.
2. Use downloaded src in your Angular CLI application. To install Angular CLI, find the link.
3. Run ng serve using command prompt.
4. Now access the URL http://localhost:4200
Find the print screen.
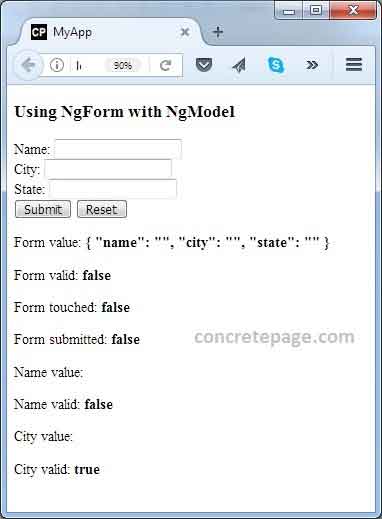
References
NgFormNgModel


