Angular HTTP POST Example
January 27, 2024
Angular HttpClient performs HTTP requests. The HttpClient methods are get(), post(), put(), delete() etc. To perform HTTP POST, we need to use HttpClient.post() method.
On this page we will provide the example to use
HttpClient.post and HttpClient.get() methods. We will display data with Observable as well as Promise. For testing purpose we are using angular in-memory web API to post and fetch data. Find the complete example step-by-step.
Contents
HttpClient.post()
TheHttpClient.post() method performs HTTP POST method. The HttpClient.post() constructs an Observable instance. The HTTP POST request is performed only when this Observable instance is subscribed. The HttpClient.post() method has more than one overloads. Find the generic syntax.
post(url, body, options): Observable
body: 'any' type. This is the content to post.
options: 'Object' type. This represents the HTTP options. HTTP options object can be as following.
options: {
headers?: HttpHeaders|{[header: string]: string | string[]},
context?: HttpContext,
observe?: 'body'|'events'|'response',
params?: HttpParams|
{[param: string]: string | number | boolean | ReadonlyArray<string|number|boolean>},
reportProgress?: boolean,
responseType?: 'arraybuffer'|'blob'|'json'|'text',
withCredentials?: boolean,
}
options parameter, then object with default values is considered by HttpClient.post() method.
To use
HttpClient.post() method in our Angular application, we need to follow below steps.
Step-1: Import
HttpClientModule in application module.
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
@NgModule({
imports: [
HttpClientModule,
------
],
---------
})
export class AppModule { }
HttpClient service as given below.
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
post() method as follows.
Observable<any> ob = this.http.post(this.url, book, options);
post() method returns instance of Observable that can be later subscribed to get result.
Angular In-Memory Web API
Angular provides in-memory web API to process HTTP request in test environment. Angular in-memory web API provides a dummy URL to test application that can be replaced by actual REST web service URL later. To use it in our Angular application, we need to follow below steps.Step-1: Install angular-in-memory-web-api using below command from root folder of the project.
npm i angular-in-memory-web-api@0.11.0 --save
InMemoryDbService interface. In our example we are creating an in-memory DB for books.
book-data.ts
import { InMemoryDbService } from 'angular-in-memory-web-api';
export class BookData implements InMemoryDbService {
createDb() {
let books = [
{ id: 1, name: 'Core Java' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Angular' },
{ id: 3, name: 'Hibernate' }
];
return { books };
}
}
Step-3: Before using DB we need to configure our above class in application module as following.
import { InMemoryWebApiModule } from 'angular-in-memory-web-api';
import { BookData } from './book-data';
@NgModule({
imports: [
------
InMemoryWebApiModule.forRoot(BookData)
],
------
})
export class AppModule { }
For testing purpose, we can also use JSON-Server instead of Angular In-Memory Web API.
HttpClient.post() with Observable
Find the code snippet to useHttpClient.post() with Observable.
addBookWithObservable(book:Book): Observable<Book> {
let httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders({
'Content-Type' : 'application/json',
'Cache-Control': 'no-cache'
});
return this.http.post(this.url, book, { headers: httpHeaders }).pipe(
map(this.extractData),
catchError(this.handleErrorObservable)
);
}
pipe(): It combines functional operators into a chain.
map: It applies a given function to each element emitted by the source
Observable and emits the resulting values as an Observable.
catchError: It catches the error thrown by
Observable and handles it by returning a new Observable.
Find the code for
extractData and handleErrorObservable methods used in the above code snippet.
private extractData(res: any) {
let body = res;
return body;
}
private handleErrorObservable(error: any) {
console.error(error.message || error);
return throwError(error);
}
HttpClient.post() with Promise
Find the code snippet to useHttpClient.post() with Promise.
addBookWithPromise(book:Book): Promise<Book> {
let httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders({
'Content-Type' : 'application/json',
'Cache-Control': 'no-cache'
});
return this.http.post(this.url, book, { headers: httpHeaders }).toPromise()
.then(this.extractData)
.catch(this.handleErrorPromise);
}
Observable into Promise using RxJS toPromise() method.
Find the code for
handleErrorPromise method used in above code.
private handleErrorPromise(error: Response | any) {
console.error(error.message || error);
return Promise.reject(error.message || error);
}
Complete Example
Now find the complete example.book.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable, throwError } from 'rxjs';
import { HttpClient, HttpHeaders, HttpResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { map, catchError } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { Book } from './book';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class BookService {
url = "api/books";
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
getBooksWithObservable(): Observable<Book[]> {
return this.http.get(this.url).pipe(
map(this.extractData),
catchError(this.handleErrorObservable)
);
}
addBookWithObservable(book: Book): Observable<Book> {
let httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders({
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Cache-Control': 'no-cache'
});
return this.http.post(this.url, book, { headers: httpHeaders }).pipe(
map(this.extractData),
catchError(this.handleErrorObservable)
);
}
getBooksWithPromise(): Promise<Book[]> {
return this.http.get(this.url).toPromise()
.then(this.extractData)
.catch(this.handleErrorPromise);
}
addBookWithPromise(book: Book): Promise<Book> {
let httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders({
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Cache-Control': 'no-cache'
});
return this.http.post(this.url, book, { headers: httpHeaders }).toPromise()
.then(this.extractData)
.catch(this.handleErrorPromise);
}
private extractData(res: any) {
let body = res;
return body;
}
private handleErrorObservable(error: any) {
console.error(error.message || error);
return throwError(error);
}
private handleErrorPromise(error: Response | any) {
console.error(error.message || error);
return Promise.reject(error.message || error);
}
}
export interface Book {
id: number;
name: string;
}
Observable.
observable.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { BookService } from './book.service';
import { Book } from './book';
@Component({
selector: 'app-observable',
templateUrl: './observable.component.html',
styleUrls: ['observable.component.css']
})
export class ObservableComponent implements OnInit {
books: Book[] = [];
errorMessage = '';
bookName = '';
book = { id: 0, name: '' };
constructor(private bookService: BookService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.fetchBooks();
}
fetchBooks() {
this.bookService.getBooksWithObservable()
.subscribe(books => this.books = books,
error => this.errorMessage = error);
}
addBook() {
this.bookService.addBookWithObservable(this.book)
.subscribe(book => {
this.fetchBooks();
this.reset();
this.bookName = book.name;
},
error => this.errorMessage = error);
}
private reset() {
this.book.id = 0;
this.book.name = '';
this.errorMessage = '';
this.bookName = '';
}
}
fetchBooks() method inside subscribe() method.
Now find the HTML template.
observable.component.html.
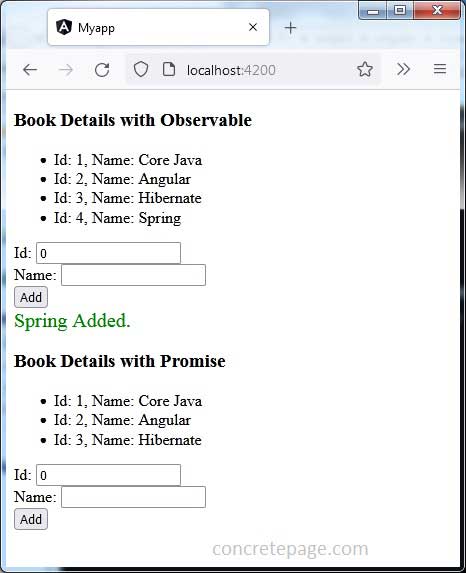
<h3>Book Details with Observable </h3>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let book of books">
Id: {{book.id}}, Name: {{book.name}}
</li>
</ul>
<div>
<div>
<label>Id: </label>
<input [(ngModel)]="book.id" />
</div>
<div>
<label>Name: </label>
<input [(ngModel)]="book.name" />
</div>
<div>
<button (click)="addBook()">Add</button>
</div>
</div>
<div *ngIf="bookName" [ngClass]="'success'"> {{bookName}} Added. </div>
<div *ngIf="errorMessage" [ngClass]="'error'"> {{errorMessage}} </div>
.success{
color: green;
font-size: 20px;
}
.error{
color: red;
font-size: 20px;
}
Promise.
promise.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { BookService } from './book.service';
import { Book } from './book';
@Component({
selector: 'app-promise',
templateUrl: './promise.component.html',
styleUrls: ['promise.component.css']
})
export class PromiseComponent implements OnInit {
books: Book[] = [];
errorMessage = '';
bookName = '';
book = { id: 0, name: '' };
constructor(private bookService: BookService) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.fetchBooks();
}
fetchBooks(): void {
this.bookService.getBooksWithPromise()
.then(books => this.books = books,
error => this.errorMessage = error);
}
addBook(): void {
this.bookService.addBookWithPromise(this.book)
.then(book => {
this.fetchBooks();
this.reset();
this.bookName = book.name;
},
error => this.errorMessage = error);
}
private reset() {
this.book.id = 0;
this.book.name = '';
this.errorMessage = '';
this.bookName = '';
}
}
fetchBooks() method inside then() method.
Now find the HTML template.
promise.component.html
<h3>Book Details with Promise </h3>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let book of books">
Id: {{book.id}}, Name: {{book.name}}
</li>
</ul>
<div>
<div>
<label>Id: </label>
<input [(ngModel)]="book.id" />
</div>
<div>
<label>Name: </label>
<input [(ngModel)]="book.name" />
</div>
<div>
<button (click)="addBook()">Add</button>
</div>
</div>
<div *ngIf="bookName" [ngClass]="'success'"> {{bookName}} Added. </div>
<div *ngIf="errorMessage" [ngClass]="'error'"> {{errorMessage}} </div>
.success{
color: green;
font-size: 20px;
}
.error{
color: red;
font-size: 20px;
}
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<app-observable></app-observable>
<app-promise></app-promise>
`
})
export class AppComponent {
}
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
import { InMemoryWebApiModule } from 'angular-in-memory-web-api';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { ObservableComponent } from './observable.component';
import { PromiseComponent } from './promise.component';
import { BookData } from './book-data';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
HttpClientModule,
InMemoryWebApiModule.forRoot(BookData)
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
ObservableComponent,
PromiseComponent
],
providers: [
],
bootstrap: [
AppComponent
]
})
export class AppModule { }