Spring Boot CrudRepository Example
December 02, 2017
This page will walk through Spring Boot CrudRepository example. Spring Boot Data enables JPA repository support by default. CrudRepository provides generic CRUD operation on a repository for a specific type. CrudRepository is a Spring data interface and to use it we need to create our interface by extending CrudRepository. Spring provides CrudRepository implementation class automatically at runtime. It contains methods such as save, findById, delete, count etc. Spring boot automatically detects our repository if the package of that repository interface is the same or sub-package of the class annotated with @SpringBootApplication.Spring Boot provides default database configurations when it scans Spring Data JPA in classpath. Spring boot uses spring-boot-starter-data-jpa starter to configure spring JPA. For data source we need to configure data source properties starting with
spring.datasource.* in application.properties. In Spring Boot 2.0 release, default database pooling technology has been switched from Tomcat Pool to HikariCP. Spring boot prefers HikariCP on first place then Tomcat pooling and then Commons DBCP2 on the basis of availability. Here on this page we will create a Spring Boot Rest web Service for CRUD operation. CRUD operation will be performed by CrudRepository. Now find the complete example step by step.
Contents
- 1. Technologies Used
- 2. Maven File used in Project
- 3. CrudRepository Interface
- 4. Steps to Use CrudRepository
- 5. Custom Repository Methods
- 6. @Transactional with CrudRepository
- 7. Configure Properties in application.properties File
- 8. Spring Boot REST + Spring Boot Data CrudRepository + JPA + Hibernate + MySQL CRUD Example
- 9. Client Code with RestTemplate
- 10. Test Application
- 11. References
- 12. Download Source Code
1. Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Java 9
2. Spring 5.0.5.RELEASE
3. Spring Boot 2.0.1.RELEASE
4. Maven 3.5.2
5. MySQL 5.5
6. Eclipse Oxygen
2. Maven File used in Project
Find thepom.xml used in our example.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.concretepage</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>spring-demo</name>
<description>Spring Boot Demo Project</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>9</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
3. CrudRepository Interface
CrudRepository is an interface and extends Spring data Repository interface. CrudRepository provides generic CRUD operation on a repository for a specific type. It has generic methods for CRUD operation. To use CrudRepository we have to create our interface and extend CrudRepository. We need not to implement our interface, its implementation will be created automatically at runtime. Find some of CrudRepository methods.
<S extends T> S save(S entity): Saves and updates the current entity and returns that entity.
Optional<T> findById(ID primaryKey): Returns the entity for the given id.
Iterable<T> findAll(): Returns all entities.
long count(): Returns the count.
void delete(T entity): Deletes the given entity.
boolean existsById(ID primaryKey): Checks if the entity for the given id exists or not.
CrudRepository has subinterface as PagingAndSortingRepository that provides additional methods to retrieve entities using the pagination and sorting abstraction.
4. Steps to Use CrudRepository
Spring boot enables JPA repository support by default. To useCrudRepository in our Spring data application we need to create an interface implementing CrudRepository and then all is done to use it. Let us discuss step wise how to use CrudRepository in our Spring data application.
4.1 Create an Interface extending CrudRepository
In our example we will perform CRUD operations on article data for demo. So I will create an interface for article extendingCrudRepository as following.
public interface ArticleRepository extends CrudRepository<Article, Long> {
}
4.2 Auto-Detection of JPA Repository
Spring boot can automatically detect our repository if the package of that interface is the same or sub-package of the class annotated with@SpringBootApplication and if not then we need to use @EnableJpaRepositories annotation with @SpringBootApplication. Let us understand by example.
Suppose we have a class annotated with
@SpringBootApplication in the package com.concretepage as given below.
package com.concretepage;
------
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
------
}
ArticleRepository and it resides in package com.concretepage or its sub-packages such as com.concretepage.repository then Spring boot will automatically detect our repository and so no need to use @EnableJpaRepositories annotation.
If we choose a package for our repository that is neither same package nor sub-package of the package of the class annotated with
@SpringBootApplication, then Spring boot will not be able to detect repository classes by default. In this case we need to use @EnableJpaRepositories annotation with @SpringBootApplication. Using @EnableJpaRepositories we will configure package name in which our repository classes reside. Suppose the package of our repository classes is com.cp.repository, we will use @EnableJpaRepositories as following.
package com.concretepage;
------
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableJpaRepositories("com.cp.repository")
public class MyApplication {
------
}
basePackageClasses attribute of the @EnableJpaRepositories annotation. Suppose we have a class ArticleRepository in the package com.cp.repository, then we can configure repository using basePackageClasses as following.
package com.concretepage;
-----
import com.cp.repository.ArticleRepository;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackageClasses= {ArticleRepository.class})
public class MyApplication {
------
}
4.3 Instantiate and Use CrudRepository
To instantiate ourArticleRepository that has extended CrudRepository, we can use dependency injection.
public class ArticleService {
@Autowired
private ArticleRepository articleRepository;
------
}
CrudRepository. Find the example for some of its methods.
a. Create and Update:
Article savedArticle = articleRepository.save(article);
Article obj = articleRepository.findById(articleId).get(); Iterable<Article> articles = articleRepository.findAll();
articleRepository.delete(article);
5. Custom Repository Methods
CrudRepository provides methods for generic CRUD operation and if we want to add custom methods in our interface that has extended CrudRepository, we can add in following ways.
a. We can start our query method names with
find...By, read...By, query...By, count...By, and get...By. Before By we can add expression such as Distinct . After By we need to add property names of our entity.
b. To get data on the basis of more than one property we can concatenate property names using
And and Or while creating method names.
c. If we want to use completely custom name for our method, we can use
@Query annotation to write query.
Find the code snippet that is using the sample method name for the above scenarios.
public interface ArticleRepository extends CrudRepository<Article, Long> {
List<Article> findByTitle(String title);
List<Article> findDistinctByCategory(String category);
List<Article> findByTitleAndCategory(String title, String category);
@Query("SELECT a FROM Article a WHERE a.title=:title and a.category=:category")
List<Article> fetchArticles(@Param("title") String title, @Param("category") String category);
}
6. @Transactional with CrudRepository
CRUD methods ofCrudRepository are transactional by default. They are annotated with @Transactional annotation with default settings in implementation class at runtime. For reading operation readOnly flag is set to true. To override default transactional settings of any CrudRepository methods we need to override that method in our interface and annotate with @Transactional using required configurations. Find the example.
public interface ArticleRepository extends CrudRepository<Article, Long> {
@Override
@Transactional(timeout = 8)
Iterable<Article> findAll();
}
timeout as 8 seconds to execute query without readOnly flag for findAll() method.
7. Configure Properties in application.properties File
Datasource, JPA properties and logging etc need to be configured inapplication.properties file located in the classpath of Spring boot application. These properties will automatically be read by Spring boot.
application.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/concretepage spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=cp spring.datasource.hikari.connection-timeout=20000 spring.datasource.hikari.minimum-idle=5 spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=12 spring.datasource.hikari.idle-timeout=300000 spring.datasource.hikari.max-lifetime=1200000 spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings = false spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql = true logging.level.org.hibernate.SQL=DEBUG logging.level.org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder=TRACE
spring-boot-starter-jdbc and spring-boot-starter-data-jpa resolve HikariCP dependency by default and spring.datasource.type property has HikariDataSource as default value. The datasource properties starting with spring.datasource.* will automatically be read by Spring boot JPA. To change the Hibernate properties we will use prefix spring.jpa.properties.* with Hibernate property name. On the basis of given data source URL, Spring boot can automatically identify data source driver class. So we need not to configure diver class.
Find the properties to configure
JpaBaseConfiguration and HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration in application.properties.
spring.data.jpa.repositories.enabled: It enables JPA repositories. The default value is true.
spring.jpa.database: It targets database to operate on. By default embedded database is auto-detected.
spring.jpa.database-platform: It is used to provide the name of database to operate on. By default it is auto- detected.
spring.jpa.generate-ddl: It is used to initialize schema on startup. By default the value is false.
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto: It is DDL mode used for embedded database. Default value is create-drop.
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.implicit-strategy: It is Hibernate 5 implicit naming strategy fully qualified name.
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.physical-strategy: It is Hibernate 5 physical naming strategy fully qualified name.
spring.jpa.hibernate.use-new-id-generator-mappings: It is used for Hibernate
IdentifierGenerator for AUTO, TABLE and SEQUENCE.
spring.jpa.open-in-view: The default value is true. It binds a JPA
EntityManager to the thread for the entire processing of the request.
spring.jpa.properties.*: It sets additional native properties to set on the JPA provider.
spring.jpa.show-sql: It enables logging of SQL statements. Default value is false.
8. Spring Boot REST + Spring Boot Data CrudRepository + JPA + Hibernate + MySQL CRUD Example
Find the project structure of our demo project.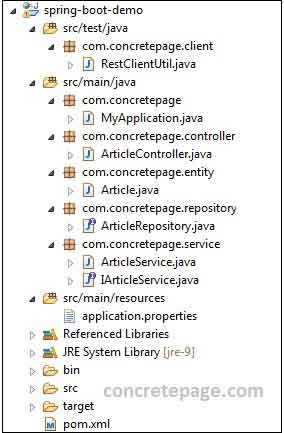
Database Table
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `concretepage`; USE `concretepage`; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `articles` ( `article_id` bigint(5) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `title` varchar(200) NOT NULL, `category` varchar(100) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`article_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB; INSERT INTO `articles` (`article_id`, `title`, `category`) VALUES (1, 'Java Concurrency', 'Java'), (2, 'Spring Boot Getting Started', 'Spring Boot'), (3, 'Lambda Expressions Java 8 Example', 'Java 8');
ArticleRepository.java
package com.concretepage.repository;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
public interface ArticleRepository extends CrudRepository<Article, Long> {
List<Article> findByTitle(String title);
List<Article> findDistinctByCategory(String category);
List<Article> findByTitleAndCategory(String title, String category);
}
package com.concretepage.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="articles")
public class Article implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name="article_id")
private long articleId;
@Column(name="title")
private String title;
@Column(name="category")
private String category;
public long getArticleId() {
return articleId;
}
public void setArticleId(long articleId) {
this.articleId = articleId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(String category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
package com.concretepage.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
public interface IArticleService {
List<Article> getAllArticles();
Article getArticleById(long articleId);
boolean addArticle(Article article);
void updateArticle(Article article);
void deleteArticle(int articleId);
}
package com.concretepage.service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
import com.concretepage.repository.ArticleRepository;
@Service
public class ArticleService implements IArticleService {
@Autowired
private ArticleRepository articleRepository;
@Override
public Article getArticleById(long articleId) {
Article obj = articleRepository.findById(articleId).get();
return obj;
}
@Override
public List<Article> getAllArticles(){
List<Article> list = new ArrayList<>();
articleRepository.findAll().forEach(e -> list.add(e));
return list;
}
@Override
public synchronized boolean addArticle(Article article){
List<Article> list = articleRepository.findByTitleAndCategory(article.getTitle(), article.getCategory());
if (list.size() > 0) {
return false;
} else {
articleRepository.save(article);
return true;
}
}
@Override
public void updateArticle(Article article) {
articleRepository.save(article);
}
@Override
public void deleteArticle(int articleId) {
articleRepository.delete(getArticleById(articleId));
}
}
package com.concretepage.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
import com.concretepage.service.IArticleService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class ArticleController {
@Autowired
private IArticleService articleService;
@GetMapping("article/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Article> getArticleById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
Article article = articleService.getArticleById(id);
return new ResponseEntity<Article>(article, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@GetMapping("articles")
public ResponseEntity<List<Article>> getAllArticles() {
List<Article> list = articleService.getAllArticles();
return new ResponseEntity<List<Article>>(list, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@PostMapping("article")
public ResponseEntity<Void> addArticle(@RequestBody Article article, UriComponentsBuilder builder) {
boolean flag = articleService.addArticle(article);
if (flag == false) {
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.CONFLICT);
}
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setLocation(builder.path("/article/{id}").buildAndExpand(article.getArticleId()).toUri());
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(headers, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@PutMapping("article")
public ResponseEntity<Article> updateArticle(@RequestBody Article article) {
articleService.updateArticle(article);
return new ResponseEntity<Article>(article, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@DeleteMapping("article/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteArticle(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
articleService.deleteArticle(id);
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
9. Client Code with RestTemplate
RestClientUtil.java
package com.concretepage.client;
import java.net.URI;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
public class RestClientUtil {
public void getArticleByIdDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/user/article/{id}";
HttpEntity<String> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<String>(headers);
ResponseEntity<Article> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestEntity, Article.class, 1);
Article article = responseEntity.getBody();
System.out.println("Id:"+article.getArticleId()+", Title:"+article.getTitle()
+", Category:"+article.getCategory());
}
public void getAllArticlesDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/user/articles";
HttpEntity<String> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<String>(headers);
ResponseEntity<Article[]> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestEntity, Article[].class);
Article[] articles = responseEntity.getBody();
for(Article article : articles) {
System.out.println("Id:"+article.getArticleId()+", Title:"+article.getTitle()
+", Category: "+article.getCategory());
}
}
public void addArticleDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/user/article";
Article objArticle = new Article();
objArticle.setTitle("Spring REST Security using Hibernate");
objArticle.setCategory("Spring");
HttpEntity<Article> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<Article>(objArticle, headers);
URI uri = restTemplate.postForLocation(url, requestEntity);
System.out.println(uri.getPath());
}
public void updateArticleDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/user/article";
Article objArticle = new Article();
objArticle.setArticleId(1);
objArticle.setTitle("Update:Java Concurrency");
objArticle.setCategory("Java");
HttpEntity<Article> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<Article>(objArticle, headers);
restTemplate.put(url, requestEntity);
}
public void deleteArticleDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/user/article/{id}";
HttpEntity<Article> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<Article>(headers);
restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.DELETE, requestEntity, Void.class, 4);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
RestClientUtil util = new RestClientUtil();
//util.getArticleByIdDemo();
//util.addArticleDemo();
//util.updateArticleDemo();
//util.deleteArticleDemo();
util.getAllArticlesDemo();
}
}
10. Test Application
To test the application, first create table in MySQL as given in the example. Then we can run REST web service in following ways.1. Using Eclipse: Download the project source code using the download link given at the end of article. Import the project into eclipse. Using command prompt, go to the root folder of the project and run.
mvn clean eclipse:eclipse
MyApplication by clicking Run as -> Java Application. Tomcat server will be started.
2. Using Maven Command: Download the project source code. Go to the root folder of the project using command prompt and run the command.
mvn spring-boot:run
3. Using Executable JAR: Using command prompt, go to the root folder of the project and run the command.
mvn clean package
java -jar target/spring-boot-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
Now we are ready to test the application. To run client, go to the
RestClientUtil class in eclipse and click on Run as -> Java Application.
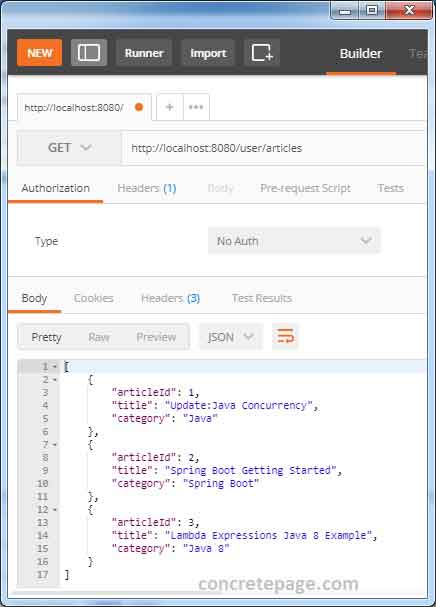
We can also test application using Postman. Find the print screen.
11. References
Accessing Data with JPASpring Data CrudRepository Example
Spring Boot REST + JPA + Hibernate + MySQL Example


