@TestPropertySource Example in Spring Test
January 24, 2019
@TestPropertySource is a class-level annotation that configures locations of property files and inlined properties in Spring integration test. The properties loaded by @TestPropertySource are added to the set of @PropertySource in the Environment for an ApplicationContext. The properties loaded by @TestPropertySource have higher precedence over the properties loaded from Java system properties, operating system's environments, property sources added by @PropertySource or programmatically. So the test property files can be used to override properties defined in system and application property sources.
The inlined properties loaded from
@TestPropertySource have higher precedence over the properties loaded from resource locations using @TestPropertySource annotation in Spring integration test.
Now find the elements of
@TestPropertySource annotation.
locations: Specify test property file locations to be loaded for integration test.
properties: Specify test inlined properties to be loaded for integration test.
value: It is the alias for
locations element.
inheritLocations: Boolean value to decide if test property source locations should be inherited from superclasses or not.
inheritProperties: Boolean value to decide if test inlined properties should be inherited from superclasses or not.
Example to specify property file locations.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@TestPropertySource("/testauth.properties")
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@TestPropertySource(properties = { "login.user=krishna", "login.pwd=k12" })
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
@TestPropertySource annotation example step-by-step.
Contents
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Java 11
2. Spring 5.1.3.RELEASE
3. Spring Boot 2.1.1.RELEASE
4. JUnit 5
5. Maven 3.5.2
6. Eclipse 2018-09
Load Property Files using @TestPropertySource
We are creating a sample application for the@TestPropertySource demo. Our application will use a property file with some properties. In our integration test class we will load a test property file that will override the properties of main property file.
Find the project structure in Eclipse IDE.
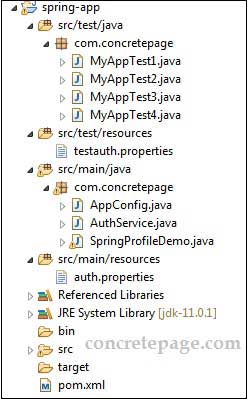
auth.properties
login.user=ram login.pwd=r12 app.name=MyApp
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.concretepage")
@PropertySource("classpath:auth.properties")
public class AppConfig {
@Autowired
Environment env;
@Bean
public AuthService myService() {
AuthService myService = new AuthService(
env.getProperty("login.user"),
env.getProperty("login.pwd"),
env.getProperty("app.name")
);
return myService;
}
}
package com.concretepage;
public class AuthService {
private String user;
private String pwd;
private String appName;
public AuthService(String user, String pwd, String appName) {
this.user = user;
this.pwd = pwd;
this.appName = appName;
System.out.println("User: " + this.user + ", Password: " + this.pwd);
System.out.println("App Name: " + appName);
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public String getAppName() {
return appName;
}
}
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId> <version>5.3.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId> <version>5.3.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId> <version>5.3.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId> <artifactId>junit-platform-launcher</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
MyAppTest1.java
package com.concretepage;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
public class MyAppTest1 {
@Autowired
private AuthService authService;
@Test
public void userTest() throws Exception {
assertTrue("ram".equals(authService.getUser()));
assertTrue("r12".equals(authService.getPwd()));
assertTrue("MyApp".equals(authService.getAppName()));
}
}
auth.properties file.
Test class to load property files using
@TestPropertySource:Here we will create a test property file to override some properties of main property file.
testauth.properties
login.user=shyam login.pwd=s12
@TestPropertySource annotation.
MyAppTest2.java
package com.concretepage;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@TestPropertySource("/testauth.properties")
public class MyAppTest2 {
@Autowired
private AuthService authService;
@Test
public void userTest() throws Exception {
assertTrue("shyam".equals(authService.getUser()));
assertTrue("s12".equals(authService.getPwd()));
assertTrue("MyApp".equals(authService.getAppName()));
}
}
testauth.properties using @TestPropertySource. The value of login.user and login.pwd properties will be loaded by application from testauth.properties instead of auth.properties file. The value of app.name will be loaded from auth.properties file.
We can load multiple test property files using
@TestPropertySource as following.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@TestPropertySource(locations = {"/testauth1.properties", "/testauth2.properties"})
public class MyAppTest2 {
------
}
Load Inlined Properties using @TestPropertySource
We can load inlined properties using@TestPropertySource annotation in our integration test.
MyAppTest3.java
package com.concretepage;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@TestPropertySource(properties = { "login.user=krishna", "login.pwd=k12" })
public class MyAppTest3 {
@Autowired
private AuthService authService;
@Test
public void userTest() throws Exception {
assertTrue("krishna".equals(authService.getUser()));
assertTrue("k12".equals(authService.getPwd()));
assertTrue("MyApp".equals(authService.getAppName()));
}
}
login.user and login.pwd properties as inlined properties using @TestPropertySource annotation. In integration test the values of login.user and login.pwd will be loaded as specified in @TestPropertySource annotation and the value of app.name will be loaded from auth.properties file by application.
Precedence of Inlined Properties over Property Files in @TestPropertySource
Here we will provide demo of test classes that are loading property values specified by inlined properties as well as property file using@TestPropertySource annotation. We will create two test classes in which one class will inherit another class.
MyAppTest4.java
package com.concretepage;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@TestPropertySource(properties = { "login.user=mahesh" })
public class MyAppTest4 extends AnotherTest {
@Autowired
private AuthService authService;
@Test
public void userTest() throws Exception {
assertTrue("mahesh".equals(authService.getUser()));
assertTrue("s12".equals(authService.getPwd()));
assertTrue("MyApp".equals(authService.getAppName()));
}
}
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@TestPropertySource("/testauth.properties")
class AnotherTest {
@Autowired
private AuthService authService;
@Test
public void anotherUserTest() throws Exception {
assertTrue("s12".equals(authService.getPwd()));
assertTrue("MyApp".equals(authService.getAppName()));
}
}
@TestPropertySource annotation, so in the above example the value for login.user has been loaded from inlined property. The value for login.pwd has been loaded from testauth.properties file and the value for app.name has been loaded from auth.properties file.
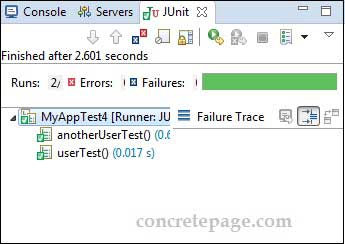
Find the print screen of the JUnit test output for above test file.
References
Spring Doc: @TestPropertySourceSpring Testing


