@ContextConfiguration Example in Spring Test
January 16, 2019
@ContextConfiguration loads an ApplicationContext for Spring integration test. @ContextConfiguration can load ApplicationContext using XML resource or the JavaConfig annotated with @Configuration. The @ContextConfiguration annotation can also load a component annotated with @Component, @Service, @Repository etc. We can also load classes annotated with javax.inject.
@ContextConfiguration annotation has following elements.
classes: The classes annotated with
@Configuration are assigned to load ApplicationContext.
inheritInitializers: A Boolean value to decide whether context initializers from test super classes should be inherited or not. Default is true.
inheritLocations: A Boolean value to decide whether resource locations or annotated classes from test super classes should be inherited or not. Default value is true.
initializers: We specify application context initializer classes that initialize
ConfigurableApplicationContext.
loader: We specify our
ContextLoader or SmartContextLoader class to load ApplicationContext.
locations: We specify resource locations to load
ApplicationContext.
name: Name of context hierarchy level represented by this configuration.
value: It is the alias for
locations element.
Contents
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Java 11
2. Spring 5.1.3.RELEASE
3. Spring Boot 2.1.1.RELEASE
4. JUnit 5
5. Maven 3.5.2
6. Eclipse 2018-09
Load JavaConfig
Find the example to define application context configuration class with@ContextConfiguration. Suppose we have AppConfig class annotated with @Configuration. We use @ContextConfiguration as following.
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
MyAppTest.java
package com.concretepage;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import com.concretepage.config.AppConfig;
import com.concretepage.service.MyService;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
public class MyAppTest {
@Autowired
private MyService myService;
@Test
public void messageTest() {
String msg = myService.getMessage();
assertEquals("Hello World!", msg);
}
@Test
public void multiplyNumTest() {
int val = myService.multiplyNum(5, 10);
assertEquals(50, val);
}
@Test
public void idAvailabilityTest() {
boolean val = myService.isIdAvailable(100);
assertTrue(val);
}
}
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {AppConfig1.class, AppConfig2.class})
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
Load XML Configuration
Here we will load XML configuration class. Suppose we havespring-config.xml in classpath. We use @ContextConfiguration as following.
@ContextConfiguration(locations= "/spring-config.xml")
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
value is the alias for locations element of @ContextConfiguration. So we can specify resource file as following, too.
@ContextConfiguration("/spring-config.xml")
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
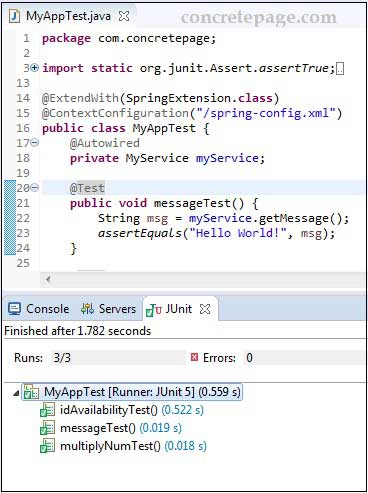
MyAppTest.java
package com.concretepage;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import com.concretepage.service.MyService;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration("/spring-config.xml")
public class MyAppTest {
@Autowired
private MyService myService;
@Test
public void messageTest() {
String msg = myService.getMessage();
assertEquals("Hello World!", msg);
}
@Test
public void multiplyNumTest() {
int val = myService.multiplyNum(5, 10);
assertEquals(50, val);
}
@Test
public void idAvailabilityTest() {
boolean val = myService.isIdAvailable(100);
assertTrue(val);
}
}
@ContextConfiguration(locations= {"/spring-config1.xml", "/spring-config2.xml"})
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
WEB-INF directory, we can load XML configurations as following.
@ContextConfiguration("file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring-config.xml")
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
Load Initializer Class
We specify application context initializers classes usinginitializers element that initializes ConfigurableApplicationContext.
@ContextConfiguration(initializers = CustomContextIntializer.class)
public class MyAppTest {
-------
}
Using Custom Loader
Here we will uselocations and loader element together. locations will specify XML configuration file and loader will specify custom context loader.
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "/spring-config.xml", loader = CustomContextLoader.class)
public class MyAppTest {
-------
}
References
Spring TestingSpring Doc: @ContextConfiguration


