Spring Boot REST API Example
November 24, 2023
On this page, we will learn to create REST web service application in Spring Boot application. REST is REpresentational State Transfer. REST or RESTful web service provides communication medium between software applications on the Internet. REST uses uniform and predefined set of stateless operations. REST API can produce and consume JSON, XML and other media types. To create a Spring REST endpoint, we need to create a Spring controller annotated with @RestController. Spring provides @RequestMapping, @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping and @PatchMapping annotations to bind the request path with Spring controller methods. For CORS support, spring provides @CrossOrigin annotation that can be annotated at class level as well as method level. In Spring Boot application, to enable REST we need to include spring-boot-starter-web in our build files. It configures Jackson JSON library i.e. jackson-databind by default. Spring Boot REST produces JSON response when it detects Jackson JSON library in classpath and if it detects Jackson XML library then it produces XML response. For Jackson XML library we need to include jackson-dataformat-xml in our build files. Spring provides RestTemplate class to create REST client application. Here on this page we will create Spring REST CRUD example using CrudRepository and MySQL with complete detail step by step.
Contents
1. Maven Dependency
To work with Spring Boot REST API, we need to providespring-boot-starter-web Maven dependency as following.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
jackson-databind for JSON response.
To support XML response in Spring Boot REST, we need to provide
jackson-dataformat-xml library with spring-boot-starter-web. Find the Maven dependency.
<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId> <version>2.9.4</version> </dependency>
pom.xml and we are all set to get XML response.
2. URLs and Response Status Code for CRUD Operation
We will use following HTTP URLs, HTTP methods and response status code in our REST API example.| HTTP Method | URL | Status Code | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create | POST | /user/article | 201 CREATED, 409 CONFLICT |
| Read | GET | /user/article/{id} | 200 OK |
| Update | PUT | /user/article | 200 OK |
| Delete | DELETE | /user/article/{id} | 204 NO CONTENT |
Find the print screen of the JSON response of our REST API example.
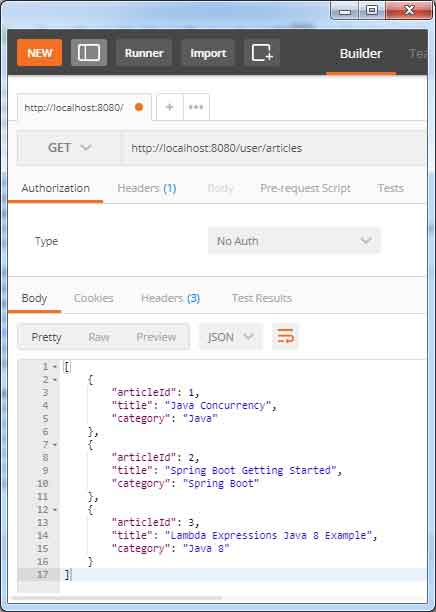
3. REST Web Service Endpoint
To create a REST endpoint, we need to create a Spring controller annotated with@RestController . Here we have created endpoints for CRUD operations. We have created different web service methods to handle create, read, update and delete operations as given below.
ArticleController.java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
@CrossOrigin(origins = {"http://localhost:4200"})
public class ArticleController {
@Autowired
private IArticleService articleService;
//Fetches article by id
@GetMapping("article/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo> getArticleById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
ArticleInfo ob = new ArticleInfo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(articleService.getArticleById(id), ob);
return new ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo>(ob, HttpStatus.OK);
}
//Fetches all articles
@GetMapping(value="articles")
public ResponseEntity<List<ArticleInfo>> getAllArticles() {
List<ArticleInfo> responseArticleList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Article> articleList = articleService.getAllArticles();
for (int i = 0; i < articleList.size(); i++) {
ArticleInfo ob = new ArticleInfo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(articleList.get(i), ob);
responseArticleList.add(ob);
}
return new ResponseEntity<List<ArticleInfo>>(responseArticleList, HttpStatus.OK);
}
//Creates a new article
@PostMapping("article")
public ResponseEntity<Void> addArticle(@RequestBody ArticleInfo articleInfo, UriComponentsBuilder builder) {
Article article = new Article();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(articleInfo, article);
boolean flag = articleService.addArticle(article);
if (flag == false) {
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.CONFLICT);
}
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setLocation(builder.path("/article/{id}").buildAndExpand(article.getArticleId()).toUri());
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(headers, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
//Updates article
@PutMapping("article")
public ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo> updateArticle(@RequestBody ArticleInfo articleInfo) {
Article article = new Article();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(articleInfo, article);
articleService.updateArticle(article);
ArticleInfo ob = new ArticleInfo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(article, ob);
return new ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo>(ob, HttpStatus.OK);
}
//Deletes article by id
@DeleteMapping("article/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteArticle(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
articleService.deleteArticle(id);
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
}
}
@RestController is combination of @Controller and @ResponseBody.
@CrossOrigin: Used for CORS support that permits cross-origin requests on class level as well as method level.
@RequestMapping: Maps web requests onto methods in REST web service endpoints to provide flexible method signature.
@GetMapping: Mapping with HTTP GET method.
@PostMapping: Mapping with HTTP POST method.
@PutMapping: Mapping with HTTP PUT method.
@DeleteMapping: Mapping with HTTP DELETE method.
@PatchMapping: Mapping with HTTP PATCH method.
@PathVariable: Indicates that a method parameter should be bound to a URI template variable.
@RequestBody: Used with the method parameter to bind the body of the web request.
@RequestParam: Used with method parameter to bind the web request parameter.
ResponseEntity: Extension of
HttpEntity that represents HTTP request or response entity, consisting of headers and body.
UriComponentsBuilder: Builder for
UriComponents that represents an immutable collection of URI components.
The annotations
@RequestMapping, @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping and @PatchMapping are having optional elements as following.
consumes: Defines an array of consumable media types of mapped request.
produces: Defines an array of producible media types of mapped request.
headers: Defines the acceptable headers of mapped request.
params: Defines the parameters of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping.
path: Defines path mapping URIs in servlet environment.
name: Assigns a name to this mapping.
value: It defines primary mapping expressed by this annotation.
4. REST Web Service Client with RestTemplate
RestTemplate is the central class for synchronous client side HTTP access. RestTemplate communicates to REST using HTTP methods. Find some of RestTemplate methods.
getForObject: Retrieves data by using HTTP GET on specified URL.
postForLocation: Creates a new resource using given object to the URI template with HTTP POST method.
put: Creates or updates resource using given object to the URI template with HTTP PUT method.
delete: Deletes the resources at the specified URI.
exchange: Execute any HTTP method to the given URI template and returns
ResponseEntity.
Find the sample example to execute
RestTemplate.exchange method.
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON); String url = "http://localhost:8080/user/articles"; RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); HttpEntity<String> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<String>(headers); ResponseEntity<Article[]> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestEntity, Article[].class);
Article type using exchange with HTTP GET method. In our demo application, RestClientUtil.java contains client code.
5. Configure Producible and Consumable Media Types
A web service method can produce and consume primary media types by default. We can restrict to only configured media types to consume and produce. The annotations@RequestMapping, @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping and @PatchMapping are having optional elements as produces and consumes that is configured with required media types. Find the sample code.
@GetMapping(value= "article/{id}", produces= { MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE },
consumes= { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE })
public ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo> getArticleById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
ArticleInfo ob = new ArticleInfo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(articleService.getArticleById(id), ob);
return new ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo>(ob, HttpStatus.OK);
}
application/xml and consume application/json media types.
If we want to configure media types at class level that will be applicable for all its web service methods, we can do it using
@RequestMapping as following.
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value= "user", produces= { MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE },
consumes= { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE })
public class ArticleController {
------
}
6. JSON Response
Spring uses the Jackson JSON library to automatically marshal instances of type resource into JSON. Our Spring REST API application will produce JSON response by default if there is Jackson JSON library i.e.jackson-databind in the classpath. In Spring Boot application, the spring-boot-starter-web library by default includes jackson-databind library. To ignore null values in JSON response using Jackson JSON, we need to use @JsonInclude in our resource class.
ArticleInfo.java
public class ArticleInfo {
@JsonInclude(Include.NON_NULL)
private long articleId;
@JsonInclude(Include.NON_NULL)
private String title;
@JsonInclude(Include.NON_NULL)
private String category;
//Getters and Setters
}
produces element of mapping annotations such as @GetMapping.
@GetMapping(value= "article/{id}", produces= { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE })
public ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo> getArticleById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
ArticleInfo ob = new ArticleInfo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(articleService.getArticleById(id), ob);
return new ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo>(ob, HttpStatus.OK);
}
HttpMessageConverter for JSON, we can create JavaConfig as following.
AppConfig.java
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.concretepage")
@EnableWebMvc
public class AppConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = new Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder();
builder.indentOutput(true);
converters.add(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
}
7. XML Response
To get XML response by our Spring REST API, we need to include Jackson XML library i.e.jackson-dataformat-xml library in our application classpath. Find the maven dependency for jackson-dataformat-xml library.
<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId> <version>2.9.4</version> </dependency>
pom.xml and we are all set to get XML response. We can use @JacksonXmlProperty annotation in our resource class to change local name etc.
ArticleInfo.java
@JacksonXmlRootElement(localName="article", namespace="com.concretepage")
public class ArticleInfo {
@JacksonXmlProperty(localName="articleId")
private long articleId;
@JacksonXmlProperty(localName="title")
private String title;
@JacksonXmlProperty(localName="category")
private String category;
//Getters and Setters
}
produces element of mapping annotations such as @GetMapping.
@GetMapping(value= "article/{id}", produces= { MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
public ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo> getArticleById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
ArticleInfo ob = new ArticleInfo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(articleService.getArticleById(id), ob);
return new ResponseEntity<ArticleInfo>(ob, HttpStatus.OK);
}
HttpMessageConverter for XML, we can create JavaConfig as following.
AppConfig.java
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.concretepage")
@EnableWebMvc
public class AppConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.xml();
builder.indentOutput(true);
converters.add(new MappingJackson2XmlHttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
}
8. CORS Support
For CORS support, Spring provides@CrossOrigin annotation. This annotation can be used at class level as well as method level in RESTful Web service controller. Find the sample code to use it at class level.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
@CrossOrigin(origins = {"http://localhost:4200"})
public class ArticleController {
------
}
http://localhost:4200 . It means a web application running at URL http://localhost:4200 can only access our REST API application.


