@WebAppConfiguration Example in Spring Test
January 19, 2019
@WebAppConfiguration is a class-level annotation that loads WebApplicationContext in Spring integration test. When our test class is annotated with @WebAppConfiguration, a WebApplicationContext is loaded for the test using default value of file:src/main/webapp for the path to the root of the web application i.e. the resource base path. MockServletContext is created using resource base path that acts as ServletContext for WebApplicationContext. The value element of @WebAppConfiguration specifies the resource path to the root directory of the web application. The default value for value element is src/main/webapp. We can override the default path using classpath or file prefix. If we are not using any prefix then file is used as default prefix.
@WebAppConfiguration is used in conjunction with @ContextConfiguration annotation. Find the sample test class example with JUnit 5.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration
@WebAppConfiguration
public class MyAppTest {
@Autowired
protected WebApplicationContext webAppContext;
------
}
@SpringBootTest annotation to create test class.
Here we will discuss
@WebAppConfiguration annotation with examples to get WebApplicationContext in Spring integration test.
Contents
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Java 11
2. Spring 5.1.3.RELEASE
3. Spring Boot 2.1.1.RELEASE
4. JUnit 5
5. Maven 3.5.2
6. Eclipse 2018-09
Using @WebAppConfiguration
Just annotating our Spring integration test class with@WebAppConfiguration, it loads WebApplicationContext using default resource base path i.e. src/main/webapp. To override default path we can specify our path using classpath or file prefix with value element of @WebAppConfiguration annotation.
1. Using
classpath prefix:Suppose we want to use
test-root-webapp directory inside classpath as root directory of web application in our integration test, we can do it using classpath prefix as following.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration
@WebAppConfiguration("classpath:test-root-webapp")
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
file prefix:Suppose we want to use
src/test/webapp path as our root directory of web application in our integration test, we can do it using file prefix as following.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration
@WebAppConfiguration("file:src/test/webapp")
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
file prefix will be default. So we can use above code as following, too.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration
@WebAppConfiguration("src/test/webapp")
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
@WebAppConfiguration + @ContextConfiguration
@WebAppConfiguration is used in conjunction with @ContextConfiguration annotation. @ContextConfiguration loads an ApplicationContext for Spring integration test. @ContextConfiguration can load ApplicationContext using XML resource or the JavaConfig annotated with @Configuration.
1. Find the sample example with JavaConfig.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@WebAppConfiguration
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration("file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring-config.xml")
@WebAppConfiguration
public class MyAppTest {
------
}
Complete Example
Here we will provide a complete example for@WebAppConfiguration demo using JavaConfig as well as XML configuration.
1. Using JavaConfig:
Find the project structure.
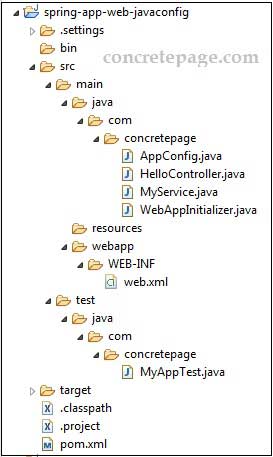
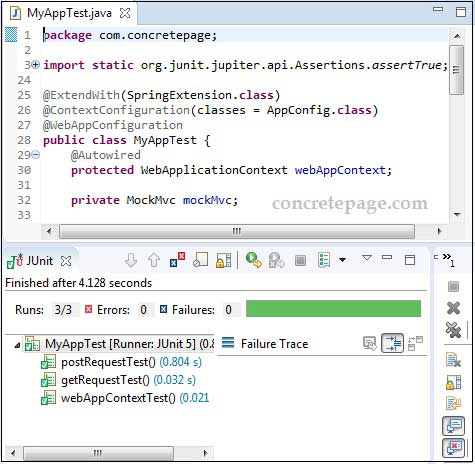
MyAppTest.java
package com.concretepage;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.post;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup;
import java.net.URI;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.mock.web.MockServletContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AppConfig.class)
@WebAppConfiguration
public class MyAppTest {
@Autowired
protected WebApplicationContext webAppContext;
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@BeforeEach
public void setup() {
mockMvc = webAppContextSetup(webAppContext).build();
}
@Test
public void webAppContextTest() throws Exception {
assertTrue(webAppContext.getServletContext() instanceof MockServletContext);
}
@Test
public void getRequestTest() throws Exception {
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUriString("/hello")
.pathSegment("Mahesh").build().encode().toUri();
mockMvc.perform(get(uri)).andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string("Hello Mahesh"));
}
@Test
public void postRequestTest() throws Exception {
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUriString("/save").build().encode().toUri();
mockMvc.perform(
post(uri)
.param("name", "Ram")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
)
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string("success"));
}
}
@ExtendWith: A JUnit 5 annotation to register extensions for test method.
SpringExtension: It is used to integrate Spring
TestContext with JUnit 5 Jupiter Test.
@ContextConfiguration: It loads an
ApplicationContext in Spring integration test.
@WebAppConfiguration: It loads
WebApplicationContext in Spring integration test.
WebApplicationContext: It provides configuration for a web application.
MockMvc: It is main entry point for Spring MVC test support.
MockServletContext: It is the mock implementation of the
ServletContext.
Now find the main application classes.
AppConfig.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.concretepage")
@EnableWebMvc
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyService();
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
MyService myService;
@GetMapping(value="hello/{name}")
public String hello(@PathVariable("name") String name){
return myService.getMessage(name);
}
@PostMapping(value="save")
public String save(@RequestBody String user){
return myService.saveUser(user);
}
}
package com.concretepage;
public class MyService {
public String getMessage(String name) {
return "Hello " + name;
}
public String saveUser(String user) {
System.out.println(user);
return "success";
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class WebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { AppConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{ "/" };
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.concretepage</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>spring-demo</name>
<description>Spring Boot Demo Project</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<context.path>spring-app</context.path>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.3.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>5.3.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId>
<version>5.3.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-launcher</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
<configuration>
<warName>${context.path}</warName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2. Using XML configuration
Find the project structure.
MyAppTest.java
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration("file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring-config.xml")
@WebAppConfiguration
public class MyAppTest {
@Autowired
protected WebApplicationContext webAppContext;
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@BeforeEach
public void setup() {
mockMvc = webAppContextSetup(webAppContext).build();
}
@Test
public void webAppContextTest() throws Exception {
assertTrue(webAppContext.getServletContext() instanceof MockServletContext);
}
------
}
WebApplicationContext in Spring Boot Test
Spring provides@SpringBootTest annotation used at class-level, to create a test class in Spring Boot application. @SpringBootTest has following features.
1. Uses
SpringBootContextLoader as the default ContextLoader.
2. Provides support for
webEnvironment modes.
3. Registers a
TestRestTemplate or WebTestClient bean for use in web tests.
4.
@SpringBootTest is annotated with
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
Find the sample example of a test class based on Spring Boot application.
MyAppTest.java
@SpringBootTest
public class MyAppTest {
@Autowired
protected WebApplicationContext webAppContext;
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@BeforeEach
public void setup() {
mockMvc = webAppContextSetup(webAppContext).build();
}
@Test
public void webAppContextTest() throws Exception {
assertTrue(webAppContext.getServletContext() instanceof MockServletContext);
}
------
}
References
Spring TestingSpring Doc: @WebAppConfiguration
Spring Doc: @SpringBootTest
@ContextConfiguration Example in Spring Test


