JUnit @RepeatedTest Example
April 27, 2021
On this page we will learn using JUnit @RepeatedTest annotation in our application unit test cases.
1. The
@RepeatedTest annotation is introduced in JUnit 5.
2. The
@RepeatedTest annotation denotes that the method annotated with this is test method that should be repeated a specified number of times with a configurable display name.
3. Each invocation of
@RepeatedTest method executes in the same way as a regular @Test method.
4. Each invocation of
@RepeatedTest method supports for same lifecycle callbacks and extensions as a regular @Test method such as calling @BeforeEach and @AfterEach methods.
5. The repetition info can be accessed by
RepetitionInfo such as current repetition and total number of repetitions. It can also be accessed using placeholders that are {displayName}, {currentRepetition} and {totalRepetitions}.
6. The
@RepeatedTest methods must not be private or static and must return void.
7. The
@RepeatedTest methods may optionally declare parameters to be resolved by ParameterResolver as we do in @Test method. We can resolve parameters such as RepetitionInfo and TestInfo in @RepeatedTest methods.
Contents
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Java 14
2. JUnit 5.7.1
3. Maven 3.8.1
Maven Dependencies
Find the Maven dependencies.<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId> <version>5.7.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId> <version>5.7.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId> <version>5.7.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId> <artifactId>junit-platform-launcher</artifactId> <version>1.7.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
Using @RepeatedTest
To create a repeated test method, just annotate the test method with @RepeatedTest in place of @Test annotation. We need to pass the number of repetition to @RepeatedTest.
@RepeatedTest(3)
void repeatedSumTest() {
int sum = 50 + 60;
assertEquals(110, sum);
}
@RepeatedTest annotation. It means, test method will execute 3 times, each with full cycle. Writing test method with @RepeatedTest(3) is same as writing test method 3 times with @Test annotation.
The test method with
@RepeatedTest will execute full cycle for every repetition i.e. @BeforeEach and @AfterEach methods will be called for each repetition.
MyAppTest1.java
public class MyAppTest1 {
@BeforeEach
void init(TestInfo testInfo) {
System.out.println("Start..." + testInfo.getDisplayName());
}
@RepeatedTest(3)
void repeatedSumTest() {
System.out.println("---Inside repeatedSumTest ---");
int sum = 50 + 60;
assertEquals(110, sum);
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown(TestInfo testInfo) {
System.out.println("Finished..." + testInfo.getDisplayName());
}
}
Start...repetition 1 of 3 ---Inside repeatedSumTest --- Finished...repetition 1 of 3 Start...repetition 2 of 3 ---Inside repeatedSumTest --- Finished...repetition 2 of 3 Start...repetition 3 of 3 ---Inside repeatedSumTest --- Finished...repetition 3 of 3
getDisplayName() method of TestInfo gives the test display name.
@RepeatedTest Display Name
The display name for @RepeatedTest is the display name for every repetition in test result. To set the display name, we use name attribute of @RepeatedTest annotation. The @RepeatedTest has following attributes.
value: The number of repetitions.
name: The display name for each repetition of the repeated test.
Find the code snippet to set a display name.
@RepeatedTest(value = 3, name= RepeatedTest.SHORT_DISPLAY_NAME)
void repeatedSumTest() {
------
}
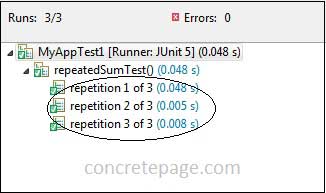
SHORT_DISPLAY_NAME is the default display name for @RepeatedTest. We can also set name to LONG_DISPLAY_NAME.
@RepeatedTest(value = 3, name= RepeatedTest.LONG_DISPLAY_NAME)
void repeatedSumTest() {
------
}
Custom Display Name:
For custom display name, JUnit provides following placeholders supported by
name attribute of @RepeatedTest.
{displayName}: Test name configured by
@DisplayName annotation.
{currentRepetition}: Current repetition count.
{totalRepetitions}: Total repetition count.
Find the examples to use custom display name for
@RepeatedTest methods.
Ex-1: Using
{currentRepetition} and {totalRepetitions} placeholders.
@RepeatedTest(value = 3, name= "Addition Test: repetition {currentRepetition}/{totalRepetitions}")
void repeatedSumTest() {
------
}
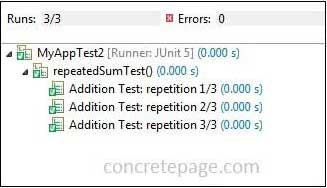
Ex-2: Using
{displayName} placeholder that takes value configured by @DisplayName annotation.
@DisplayName("Addition Test")
@RepeatedTest(value = 3, name = "{displayName}: repetition {currentRepetition}/{totalRepetitions}")
void repeatedSumTest() {
------
}
The format of
SHORT_DISPLAY_NAME :
"repetition {currentRepetition} of {totalRepetitions}"
LONG_DISPLAY_NAME :
"{displayName} :: repetition {currentRepetition} of {totalRepetitions}"
Using RepetitionInfo
JUnit provides RepetitionInfo and TestInfo to fetch test execution informations. The RepetitionInfo gives test repetition information such as current repetition and total repetitions. Using TestInfo, we fetch test execution display name.
To use
RepetitionInfo and TestInfo, just use them as test method parameters and JUnit will resolve dependency injection.
The
RepetitionInfo has following methods.
getCurrentRepetition(): Returns the current repetition.
getTotalRepetitions(): Returns the total number of repetitions.
Find the sample code.
@RepeatedTest(3)
void repeatedSumTest(RepetitionInfo repetitionInfo, TestInfo testInfo) {
System.out.println("Display name: " + testInfo.getDisplayName());
System.out.println("Current repetition: " + repetitionInfo.getCurrentRepetition());
System.out.println("Total repetition: " + repetitionInfo.getTotalRepetitions());
int sum = 50 + 60;
assertEquals(110, sum);
}
References
Annotation Type RepeatedTestInterface RepetitionInfo


