Spring @ResponseBody Example
April 23, 2020
This page will walk through Spring @ResponseBody example. The @ResponseBody annotation indicates that the return value of the method will be the body of web response. The @ResponseBody annotation is used at method level or method return type level. The @ResponseBody constructs the response body as JSON or XML or other media type based on following points.
1.
MessageConverter configured in the application.
2. Media-type configured by
produces attribute in annotations @RequestMapping, @GetMapping etc.
3. Media-type configured by accept request header.
The
@ResponseBody only configures body of response. To set response status code we use @ResponseStatus annotation at method level. If status code is not set explicitly, default status code is set to response.
The
@ResponseBody is used with @Controller annotation, the @ResponseBody is annotated at method level whereas @Controller is annotated at class level. If we use @RestController annotation, then @ResponseBody is not needed to use. This is because
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
Now find the examples to use
@ResponseBody in our web application.
Contents
1. Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Java 11
2. Spring 5.2.5.RELEASE
3. Spring Boot 2.2.6.RELEASE
4. Maven 3.5.2
2. Using @ResponseBody
The@ResponseBody can be used at method level as well as method return type level. 1. Find the code to use
@ResponseBody at method level.
@GetMapping(value = "book")
@ResponseBody
public List<Book> getBooks() {
List<Book> list = bookService.getAllBooks();
return list;
}
@ResponseBody at method return type level.
@GetMapping(value = "book")
public @ResponseBody List<Book> getBooks() {
------
}
produces attribute of @GetMapping and assign it application/json. Find the code that will produce JSON response body.
@GetMapping(value = "book", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE})
@ResponseBody
public List<Book> getBooks() {
------
}
application/xml media-type.
@GetMapping(value = "book", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE})
@ResponseBody
public List<Book> getBooks() {
------
}
@ResponseStatus at method level with @ResponseBody. Find the code.
@GetMapping(value = "book")
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<Book> getBooks() {
------
}
3. Complete Example
Find the server code of our demo application.pom.xml
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath /> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId> <version>2.10.3</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
package com.concretepage.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import com.concretepage.domain.Book;
import com.concretepage.service.BookService;
@Controller
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
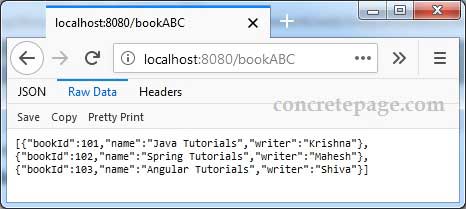
@GetMapping(value = "bookABC", produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE })
public @ResponseBody List<Book> getBooksABC() {
List<Book> list = bookService.getAllBooks();
return list;
}
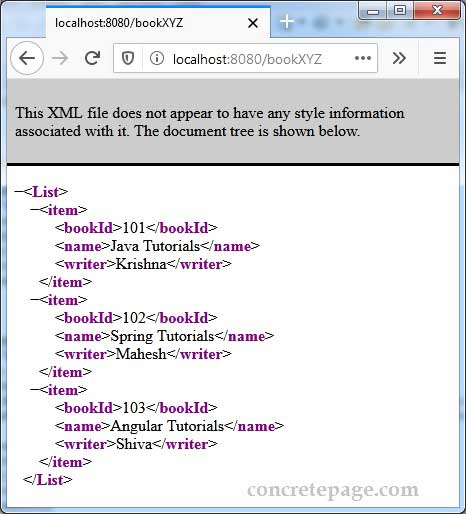
@GetMapping(value = "bookXYZ", produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<Book> getBooksXYZ() {
List<Book> list = bookService.getAllBooks();
return list;
}
}
package com.concretepage.domain;
public class Book {
private int bookId;
private String name;
private String writer;
public Book() {}
public Book(int bookId, String name, String writer) {
this.bookId = bookId;
this.name = name;
this.writer = writer;
}
//Setters and Getters
}
package com.concretepage.service;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.concretepage.domain.Book;
@Service
public class BookService {
public List<Book> getAllBooks() {
// Perform database operation
Book b1 = new Book(101, "Java Tutorials", "Krishna");
Book b2 = new Book(102, "Spring Tutorials", "Mahesh");
Book b3 = new Book(103, "Angular Tutorials", "Shiva");
return Arrays.asList(b1, b2, b3);
}
}
Find the client code using
RestTemplate.
RestClientUtil.java
package com.concretepage.client;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.core.ParameterizedTypeReference;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.RequestEntity;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import com.concretepage.domain.Book;
public class RestClientUtil {
public void getBookDemoABC() throws URISyntaxException {
URI uri = new URI("http://localhost:8080/bookABC");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<Book[]> resEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(uri, Book[].class);
System.out.println(resEntity.getStatusCode());
for (Book b : resEntity.getBody()) {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
public void getBookDemoXYZ() throws URISyntaxException {
URI uri = new URI("http://localhost:8080/bookXYZ");
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setAccept(Arrays.asList(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML));
RequestEntity<List<Book>> reqEntity = new RequestEntity<>(headers, HttpMethod.GET, uri);
ParameterizedTypeReference<List<Book>> typeRef = new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<Book>>() {
};
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<List<Book>> resEntity = restTemplate.exchange(reqEntity, typeRef);
System.out.println(resEntity.getStatusCode());
for (Book b : resEntity.getBody()) {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws URISyntaxException {
RestClientUtil util = new RestClientUtil();
util.getBookDemoABC();
util.getBookDemoXYZ();
}
}
4. Run Application
Download the project and run the following command from root folder of the project using command prompt.mvn spring-boot:run
a. Now run
RestClientUtil as Java Application and we will get below Output.
200 OK 101, Java Tutorials, Krishna 102, Spring Tutorials, Mahesh 103, Angular Tutorials, Shiva 200 OK 101, Java Tutorials, Krishna 102, Spring Tutorials, Mahesh 103, Angular Tutorials, Shiva
http://localhost:8080/bookABC
c. Access URL
http://localhost:8080/bookXYZ