Spring JMS Integration Tutorial
August 14, 2020
This page will walk through Spring JMS integration tutorial. JMS is Java Message Service that is a messaging standard API to create, send, receive and read messages. Spring provides JMS integration framework to use JMS API in simplified way. We can use JMS with Spring in the same way as we use Spring with JDBC. The Spring JMS provides JmsTemplate class in the same way as JdbcTemplate class.
Here on this page we will understand Spring JMS integration in detail with examples. We will create Spring Boot JMS application with annotation based listener endpoints.
Contents
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Java 11
2. Spring 5.2.8.RELEASE
3. Spring Boot 2.3.2.RELEASE
4. Maven 3.5.2
Understanding JMS with Spring
Let us understand JMS with Spring point-wise.1. JMS mainly performs production and consumption of messages.
2. Spring provides
JmsTemplate class that is used for message production and synchronous message reception.
3. For asynchronous message reception, Spring provides a number of message-listener containers that we can use to create Message-driven POJOs. Spring also provides declarative way to create message listeners.
4. The package
org.springframework.jms.core provides the core functionality to use JMS such as JmsTemplate class.
5.The package
org.springframework.jms.support provides JMSException translation functionality i.e. converting the checked JMSException hierarchy to a mirrored hierarchy of unchecked exceptions.
6. The package
org.springframework.jms.support.converter
MessageConverter abstraction to convert between Java objects and JMS messages.
7. The package
org.springframework.jms.support.destination
8. The package
org.springframework.jms.annotation
@JmsListener.
9. The package
org.springframework.jms.config provides jms namespace as well as the JavaConfig support for listeners.
10. The package
org.springframework.jms.connection
ConnectionFactory and JmsTransactionManager.
11. To handle JMS exception, Spring provides
JmsException as a base class. Some of its subclasses are DestinationResolutionException, IllegalStateException, InvalidClientIDException etc. The JMS exceptions are thrown whenever application encounters a problem related to JMS.
12. For JMS transaction management, Spring provides
JmsTransactionManager which is the implementation class of PlatformTransactionManager interface. The JmsTransactionManager is for single JMS ConnectionFactory.
13. In Spring Boot application, the beans for
JmsTemplate and ConnectionFactory are created automatically and the ActiveMQ broker runs embedded.
14. To work with JMS we should be aware with following terminologies.
JMS provider: An implementation of JMS interfaces for message-oriented middleware (MOM).
JMS client: An application that produces/receives messages.
JMS producer/publisher: A JMS client that creates messages.
JMS consumer/subscriber: A JMS client that receives messages.
JMS message: An object that contains the content to be transferred between JMS clients.
JMS queue: JMS queue sends messages to one and only subscriber. It is for point-to-point.
JMS topic: JMS topic sends messages to all subscribers.
Connection Factory
JavaConnectionFactory is a JMS specification that is used to create connections with the JMS provider. The ConnectionFactory contains parameters to change configurations such as vendor-specific SSL configuration options. In Spring Boot application, ConnectionFactory is created automatically and the ActiveMQ broker runs embedded.
From creating connection factory to sending message, following steps take place.
ConnectionFactory->Connection->Session->MessageProducer->send
Between the
ConnectionFactory and send process, three objects are created and destroyed. Keeping in mind to optimize them and increase the performance, Spring provides two implementations of ConnectionFactory.
1. SingleConnectionFactory: This is useful for testing and standalone environment. The
SingleConnectionFactory returns the same Connection on all createConnection() calls and ignores calls to close() method.
2. CachingConnectionFactory: The
CachingConnectionFactory adds the caching of Session, MessageProducer, and MessageConsumer instances and also extends the functionality of SingleConnectionFactory.
Message Listener Container
Spring provides two standard JMS message listener containers.1. SimpleMessageListenerContainer: The
SimpleMessageListenerContainer is simpler and it creates a fixed number of JMS sessions and consumers at startup. To build SimpleMessageListenerContainer, Spring provides
SimpleJmsListenerContainerFactory
DefaultMessageListenerContainer uses plane JMS client APIs. It is designed to work in a native JMS environment as well as in a Java EE environment. To build DefaultMessageListenerContainer, Spring provides
DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory
@Bean
public DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory containerFactory() {
DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory factory = new DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory();
factory.setSessionTransacted(true);
factory.setMaxMessagesPerTask(1);
factory.setConcurrency("1-5");
return factory;
}
JmsTemplate
TheJmsTemplate is the helper class that handles the creation and release of resources when sending or synchronously receiving messages. While creating JmsTemplate, we can change its default configurations. Find some of its methods to change configurations.
setPubSubDomain(boolean pubSubDomain): Sets publish and subscribe domain. For true value Publish/Subscribe domain is set and for false value Point-to-Point domain (Queues) is set. The default value is false.
setSessionTransacted(boolean sessionTransacted): Sets the transaction mode that is used to create session. Default is false.
setSessionAcknowledgeMode(String constantName): Sets the JMS acknowledge mode such as
Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE, Session.CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE etc.
Find the methods of
JmsTemplate to send and receive messages.
convertAndSend(): Converts the specified object to JMS message with configured
MessageConverter and sends to specified destination.
void convertAndSend(Destination destination, Object message, MessagePostProcessor postProcessor)
void send(Destination destination, MessageCreator messageCreator)
Message sendAndReceive(Destination destination, MessageCreator messageCreator)
Message receive(Destination destination)
Find the code snippet to use
JmsTemplate.
JmsTemplate jmsTemplate = context.getBean(JmsTemplate.class);
jmsTemplate.convertAndSend("java", javaArticle);
JmsTemplate is created automatically. We need not to create its bean explicitly in Spring configuration file.
Listener Endpoints
Here we will discuss creating listener endpoints using annotations. To create annotation based listener, first use@EnableJms with @Configuration.
@Configuration
@EnableJms
public class JMSConfig {
------
}
@JmsListener: This annotation marks a method to be the target of a JMS message listener. We need to specify a required attribute
destination in the @JmsListener. The destination is used to send the message by JmsTemplate to message listener. The other optional attributes of @JmsListener are concurrency, containerFactory, id, selector and subscription.
Find the sample code to use
@JmsListener annotation.
@JmsListener(destination = "java")
public void receiveJavaMessage(Article article) {
System.out.println("Received: " + article);
}
containerFactory, then we need not to configure containerFactory attribute in @JmsListener. But if container factory bean name is different, we need to configure it as following.
@JmsListener(destination = "java", containerFactory = "myConFactory")
Message if necessary and sent to the specified destination. Find the code snippet.
@JmsListener(destination = "spring")
@SendTo("review")
public Article receiveSpringMessage(Article article) {
article.setText("Spring JMS Tutorial");
return article;
}
JmsTemplate to 'spring' destination, after processing the message is forwarded to 'review' destination automatically.
Message Converters
TheJmsTemplate methods such as convertAndSend() and receiveAndConvert() can send domain model objects. So the message needs to be converted between domain model objects and JMS message type.
Spring provides
MessageConverter that works as converter between Java objects and JMS messages. The implementation classes of MessageConverter are MappingJackson2MessageConverter, MarshallingMessageConverter, MessagingMessageConverter, SimpleMessageConverter. The default implementation is SimpleMessageConverter that converts between standard message payloads and JMS message types.
In our application we are configuring
MappingJackson2MessageConverter as message converter.
@Bean
public MessageConverter jacksonJmsMessageConverter() {
MappingJackson2MessageConverter converter = new MappingJackson2MessageConverter();
converter.setTargetType(MessageType.TEXT);
converter.setTypeIdPropertyName("_type");
return converter;
}
Complete Example using Spring Boot
1. Maven to resolve dependencies for Spring and JMS.pom.xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath />
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId>
<artifactId>activemq-broker</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
@EnableJms and configuring container factory and message converter.
JMSConfig.java
package com.concretepage.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jms.annotation.EnableJms;
import org.springframework.jms.config.DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MappingJackson2MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MessageType;
@Configuration
@EnableJms
public class JMSConfig {
@Bean
public DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory containerFactory() {
DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory factory = new DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory();
factory.setSessionTransacted(true);
factory.setMaxMessagesPerTask(1);
factory.setConcurrency("1-5");
return factory;
}
@Bean
public MessageConverter jacksonJmsMessageConverter() {
MappingJackson2MessageConverter converter = new MappingJackson2MessageConverter();
converter.setTargetType(MessageType.TEXT);
converter.setTypeIdPropertyName("_type");
return converter;
}
}
Article.java
package com.concretepage;
public class Article {
private int id;
private String text;
public Article() {}
public Article(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Article(int id, String text) {
this.id = id;
this.text = text;
}
public void setText(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getText() {
return text;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + ", " + text;
}
}
JavaMsgReceiver.java
package com.concretepage.receiver;
import org.springframework.jms.annotation.JmsListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.concretepage.Article;
@Component
public class JavaMsgReceiver {
@JmsListener(destination = "java")
public void receiveJavaMessage(Article article) {
System.out.println("Received: " + article);
}
}
package com.concretepage.receiver;
import org.springframework.jms.annotation.JmsListener;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.SendTo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.concretepage.Article;
@Component
public class SpringMsgReceiver {
@JmsListener(destination = "spring")
@SendTo("review")
public Article receiveSpringMessage(Article article) {
article.setText("Spring JMS Tutorial");
return article;
}
}
package com.concretepage.receiver;
import org.springframework.jms.annotation.JmsListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.concretepage.Article;
@Component
public class ReviewMsgReceiver {
@JmsListener(destination = "review")
public void reviewMessage(Article article) {
System.out.println("Received: " + article);
}
}
JmsTemplate class.
Application.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
JmsTemplate jmsTemplate = context.getBean(JmsTemplate.class);
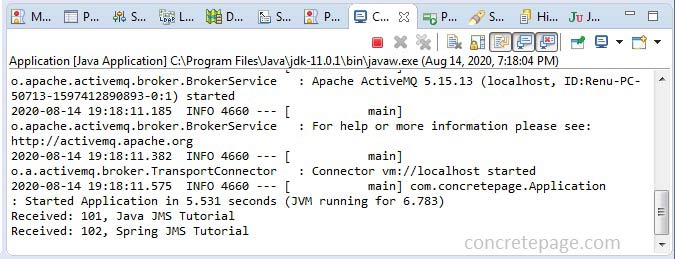
Article javaArticle = new Article(101, "Java JMS Tutorial");
jmsTemplate.convertAndSend("java", javaArticle);
Article springArticle = new Article(102);
jmsTemplate.convertAndSend("spring", springArticle);
}
}
References
JMS (Java Message Service)Messaging with JMS


