Spring REST + Spring Security Example
June 24, 2019
We will create a Spring REST web service security application that will be authenticated using JPA with Hibernate and MySQL database. For authentication we will use Basic authentication scheme using HTTP header. In our example we will create two demo applications, one with java configuration and other with XML configuration. We will perform create, read, update and delete (CRUD) operation. Our service layer will be protected by spring @Secured annotation. Our DAO will use JPA EntityManager to perform database operations. In the controller class we will create methods that will map URL and HTTP method to accept request. It will return proper HTTP status code in HTTP header and JSON output in response body. To perform header based Basic authentication, we need to use BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint and override its commence() method that will return HTTP status code (401) and authentication scheme as Basic authentication. When the HTTP header request for authentication is received user is authenticated and if an unauthenticated request is received then it is handled by BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint and HTTP status code (401) is sent back with the header information that contains authentication scheme as Basic authentication. For security purpose request should be HTTPS and password should be stored in encoded form in database. We have integrated BCrypt password encoding with UserDetailsService in our example. In our MVC configuration we will use Jackson2 message converter to indent JSON output. At client side we will use RestTemplate. Client will send user credential encoded with Base64 using username:password token in HttpHeaders for every request. Now we will provide complete example step by step.
Contents
- Software Used
- Gradle and Maven to Build the Project
- MySQL Database Schema and JPA Entity
- Spring REST Security + JPA 2 + Hibernate 5 CRUD Example using Annotation
- Spring REST Security + JPA 2 + Hibernate 5 CRUD Example using XML Configuration
- Create REST Web Service Client using RestTemplate
- Run Application
- Reference
- Download Source Code
Software Used
We are using following software in our example.1. Java 8
2. Spring 4.3
3. Gradle 3.3
4. Maven 3.3
5. Tomcat 8.0
6. MySQL 5.5
7. Eclipse Mars
Gradle and Maven to Build the Project
Find the gradle file to build the project.build.gradle
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
apply plugin: 'war'
war.archiveName 'spring-app.war'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:1.5.1.RELEASE'
compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa:1.5.1.RELEASE'
compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security:1.5.1.RELEASE'
compile 'mysql:mysql-connector-java:6.0.5'
compile 'org.apache.commons:commons-dbcp2:2.1.1'
providedRuntime 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-tomcat:1.5.1.RELEASE'
}
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.concretepage</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>SpringSecurity</name>
<description>Spring Demo Project</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<context.path>spring-app</context.path>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
<configuration>
<warName>${context.path}</warName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
MySQL Database Schema and JPA Entity
In our application, I am using MySQL and have created two tables. The table users have information about user and its credentials. Password has been encoded using BCrypt password encoding scheme. The table articles keeps article related data.Database Schema
-- Dumping database structure for concretepage
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `concretepage`;
USE `concretepage`;
-- Dumping structure for table concretepage.articles
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `articles` (
`article_id` int(5) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` varchar(200) NOT NULL,
`category` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`article_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
-- Dumping data for table concretepage.articles: ~3 rows (approximately)
INSERT INTO `articles` (`article_id`, `title`, `category`) VALUES
(1, 'Java Concurrency', 'Java'),
(2, 'Hibernate HQL ', 'Hibernate'),
(3, 'Spring MVC with Hibernate', 'Spring');
-- Dumping structure for table concretepage.users
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `users` (
`username` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`full_name` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`role` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`country` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`enabled` tinyint(1) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`username`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
-- Dumping data for table concretepage.users: ~2 rows (approximately)
INSERT INTO `users` (`username`, `password`, `full_name`, `role`, `country`, `enabled`) VALUES
('mukesh', '$2a$10$N0eqNiuikWCy9ETQ1rdau.XEELcyEO7kukkfoiNISk/9F7gw6eB0W', 'Mukesh Sharma', 'ROLE_ADMIN', 'India', 1),
('tarun', '$2a$10$QifQnP.XqXDW0Lc4hSqEg.GhTqZHoN2Y52/hoWr4I5ePxK7D2Pi8q', 'Tarun Singh', 'ROLE_USER', 'India', 1);
Main.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
System.out.println(encoder.encode("m123"));
}
}
UserInfo.java
package com.concretepage.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="users")
public class UserInfo implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@Column(name="username")
private String userName;
@Column(name="password")
private String password;
@Column(name="role")
private String role;
@Column(name="full_name")
private String fullName;
@Column(name="country")
private String country;
@Column(name="enabled")
private short enabled;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getRole() {
return role;
}
public void setRole(String role) {
this.role = role;
}
public String getFullName() {
return fullName;
}
public void setFullName(String fullName) {
this.fullName = fullName;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public short getEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(short enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
}
package com.concretepage.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="articles")
public class Article implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name="article_id")
private int articleId;
@Column(name="title")
private String title;
@Column(name="category")
private String category;
public int getArticleId() {
return articleId;
}
public void setArticleId(int articleId) {
this.articleId = articleId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(String category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
Spring REST Security + JPA 2 + Hibernate 5 CRUD Example using Annotation
We will create Spring REST security + JPA 2 + hibernate 5 CRUD example using annotation here. We will create Java configuration file for spring security, JPA integration and MVC configuration. Using JPA entity manager we will perform create, read, update and delete operation.1. Project Structure using JavaConfig in Eclipse
Find the project structure using JavaConfig in eclipse.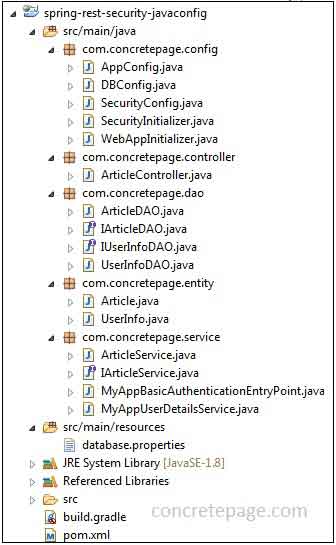
2. Implement BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint
This is used byExceptionTraslationFilter to commence authentication via the BasicAuthenticationFilter. We need to override commence() method of BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint that will return HTTP status code (401) indicating that the request requires HTTP authentication.
MyAppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint.java
package com.concretepage.service;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyAppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint extends BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.addHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=\"" + getRealmName() + "\"");
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED, authException.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
setRealmName("MY APP REALM");
}
}
3. Implement UserDetailsService
UserDetailsService loads user authentication and authorization related data. To authenticate user using database, we need to implement it and override loadUserByUsername() method. We fetch username, password and roles from the database that is used by spring UserDetailsService to authenticate the user.
MyAppUserDetailsService.java
package com.concretepage.service;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.concretepage.dao.IUserInfoDAO;
import com.concretepage.entity.UserInfo;
@Service
public class MyAppUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private IUserInfoDAO userInfoDAO;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userName)
throws UsernameNotFoundException {
UserInfo activeUserInfo = userInfoDAO.getActiveUser(userName);
GrantedAuthority authority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(activeUserInfo.getRole());
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails)new User(activeUserInfo.getUserName(),
activeUserInfo.getPassword(), Arrays.asList(authority));
return userDetails;
}
}
4. Spring REST Security JavaConfig
In spring security configuration we are using HTTP basic authentication. We will configure realm name and authentication entry point. For password encoding we are using BCrypt password encoder.SecurityConfig.java
package com.concretepage.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import com.concretepage.service.MyAppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import com.concretepage.service.MyAppUserDetailsService;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled=true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyAppUserDetailsService myAppUserDetailsService;
@Autowired
private MyAppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint myAppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasAnyRole("ADMIN","USER")
.and().httpBasic().realmName("MY APP REALM")
.authenticationEntryPoint(myAppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint);
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
auth.userDetailsService(myAppUserDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
}
}
@EnableWebSecurity enables the spring web security. @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity is used to enable method level security in service layer. Now find the spring security initializer.
SecurityInitializer.java
package com.concretepage.config;
import org.springframework.security.web.context.AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer;
public class SecurityInitializer extends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer {
}
5. Spring, JPA and Hibernate Integration using JavaConfig
Find the java configuration file that will integrate spring, JPA and hibernate.DBConfig.java
package com.concretepage.config;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@PropertySource("classpath:database.properties")
public class DBConfig {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean getEntityManagerFactoryBean() {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean lcemfb = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
lcemfb.setJpaVendorAdapter(getJpaVendorAdapter());
lcemfb.setDataSource(getDataSource());
lcemfb.setPersistenceUnitName("myJpaPersistenceUnit");
lcemfb.setPackagesToScan("com.concretepage.entity");
lcemfb.setJpaProperties(jpaProperties());
return lcemfb;
}
@Bean
public JpaVendorAdapter getJpaVendorAdapter() {
JpaVendorAdapter adapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
return adapter;
}
@Bean
public DataSource getDataSource() {
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("database.driverClassName"));
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("database.url"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("database.username"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("database.password"));
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager txManager(){
JpaTransactionManager jpaTransactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager(
getEntityManagerFactoryBean().getObject());
return jpaTransactionManager;
}
private Properties jpaProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", env.getProperty("hibernate.dialect"));
properties.put("hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings", env.getProperty("hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings"));
properties.put("hibernate.show_sql", env.getProperty("hibernate.show_sql"));
properties.put("hibernate.format_sql", env.getProperty("hibernate.format_sql"));
return properties;
}
}
1. Create data source using
BasicDataSource class from the commons.dbcp2 library. Using this class we configure database driver class name, URL, username and password.
2. Create entity manager factory bean using the following class.
org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean
EntityManagerFactory according to the standard container bootstrap contract of JPA. In this way we get a shared EntityManagerFactory in our spring application context. To use it in DAO we just do dependency injection to get its instance.
3. For database transaction management, spring provides
JpaTransactionManager that is the implementation of PlatformTransactionManager. JpaTransactionManager is appropriate for single JPA EntityManagerFactory for transactional data access.
4.
@EnableTransactionManagement enables annotation-driven transaction management capability. To handle transaction at DAO layer, we annotate DAO class or method with @Transactional annotation.
Now find the database property file.
database.properties
database.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver database.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/concretepage database.username=root database.password= hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings = false hibernate.show_sql = true hibernate.format_sql = true
6. Spring MVC JavaConfig
Find the java configuration for spring MVC.AppConfig.java
package com.concretepage.config;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.concretepage")
@EnableWebMvc
public class AppConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = new Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder();
builder.indentOutput(true);
converters.add(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
}
package com.concretepage.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class WebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { AppConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
7. Create DAO
Find the DAO class in which we have created a method to load user information that will be called to instantiateUserDetailsService.
IUserInfoDAO.java
package com.concretepage.dao;
import com.concretepage.entity.UserInfo;
public interface IUserInfoDAO {
UserInfo getActiveUser(String userName);
}
package com.concretepage.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.concretepage.entity.UserInfo;
@Repository
@Transactional
public class UserInfoDAO implements IUserInfoDAO {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
public UserInfo getActiveUser(String userName) {
UserInfo activeUserInfo = new UserInfo();
short enabled = 1;
List<?> list = entityManager.createQuery("SELECT u FROM UserInfo u WHERE userName=? and enabled=?")
.setParameter(1, userName).setParameter(2, enabled).getResultList();
if(!list.isEmpty()) {
activeUserInfo = (UserInfo)list.get(0);
}
return activeUserInfo;
}
}
IArticleDAO.java
package com.concretepage.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
public interface IArticleDAO {
List<Article> getAllArticles();
Article getArticleById(int articleId);
void addArticle(Article article);
void updateArticle(Article article);
void deleteArticle(int articleId);
boolean articleExists(String title, String category);
}
package com.concretepage.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
@Transactional
@Repository
public class ArticleDAO implements IArticleDAO {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Override
public Article getArticleById(int articleId) {
return entityManager.find(Article.class, articleId);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public List<Article> getAllArticles() {
String hql = "FROM Article as atcl ORDER BY atcl.articleId";
return (List<Article>) entityManager.createQuery(hql).getResultList();
}
@Override
public void addArticle(Article article) {
entityManager.persist(article);
}
@Override
public void updateArticle(Article article) {
Article artcl = getArticleById(article.getArticleId());
artcl.setTitle(article.getTitle());
artcl.setCategory(article.getCategory());
entityManager.flush();
}
@Override
public void deleteArticle(int articleId) {
entityManager.remove(getArticleById(articleId));
}
@Override
public boolean articleExists(String title, String category) {
String hql = "FROM Article as atcl WHERE atcl.title = ? and atcl.category = ?";
int count = entityManager.createQuery(hql).setParameter(1, title)
.setParameter(2, category).getResultList().size();
return count > 0 ? true : false;
}
}
8. Create Service
In our application we will perform create, read, update and delete (CRUD) operation. We have secured our service methods using@Secured.
IArticleService.java
package com.concretepage.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.Secured;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
public interface IArticleService {
@Secured ({"ROLE_ADMIN", "ROLE_USER"})
List<Article> getAllArticles();
@Secured ({"ROLE_ADMIN", "ROLE_USER"})
Article getArticleById(int articleId);
@Secured ({"ROLE_ADMIN"})
boolean addArticle(Article article);
@Secured ({"ROLE_ADMIN"})
void updateArticle(Article article);
@Secured ({"ROLE_ADMIN"})
void deleteArticle(int articleId);
}
package com.concretepage.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.concretepage.dao.IArticleDAO;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
@Service
public class ArticleService implements IArticleService {
@Autowired
private IArticleDAO articleDAO;
@Override
public Article getArticleById(int articleId) {
Article obj = articleDAO.getArticleById(articleId);
return obj;
}
@Override
public List<Article> getAllArticles(){
return articleDAO.getAllArticles();
}
@Override
public synchronized boolean addArticle(Article article){
if (articleDAO.articleExists(article.getTitle(), article.getCategory())) {
return false;
} else {
articleDAO.addArticle(article);
return true;
}
}
@Override
public void updateArticle(Article article) {
articleDAO.updateArticle(article);
}
@Override
public void deleteArticle(int articleId) {
articleDAO.deleteArticle(articleId);
}
}
9. Create Controller
Find the controller class.ArticleController.java
package com.concretepage.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder;
import com.concretepage.entity.Article;
import com.concretepage.service.IArticleService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class ArticleController {
@Autowired
private IArticleService articleService;
@GetMapping("article/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Article> getArticleById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
Article article = articleService.getArticleById(id);
return new ResponseEntity<Article>(article, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@GetMapping("articles")
public ResponseEntity<List<Article>> getAllArticles() {
List<Article> list = articleService.getAllArticles();
return new ResponseEntity<List<Article>>(list, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@PostMapping("article")
public ResponseEntity<Void> addArticle(@RequestBody Article article, UriComponentsBuilder builder) {
boolean flag = articleService.addArticle(article);
if (flag == false) {
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.CONFLICT);
}
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setLocation(builder.path("/article/{id}").buildAndExpand(article.getArticleId()).toUri());
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(headers, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@PutMapping("article")
public ResponseEntity<Article> updateArticle(@RequestBody Article article) {
articleService.updateArticle(article);
return new ResponseEntity<Article>(article, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@DeleteMapping("article/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteArticle(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
articleService.deleteArticle(id);
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
}
}
@GetMapping for HTTP GET method
@PostMapping for HTTP POST method
@PutMapping for HTTP PUT method
@DeleteMapping for HTTP DELETE method
We have created following URLS for CRUD operation.
1. Create :
HTTP Method: POST, URL: /user/article
2. Read :
HTTP Method: GET, URL: /user/article/{id}
HTTP Method: GET, URL: /user/articles
3. Update :
HTTP Method: PUT, URL: /user/article
4. Delete :
HTTP Method: DELETE, URL: /user/article/{id}
Spring REST Security + JPA 2 + Hibernate 5 CRUD Example using XML Configuration
In this application we will create Spring REST security + JPA 2 + hibernate 5 CRUD example using XML configuration. We will create XML configuration for spring security, JPA integration and MVC configuration.1. Project Structure using XML Configuration in Eclipse
Find the project structure using XML configuration in eclipse.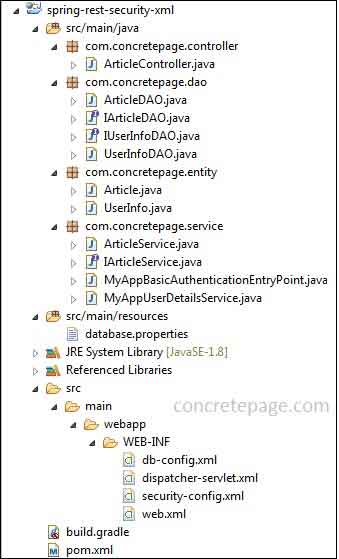
2. Spring REST Security XML Configuration
Find the spring security configuration using XML.security-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd">
<http realm="MY APP REALM">
<csrf disabled="true"/>
<intercept-url pattern="/user/**" access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_ADMIN','ROLE_USER')" />
<http-basic entry-point-ref="basicAuthenticationEntryPoint" />
</http>
<beans:bean name="bcryptEncoder"
class="org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder"/>
<beans:bean name="myAppUserDetailsService"
class="com.concretepage.service.MyAppUserDetailsService"/>
<beans:bean class="com.concretepage.service.ArticleService"/>
<beans:bean name="basicAuthenticationEntryPoint"
class="com.concretepage.service.MyAppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint"/>
<authentication-manager>
<authentication-provider user-service-ref="myAppUserDetailsService">
<password-encoder ref="bcryptEncoder"/>
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>
<global-method-security secured-annotations="enabled" />
</beans:beans>
3. Spring, JPA and Hibernate Integration using XML Configuration
Find the spring and hibernate integration using XML configuration.db-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:database.properties"/>
<bean id="basicDataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${database.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${database.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${database.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${database.password}" />
</bean>
<bean name="hibernateJpaVendorAdapter" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter"/>
<bean id="entityManagerFactoryBean" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="jpaVendorAdapter" ref="hibernateJpaVendorAdapter" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="basicDataSource" />
<property name="persistenceUnitName" value="myJpaPersistenceUnit" />
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>com.concretepage.entity</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="jpaProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">${hibernate.dialect}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings">${hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">${hibernate.show_sql}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.format_sql">${hibernate.format_sql}</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactoryBean" />
</bean>
<bean class="com.concretepage.dao.ArticleDAO" />
<bean class="com.concretepage.dao.UserInfoDAO" />
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager" />
</beans>
4. Spring MVC XML Configuration
Find the spring MVC configuration with message converter using XML configuration.dispatcher-servlet.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.concretepage" />
<bean name="jackson2ObjectMapper" class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.Jackson2ObjectMapperFactoryBean">
<property name="indentOutput" value="true"/>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
<property name="objectMapper" ref="jackson2ObjectMapper" />
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
</beans>
5. Create web.xml
Find theweb.xml file.
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>Spring 4 REST Security Example</display-name>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/dispatcher-servlet.xml
/WEB-INF/security-config.xml
/WEB-INF/db-config.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- Spring Security Configuration -->
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
Create REST Web Service Client using RestTemplate
To consume the REST web service, we are usingRestTemplate. For authentication we will pass Base64 encoded credential as username:password token in HttpHeaders with Basic authorization.
RestClientUtil.java
package com.concretepage.util;
import java.net.URI;
import org.apache.tomcat.util.codec.binary.Base64;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
public class RestClientUtil {
private HttpHeaders getHeaders() {
String credential="mukesh:m123";
//String credential="tarun:t123";
String encodedCredential = new String(Base64.encodeBase64(credential.getBytes()));
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
headers.add("Authorization", "Basic " + encodedCredential);
return headers;
}
public void getArticleByIdDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = getHeaders();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/spring-app/user/article/{id}";
HttpEntity<String> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<String>(headers);
ResponseEntity<Article> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestEntity, Article.class, 1);
Article article = responseEntity.getBody();
System.out.println("Id:"+article.getArticleId()+", Title:"+article.getTitle()
+", Category:"+article.getCategory());
}
public void getAllArticlesDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = getHeaders();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/spring-app/user/articles";
HttpEntity<String> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<String>(headers);
ResponseEntity<Article[]> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestEntity, Article[].class);
Article[] articles = responseEntity.getBody();
for(Article article : articles) {
System.out.println("Id:"+article.getArticleId()+", Title:"+article.getTitle()
+", Category: "+article.getCategory());
}
}
public void addArticleDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = getHeaders();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/spring-app/user/article";
Article objArticle = new Article();
objArticle.setTitle("Spring REST Security using Hibernate");
objArticle.setCategory("Spring");
HttpEntity<Article> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<Article>(objArticle, headers);
URI uri = restTemplate.postForLocation(url, requestEntity);
System.out.println(uri.getPath());
}
public void updateArticleDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = getHeaders();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/spring-app/user/article";
Article objArticle = new Article();
objArticle.setArticleId(1);
objArticle.setTitle("Update:Java Concurrency");
objArticle.setCategory("Java");
HttpEntity<Article> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<Article>(objArticle, headers);
restTemplate.put(url, requestEntity);
}
public void deleteArticleDemo() {
HttpHeaders headers = getHeaders();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/spring-app/user/article/{id}";
HttpEntity<Article> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<Article>(headers);
restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.DELETE, requestEntity, Void.class, 4);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
RestClientUtil util = new RestClientUtil();
//util.getArticleByIdDemo();
util.getAllArticlesDemo();
//util.addArticleDemo();
//util.updateArticleDemo();
//util.deleteArticleDemo();
}
}
Run Application
To build and run the demo application, follow the steps.1. Import database in MySQL given above on this page.
2. Download the source code from the link given below on this page.
3. Go to the root directory of the project using command prompt.
4. Build the project using gradle with following command.
gradle clean build
mvn clean package
5. Deploy the WAR file using tomcat.
6. To test the application, run
RestClientUtil file with main() method. Suppose we want to perform read operation to fetch all articles, we will get following output.
Id:1, Title:Java Concurrency, Category: Java Id:2, Title:Hibernate HQL , Category: Hibernate Id:3, Title:Spring MVC with Hibernate, Category: Spring
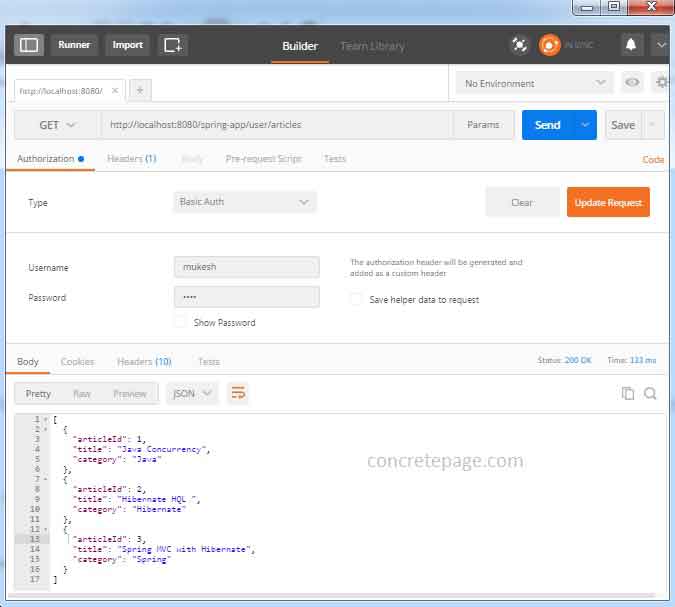
7. We can also use
Postman to test the application. Find the print screen.
I am done now. Happy Spring learning!


