Spring MVC Internationalization (i18n) and Localization (l10n) Example
June 26, 2019
This page will provide Spring MVC internationalization (i18n) and localization (l10n) annotation example. Here internalization (i18n) is creating our website in more than one languages and Localization (l10) is accessing website in any specific language by setting the locale. Here we will discuss in detail how to achieve it in Spring MVC. We will use java configuration to define beans using annotation. To achieve internalization and localization there are some classes and its implementation which has the major role that are MessageSource, LocaleResolver, LocaleChangeInterceptor etc. MessageSource access the resource bundle. LocaleResolver resolves the locale changed by the user by calling locale setter method. LocaleChangeInterceptor is the interceptor which observes the locale changes.
In our example we will create a simple form which will have two links to localize the website in English and German languages. By default page will open in English.
Contents
- Software Used in Demo Project
- Demo Project Structure in eclipse
- Gradle File to Resolve JAR Dependencies
- Java Configuration for Internationalization (i18n) and Localization (l10n)
- Create MessageSource Bean
- Create LocaleResolver Bean
- Add LocaleChangeInterceptor
- Create Message Source Property File
- Create Sample JSP file for Demo
- Create Controller
- Spring Web Application Initializer Class
- Output
Software Used in Demo Project
We are using following software and tools in our demo project of internalization and localization.1. Java 7
2. Tomcat 8
3. Gradle
4. Eclipse
5. Spring 4
Demo Project Structure in eclipse
Find the print screen of project structure in eclipse.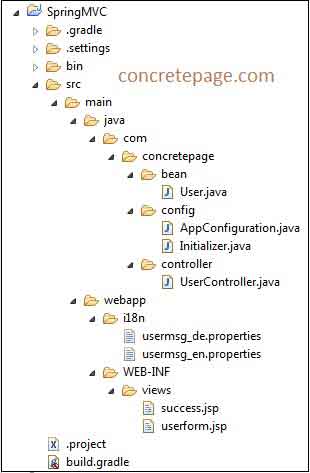
Gradle File to Resolve JAR Dependencies
Find the Gradle file to resolve the JAR dependencies and build the project.build.gradle
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
apply plugin: 'war'
archivesBaseName = 'concretepage'
version = '1'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:1.2.2.RELEASE'
compile 'jstl:jstl:1.2'
providedCompile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-tomcat:1.2.2.RELEASE'
}
Java Configuration for Internationalization (i18n) and Localization (l10n)
In java configuration, we will create beans for Internationalization and Localization. To import Spring MVC configuration , annotate the class with @EnableWebMvc. To add interceptor, extend WebMvcConfigurerAdapter class.
AppConfiguration.java
package com.concretepage.config;
import java.util.Locale;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.concretepage")
@EnableWebMvc
public class AppConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return resolver;
}
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource();
messageSource.setBasename("/i18n/usermsg");
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
return messageSource;
}
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
CookieLocaleResolver resolver = new CookieLocaleResolver();
resolver.setDefaultLocale(new Locale("en"));
resolver.setCookieName("myLocaleCookie");
resolver.setCookieMaxAge(4800);
return resolver;
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
LocaleChangeInterceptor interceptor = new LocaleChangeInterceptor();
interceptor.setParamName("mylocale");
registry.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
InternalResourceViewResolver bean has been created. Set prefix and suffix that will resolve view name returned by the controller.
Create MessageSource Bean
org.springframework.context.MessageSource is an interface that is used to define the message source property name for internalization and localization. We can use two implementations of MessageSource.
ResourceBundleMessageSource: It is used to handle message source by specifying property file base name. It uses java.util.ResourceBundle that caches the bundle forever which is a limitation.
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource: It also loads message source property file which is reloadable. It uses java.util.Properties .
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource();
messageSource.setBasename("/i18n/usermsg");
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
return messageSource;
}
usermsg_en.properties: For english language.
usermsg_en_US.properties : For english language of United States of America country.
We can set default encoding of message source file like UTF-8 and ISO-8859-1 etc. The bean name of message source must be messageSource. We can achieve it by giving a bean name as
@Bean(name ="messageSource")
public MessageSource anyName() {}
public MessageSource messageSource() {}
Create LocaleResolver Bean
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver is an interface that resolves locale. It can be implemented for request, session and cookies. The default implementation is AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver provided by spring MVC. But it does not support to change the locale using setLocale() method. It can be changed by changing client's locale setting. In our Internalization and localization requirement, we can use the below implementations of LocaleResolver.
CookieLocaleResolver : This is the implementation class of LocaleResolver which uses cookie that is sent back on the browser for custom settings to handle locale used in internalization and localisation. This class is used for stateless web application. The LocaleResolver bean for CookieLocaleResolver is created as below.
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
CookieLocaleResolver resolver = new CookieLocaleResolver();
resolver.setDefaultLocale(new Locale("en"));
resolver.setCookieName("myLocaleCookie");
resolver.setCookieMaxAge(4800);
return resolver;
}
setDefaultLocale() . Here we have set en locale as default . Set cookie name by setCookieName(). The max age of cookie in seconds can be set by setCookieMaxAge(). We can also set default time zone with determineDefaultTimeZone() method. Once the cookie is set in browser, then for every page we will get custom message source till the cookie expires.
SessionLocaleResolver : This class is useful when there is a user session based application. This class sets a locale attribute in session for custom locale setting. In java configuration we can use it as below.
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
SessionLocaleResolver resolver = new SessionLocaleResolver ();
resolver.setDefaultLocale(new Locale("en"));
return resolver;
}
SessionLocaleResolver() also sets default time zone using determineDefaultTimeZone() method. Once we set custom locale in session, then for every page we will get message source file for the custom locale till the user session expires.
While using
LocaleResolver, we need to take care that either the bean name should be localeResolver as
@Bean(name="localeResolver")
public LocaleResolver anyName(){}
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){}
Add LocaleChangeInterceptor
org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor has the responsibility of changing the current locale if requested. Find the code snippet.
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
LocaleChangeInterceptor interceptor = new LocaleChangeInterceptor();
interceptor.setParamName("mylocale");
registry.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
LocaleChangeInterceptor by the method setParamName(). The default parameter name is locale. We need to add this interceptor to InterceptorRegistry that is the argument of method addInterceptors defined in our java configuration overridden from WebMvcConfigurerAdapter. To change the locale in any request we need to add the query string in our URL as below.
?mylocale=en: Change the locale for English message source
?mylocale=de: Change the locale for German message source.
Create Message Source Property File
In our demo project we are using two message source. We have set message source base name as /i18n/usermsg . It means we need to create file name starting with usermsg and will be kept in the folder i18n parallel to WEB-INF. Find the properties fileusermsg_en.properties
user.title= Fill User Form user.name= Enter Name user.age= Enter Age user.submit= Submit user.success= You have successfully submitted the form
usermsg_de.properties
user.title= Fullen User Form user.name= Name eingeben user.age= Geben Alter user.submit= einreichen user.success= Sie haben die Form eingereicht
Create Sample JSP file for Demo
Find the sample JSP file which we are using in our demo. We are creating a user form. There will be two link in our form, one for selecting en locale and second for selecting de locale.userform.jsp
<%@taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring"%>
<%@taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="form"%>
<html>
<head><title><spring:message code="user.title"/></title></head>
<body>
<a href="user?mylocale=en">English </a> | <a href="user?mylocale=de">German </a>
<h3> <spring:message code="user.title"/></h3>
<table>
<form:form action="save" method="post" commandName="user">
<tr><td><spring:message code="user.name"/>:</td> <td><form:input path="name"/> </td> </tr>
<tr> <td> <spring:message code="user.age"/> :</td> <td><form:input path="age"/> </td> </tr>
<tr> <td colspan=2>
<spring:message code="user.submit" var="valSubmit"></spring:message>
<input type="submit" value="${valSubmit}">
</td></tr>
</form:form>
</table>
</body>
</html>
<%@taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring"%> <html> <head><title><spring:message code="user.title"/></title></head> <body> <a href="user?mylocale=en">English </a> | <a href="user?mylocale=de">German </a> <h3> <spring:message code="user.success"/></h3> </body> </html>
Create Controller
Find the controller which we are using in our demo. There is nothing locale specific code in controller. This is just a simple controller that will accept a form submission. We are also using a bean which attributes are attached with the form input fields.UserController.java
package com.concretepage.controller;
import java.util.Locale;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import com.concretepage.bean.User;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(value="/user", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView user(Locale locale){
return new ModelAndView("userform","user",new User());
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/save", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String save(@ModelAttribute("user") User user) {
return "success";
}
}
package com.concretepage.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
Spring Web Application Initializer Class
Find the spring web application initializer. We use it to avoid web.xml.Initializer.java
package com.concretepage.config;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration.Dynamic;
import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
public class Initializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(AppConfiguration.class);
ctx.setServletContext(servletContext);
Dynamic dynamic = servletContext.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(ctx));
dynamic.addMapping("/");
dynamic.setLoadOnStartup(1);
}
}
Output
To check the output, start from the URL http://localhost:8080/concretepage-1/user and we will get the page as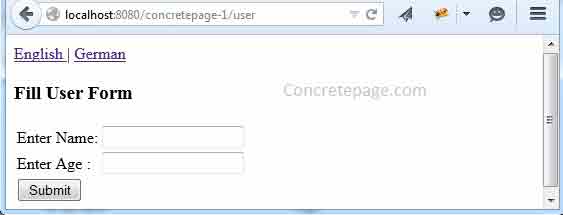
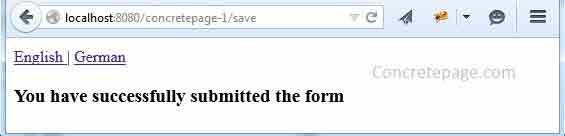
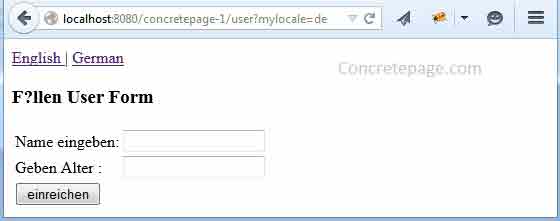
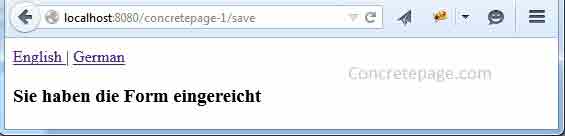
CookieLocaleResolver, so what happens that it sets a cookie named as myLocaleCookie. Check it in the browser.
Now I am done. Happy Spring Learning!.


