JPA + Hibernate @Inheritance - JOINED Example
February 27, 2023
On this page, we will learn to use JPA @Inheritance annotation with JOINED strategy in our Hibernate application.
1. The
@Inheritance annotation specifies the inheritance strategy to be used for an entity class hierarchy. The inheritance strategy can be JOINED, SINGLE_TABLE and TABLE_PER_CLASS.
2. In JOINED inheritance strategy, the fields that are specific to a subclass are mapped to a separate table than the fields that are common to the parent class, and a join is performed to instantiate the subclass.
3. The
@Inheritance annotation with JOINED strategy is specified at the root entity. The root entity persist data in parent table and subclass entity persist data in child table.
4. Parent table and child table are joined with foreign key and hence we need to specify
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn at subclass entity.
5. To use JOINED inheritance, we need to create a root class and some subclasses. Root class is annotated with
@Entity and @Inheritance annotations.
@Entity(name = "account")
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
public class Account {
------
}
@Entity and @PrimaryKeyJoinColumn annotations.
@Entity(name = "credit_account")
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn(name = "ca_id")
public class CreditAccount extends Account {
------
}
Complete Example
1. Technologies Used1. Java 19
2. Hibernate 6
3. Jakarta Persistence API 3
4. MySQL 5.5
2. pom.xml
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>6.1.6.Final</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId> <version>6.0.0.Alpha7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.32</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<persistence xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence
https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<persistence-unit name="com.concretepage">
<description>Procedure Demo</description>
<provider>org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider</provider>
<properties>
<property name="hibernate.dialect"
value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.driver"
value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost/concretepage" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.user" value="root" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.password"
value="cp" />
<property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true" />
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
Find the tables.
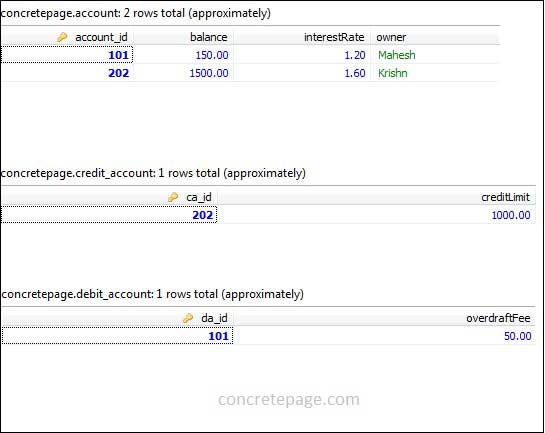
CREATE TABLE `account` ( `account_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL, `balance` DECIMAL(19,2) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `interestRate` DECIMAL(19,2) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `owner` VARCHAR(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`account_id`) ) CREATE TABLE `credit_account` ( `ca_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL, `creditLimit` DECIMAL(19,2) NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`ca_id`), CONSTRAINT `credit_account_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`ca_id`) REFERENCES `account` (`account_id`) ) CREATE TABLE `debit_account` ( `da_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL, `overdraftFee` DECIMAL(19,2) NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`da_id`), CONSTRAINT `debit_account_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`da_id`) REFERENCES `account` (`account_id`) )
5. Java Code
Find the root class. Root class contains common fields for entity subclasses.
Account.java
@Entity(name = "account")
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
public class Account {
@Id
@Column(name = "account_id")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "balance")
private BigDecimal balance;
@Column(name = "interestRate")
private BigDecimal interestRate;
@Column(name = "owner")
private String owner;
public Account(Long id, BigDecimal balance, BigDecimal interestRate, String owner) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
this.interestRate = interestRate;
this.owner = owner;
}
// Setters and Getters
}
@Entity(name = "credit_account")
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn(name = "ca_id")
public class CreditAccount extends Account {
@Column(name = "creditLimit")
private BigDecimal creditLimit;
public CreditAccount(Long id, BigDecimal balance, BigDecimal interestRate, String owner, BigDecimal creditLimit) {
super(id, balance, interestRate, owner);
this.creditLimit = creditLimit;
}
// Setters and Getters
}
@Entity(name = "debit_account")
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn(name = "da_id")
public class DebitAccount extends Account {
@Column(name = "overdraftFee")
private BigDecimal overdraftFee;
public DebitAccount(Long id, BigDecimal balance, BigDecimal interestRate, String owner, BigDecimal overdraftFee) {
super(id, balance, interestRate, owner);
this.overdraftFee = overdraftFee;
}
// Setters and Getters
}
Now run the code.
HibernateUtil.java
public class HibernateUtil {
private static final EntityManagerFactory emFactory;
static {
emFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("com.concretepage");
}
public static EntityManager getEntityManager(){
return emFactory.createEntityManager();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManager entityManager = HibernateUtil.getEntityManager();
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
DebitAccount debitAccount = new DebitAccount(101L, BigDecimal.valueOf(150), BigDecimal.valueOf(1.2d), "Mahesh",
BigDecimal.valueOf(50));
CreditAccount creditAccount = new CreditAccount(202L, BigDecimal.valueOf(1500), BigDecimal.valueOf(1.6d), "Krishn",
BigDecimal.valueOf(1000));
entityManager.persist(debitAccount);
entityManager.persist(creditAccount);
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
entityManager.close();
}
}
Hibernate: insert into account (balance, interestRate, owner, account_id) values (?, ?, ?, ?) Hibernate: insert into debit_account (overdraftFee, da_id) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into account (balance, interestRate, owner, account_id) values (?, ?, ?, ?) Hibernate: insert into credit_account (creditLimit, ca_id) values (?, ?)