JPA + Hibernate - @Embeddable and @Embedded Example
February 12, 2023
On this page, we will learn to use JPA @Embeddable and @Embedded annotations in our Hibernate application. An entity can be embedded in other entities using @Embeddable and @Embedded annotations. It is used where there are common attributes in entities. In this case, we can create an embeddable entity and this embeddable entity can be embedded in those entities.
1. @Embeddable Annotation
The@Embeddable annotation is annotated at a class level and makes this class embeddable to another entity class. All the fields of @Embeddable class are added to owning class and mapped to the database.
Find an embeddable class having common fields of some entities.
@Embeddable
public class ContactNumber {
@Column(name = "landline_num")
private String landline;
@Column(name = "mobile_num")
private String mobile;
------
}
ContactNumber with landline and mobile fields. Wherever we embed this class, its fields will be added to that owning entity class. The @Embeddable classes are added to an entity class using @Embedded annotation.
Note: If
@Transient are used with @Embeddable, then its fields will not persist in database.
2. @Embedded Annotation
The@Embedded annotation specifies a persistent field or property of an entity whose value is an instance of an @Embeddable class. All the fields of embeddable class are added to owning class.
Find the sample code to use
@Embedded annotation.
@Entity
@Table(name="person")
public class Person {
@Id
@Column(name = "person_id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "person_name")
private String name;
@Embedded
private Address address;
@Embedded
private ContactNumber contactNum;
------
}
Address and ContactNumber are embeddable classes. If column names of owning class, mismatch from the embeddable class, we can use AttributeOverride and AssociationOverride annotations to map the column names.
3. @Embedded with @AttributeOverride Annotation
The@AttributeOverride is used to override the mappings declared in embeddable class.
Suppose we have an embeddable class.
@Embeddable
public class Address {
@Column(name = "person_country")
private String country;
@Column(name = "person_city")
private String city;
------
}
Address class into Employee class that represents employee table. But the country and city columns in employee table are named as emp_country and emp_city respectively which are different from columns mapped in Address class. We can use @AttributeOverride annotation to map them into Employee as following.
@Embedded
@AttributeOverrides({
@AttributeOverride(
name = "country",
column = @Column(name = "emp_country")
),
@AttributeOverride(
name = "city",
column = @Column(name = "emp_city")
)
})
private Address address;
4. Complete Example
1. Technologies Used1. Java 19
2. Hibernate 6
3. Jakarta Persistence API 3
4. MySQL 5.5
2. MySQL Database
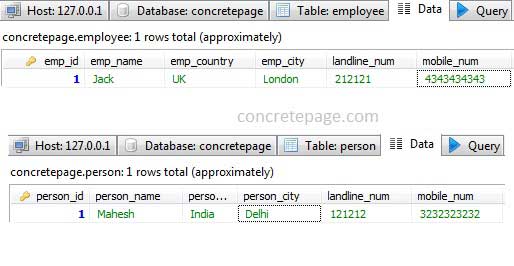
CREATE TABLE `person` ( `person_id` INT(5) NOT NULL, `person_name` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, `person_country` VARCHAR(100), `person_city` VARCHAR(100), `landline_num` VARCHAR(20), `mobile_num` VARCHAR(20), PRIMARY KEY (`person_id`) ) CREATE TABLE `employee` ( `emp_id` INT(5) NOT NULL, `emp_name` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, `emp_country` VARCHAR(100), `emp_city` VARCHAR(100), `landline_num` VARCHAR(20), `mobile_num` VARCHAR(20), PRIMARY KEY (`emp_id`) )
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>6.1.6.Final</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId> <version>6.0.0.Alpha7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.32</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<persistence xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence
https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<persistence-unit name="com.concretepage">
<description>Procedure Demo</description>
<provider>org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider</provider>
<properties>
<property name="hibernate.dialect"
value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.driver"
value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost/concretepage" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.user" value="root" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.password"
value="cp" />
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
HibernateUtil.java
package com.concretepage.util;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import jakarta.persistence.Persistence;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static final EntityManagerFactory emFactory;
static {
emFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("com.concretepage");
}
public static EntityManager getEntityManager(){
return emFactory.createEntityManager();
}
}
package com.concretepage.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Embeddable;
@Embeddable
public class ContactNumber {
@Column(name = "landline_num")
private String landline;
@Column(name = "mobile_num")
private String mobile;
public ContactNumber() {}
public ContactNumber(String landline, String mobile) {
this.landline = landline;
this.mobile = mobile;
}
// setters and getters
}
package com.concretepage.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Embeddable;
@Embeddable
public class Address {
@Column(name = "person_country")
private String country;
@Column(name = "person_city")
private String city;
public Address() {}
public Address(String country, String city) {
this.country = country;
this.city = city;
}
// setters and getters
}
package com.concretepage.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Embedded;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="person")
public class Person {
@Id
@Column(name = "person_id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "person_name")
private String name;
@Embedded
private Address address;
@Embedded
private ContactNumber contactNum;
public Person() {}
public Person(int id, String name, Address address, ContactNumber contactNum){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
this.contactNum = contactNum;
}
// setters and getters
}
package com.concretepage.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.AttributeOverride;
import jakarta.persistence.AttributeOverrides;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Embedded;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employee")
public class Employee {
@Id
@Column(name = "emp_id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "emp_name")
private String name;
@Embedded
@AttributeOverrides({
@AttributeOverride(
name = "country",
column = @Column(name = "emp_country")
),
@AttributeOverride(
name = "city",
column = @Column(name = "emp_city")
)
})
private Address address;
@Embedded
private ContactNumber contactNum;
public Employee() {}
public Employee(int id, String name, Address address, ContactNumber contactNum){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
this.contactNum = contactNum;
}
// setters and getters
}
package com.concretepage;
import com.concretepage.entity.Address;
import com.concretepage.entity.ContactNumber;
import com.concretepage.entity.Employee;
import com.concretepage.entity.Person;
import com.concretepage.util.HibernateUtil;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManager entityManager = HibernateUtil.getEntityManager();
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
Address personAddress = new Address("India", "Delhi");
ContactNumber personContactNum = new ContactNumber("121212", "3232323232");
Person person = new Person(1, "Mahesh", personAddress, personContactNum);
Address empAddress = new Address("UK", "London");
ContactNumber empContactNum = new ContactNumber("212121", "4343434343");
Employee employee = new Employee(1, "Jack", empAddress, empContactNum);
entityManager.persist(person);
entityManager.persist(employee);
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
entityManager.close();
}
}