Hibernate Bidirectional Mapping Example with @JoinTable Annotation
February 22, 2015
In this page, we will learn hibernate bidirectional mapping example with @JoinTable annotation. Bidirectional mapping means two entities are associated in a way that one can be fetched from another entity. @JoinTable annotation joins the associating table with the help of third table. In our example for bidirectional mapping OneToMany/OneToOne association is being used.
@JoinTable
@JoinTable annotation is used to join two table using a third table. This third table associates two table by their Ids. To define @JoinTable we can use below attributes.name: This is the name of third table.
joinColumns: Assign the column of third table related to entity itself.
inverseJoinColumns: Assign the column of third table related to associated entity.
Look at the below code snippet.
@Entity
@Table(name="company")
public class Company {
-----------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------
@OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinTable(name="Company_Employee", joinColumns={@JoinColumn(name ="companyId", referencedColumnName ="id")},
inverseJoinColumns={@JoinColumn(name ="employeeId", referencedColumnName ="id")})
private Set<Employee> employees;
-----------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------
}
@Entity
@Table(name="employee")
public class Employee {
-----------------------
-----------------------
@OneToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinTable(name="Company_Employee", joinColumns={@JoinColumn(name ="employeeId", referencedColumnName ="id")},
inverseJoinColumns={@JoinColumn(name ="companyId", referencedColumnName ="id")})
private Company company;
-----------------------
-----------------------
}
Database Structure
Find database schema and the relationship between the tables as below. In the third table, there is two column for the id of both table.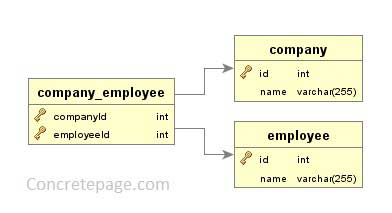
Create An Entity Using @OneToMany
Find the entity which is using @OneToMany mapping with @JoinTable.Company.java
package com.concretepage;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.JoinTable;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="company")
public class Company {
@Id
@Column(name="id")
private Integer id;
@Column(name="name")
private String name;
@OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinTable(name="Company_Employee", joinColumns={@JoinColumn(name ="companyId", referencedColumnName ="id")},
inverseJoinColumns={@JoinColumn(name ="employeeId", referencedColumnName ="id")})
private Set<Employee> employees;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Set<Employee> getEmployees() {
return employees;
}
public void setEmployees(Set<Employee> employees) {
this.employees = employees;
}
}
Create An Entity Using @OneToOne
Find the entity which is using @OneToOne mapping with @JoinTable.Employee.java
package com.concretepage;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.JoinTable;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="employee")
public class Employee {
@Id
@Column(name="id")
private Integer id;
@Column(name="name")
private String name;
@OneToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinTable(name="Company_Employee", joinColumns={@JoinColumn(name ="employeeId", referencedColumnName ="id")},
inverseJoinColumns={@JoinColumn(name ="companyId", referencedColumnName ="id")})
private Company company;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Company getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(Company company) {
this.company = company;
}
}
hibernate.cfg.xml
Find the hibernate.cfg.xml file.hibernate.cfg.xml
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/concretepage</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password"></property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.pool_size">10</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<mapping class="com.concretepage.Company"/>
<mapping class="com.concretepage.Employee"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Hibernate Utility Class
Find the hibernate utility class.HibernateUtil.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory ;
static {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder builder = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties());
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(builder.build());
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
}
Main Class to Test Bidirectional Mapping
Now run the example to test the bidirectional mapping.JoinTableDemo.java
package com.concretepage;
import java.util.Set;
import org.hibernate.Session;
public class JoinTableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
System.out.println("---Fetch Employess---");
Company company = (Company) session.get(Company.class, new Integer(1));
Set<Employee> employees = company.getEmployees();
for(Employee e: employees){
System.out.println("Id:"+e.getId()+", Name:"+e.getName());
}
System.out.println("---Fetch Company---");
Employee emp = (Employee) session.get(Employee.class, new Integer(2));
System.out.println("Name:"+emp.getName()+", Company Name:"+ emp.getCompany().getName());
session.close();
}
}
---Fetch Employess--- Hibernate: select company0_.id as id1_1_0_, company0_.name as name2_1_0_ from company company0_ where company0_.id=? Hibernate: select employees0_.companyId as companyI1_1_0_, employees0_.employeeId as employee2_0_0_, employee1_.id as id1_2_1_, employee1_.name as name2_2_1_, employee1_1_.companyId as companyI1_0_1_ from Company_Employee employees0_ inner join employee employee1_ on employees0_.employeeId=employee1_.id left outer join Company_Employee employee1_1_ on employee1_.id=employee1_1_.employeeId where employees0_.companyId=? Id:1, Name:A Id:2, Name:B Id:4, Name:D ---Fetch Company--- Name:B, Company Name:ABC


