Angular Title Service and Canonical URL
February 13, 2024
On this page we will provide Angular Title service and canonical URL example. The Title service is used to get and set title of a current HTML document. To get title, it has getTitle() method and to set title it has setTitle() method.
In server-side rendering using Angular Universal,
platform-server library is used which does not execute in browser. So we may not use some browser API such as document in our Angular application. Hence Angular provides injectable abstraction over Document object. Angular provides a constant DOCUMENT as a DI token that will be used as a DOM document in our Angular application.
Now we will provide complete example for Angular
Title service and canonical URL using Angular DOCUMENT step-by-step.
Contents
1. Title
Title is a service in Angular to get and set title of a current HTML document. Title is imported from @angular/platform-browser library. It is instantiated using dependency injection with constructor. Find the code snippet.
import { Title } from '@angular/platform-browser';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class SEOService {
constructor(private title: Title) {
}
}
Title has following methods to set and get titles.
setTitle(): Sets the title of current HTML document.
getTitle(): Gets the title of current HTML document.
1.1. setTitle()
setTitle(newTitle: string) method of Title service sets the title of current HTML document. Find the code to use it.
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class SEOService {
constructor(private title: Title) {
title.setTitle('This is page title');
}
}
1.2. getTitle()
getTitle() method of Title service gets the title of current HTML document. Find the code to use it.
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class SEOService {
constructor(private title: Title) {
}
getPageTitle() {
return this.title.getTitle();
}
}
2. DOCUMENT
DOCUMENT is an Angular const that is used as browser DOM document. DOCUMENT is a DI token representing the main rendering context. Angular creates DOCUMENT DI token as following.
const DOCUMENT: InjectionToken<Document>;;
DOCUMENT in our code. It is imported from @angular/common library. We inject DOCUMENT in constructor using @Inject decorator as following.
import { DOCUMENT } from '@angular/common';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class SEOService {
constructor(@Inject(DOCUMENT) private doc: any) {
}
}
doc we can access and manipulate DOM properties such as creating canonical link at run time. If we manipulate DOM using browser API document, then it will not run in server-side rendering. So it is good to use Angular DOCUMENT. On this page we will provide example to create canonical link using DOCUMENT.
3. Canonical URL
HTML canonical link element helps in search engine optimization (SEO) by preventing duplicate content. Canonical link element has canonical URL using which search engines identify the preferred version of the web page. Here we will create canonical link and assign canonical URL using AngularDOCUMENT.
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class SEOService {
constructor(@Inject(DOCUMENT) private doc: any) {
let link: HTMLLinkElement = doc.createElement('link');
link.setAttribute('rel', 'canonical');
doc.head.appendChild(link);
link.setAttribute('href', doc.URL);
}
}
4. Complete Example
seo.service.ts
import { Injectable, Inject } from '@angular/core';
import { Title } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { DOCUMENT } from '@angular/common';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class SEOService {
constructor(private title: Title, @Inject(DOCUMENT) private doc: any) {
}
setPageTitle(title: string) {
this.title.setTitle(title);
}
getPageTitle() {
return this.title.getTitle();
}
createLinkForCanonicalURL() {
let link: HTMLLinkElement = this.doc.createElement('link');
link.setAttribute('rel', 'canonical');
this.doc.head.appendChild(link);
link.setAttribute('href', this.doc.URL);
}
}
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { SEOService } from './seo.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-data',
templateUrl: './data.component.html'
})
export class DataComponent implements OnInit {
pageTitle = '';
constructor(private seoService: SEOService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.setPageTitle('This is page title');
this.createLinkForCanonicalURL();
}
setPageTitle(title: string) {
this.seoService.setPageTitle(title);
}
getPageTitle() {
this.pageTitle = this.seoService.getPageTitle();
}
createLinkForCanonicalURL() {
this.seoService.createLinkForCanonicalURL();
}
}
<button (click)="getPageTitle()"> Get Page Title </button>
<br/><br/>{{pageTitle}}
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<app-data></app-data>
`
})
export class AppComponent {
}
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { DataComponent } from './data.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
DataComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [ ],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule { }
5. Output
Find the print-screen of the output.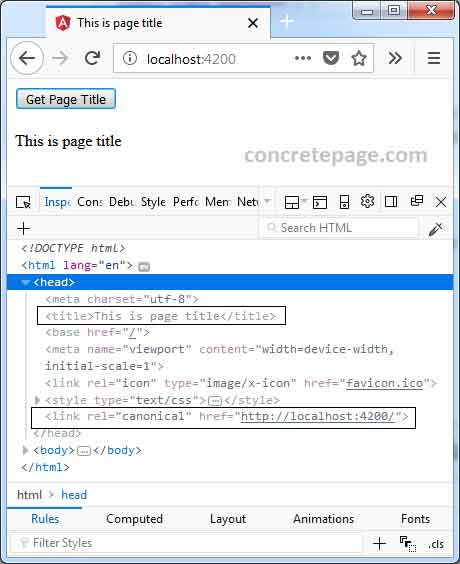
6. References
Angular doc: TitleAngular doc: DOCUMENT


