Angular Test HTTP GET Request
March 02, 2020
This page will walk through Angular unit testing for HTTP GET request using HttpClientTestingModule and TestBed API. We will test Angular HttpClient.get method in our example.
1. When we create the project using CLI, it downloads and installs everything we need to test an Angular application. Angular uses Jasmine test framework. To test Angular application, we need to run following command.
ng test
http://localhost:9876/
karma.conf.js and the src/test.ts file.
3. For Angular testing, we need to use following Angular testing library.
@angular/core/testing contains core testing API such as
TestBed.
@angular/common/http/testing contains HTTP testing API such as
HttpClientTestingModule and HttpTestingController.
Contents
1. Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Angular 9.0.2
2. Node.js 12.5.0
3. Jasmine Core 3.5.0
4. Karma 4.3.0
2. .spec.ts file for Unit Test
Test file name is sibling and is in same folder for a file for which we are writing tests. We need to create test file name by appending .spec to the original file. Find some examples.
Component
|--app.component.ts |--app.component.spec.ts
|--employee.service.ts |--employee.service.spec.ts
3. Jasmine Test Framework
Jasmine is a test framework to test JavaScript code. It can run without a DOM. We write test code as following.
describe("Test name", function() {
var msg;
it("Test description", function() {
msg = 'Hello';
expect(msg).toEqual('Hello');
});
});
describe() : Creates a group of specs. The call to
describe can be nested.
beforeEach() : It is executed before each of the specs in the
describe in which it is called.
afterEach() : It is executed after each of the specs in the
describe in which it is called.
it() : Defines a single spec. It contains one or more than one
expect.
expect() : Creates an expectation for a spec.
fail() : It marks a spec as failed.
When we create Angular project using Angular CLI, it downloads Jasmine dependencies by default. We can look into our
package.json file for the Jasmine dev dependencies.
package.json
{
------
"devDependencies": {
"jasmine-core": "~3.5.0",
"jasmine-spec-reporter": "~4.2.1",
"karma": "~4.3.0",
"karma-chrome-launcher": "~3.1.0",
"karma-coverage-istanbul-reporter": "~2.1.0",
"karma-jasmine": "~2.0.1",
"karma-jasmine-html-reporter": "^1.4.2",
------
}
}
Karma test runner
When we run ng test command, it builds app in watch mode and it launches Karma test runner. Karma is a test runner for JavaScript application. The Angular CLI takes care of Jasmine and Karma configuration for us. We can fine-tune our configurations by editing
karma.conf.js and test.ts files. Their locations are as following.
my-app | |--karma.conf.js | |--src | | | |--test.ts
4. HttpTestingController
TheHttpTestingController is a controller to be injected into tests that allows for mocking and flushing of requests. The HttpTestingController has following methods.
match() : Search for the requests that matches the given URL. This method expects nothing.
expectOne() : Expects that the request for the matching given URL has been made only one time and returns
TestRequest.
expectNone : Expects that for the matching given URL, no request has been made.
verify : Verifies that no requests are outstanding.
The
HttpTestingController can be imported as following.
import { HttpTestingController } from '@angular/common/http/testing';
5. HttpClientTestingModule
TheHttpClientTestingModule injects HttpTestingController to expect and flush requests in our tests. It is imported as following.
import { HttpClientTestingModule } from '@angular/common/http/testing';
6. TestBed
TheTestBed is the primary API used in Angular testing applications. The TestBed configures and initializes test environment. It also creates components and services required for unit testing. We will use some of its methods in our unit tests as given below.
configureTestingModule() : Configures testing module. It can import required modules, declare required components and can provide required services.
inject() : Instantiates components, services and other classes required for testing.
The
TestBed is imported in our test spec file as following.
import { TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
7. TestRequest
TheTestRequest is a mock request which is ready to be answered. It access to the underlying HttpRequest and allows responding as response data or error. The TestRequest is returned by expectOne() method of HttpTestingController. The TestRequest has following methods.
flush() : Handles the request by returning HTTP body and headers.
error() : Returns error for the request.
event() : Deliver an arbitrary
HttpEvent.
The
TestRequest has also request property of HttpRequest type using which we can get request information, such as HTTP method name.
8. Example: Testing HttpClient.get
In our unit test case, we will test a service class which will contain a method for HTTP GET usingHttpClient.get method. Find the service class.
employee.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { HttpErrorResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
import { map, catchError, tap } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { Employee } from './employee';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class EmployeeService {
empUrl = "/api/employees";
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
getAllEmployees(): Observable<Employee[]> {
return this.http.get<Employee[]>(this.empUrl).pipe(
tap(employees => console.log("employees: " + JSON.stringify(employees))),
catchError(this.handleError<Employee[]>([]))
);
}
private handleError<T>(result = {} as T) {
return (error: HttpErrorResponse): Observable<T> => {
console.error(error);
return of(result);
};
}
}
export interface Employee {
id: number;
name: string;
}
getAllEmployees() method of EmployeeService class. Find the unit test cases.
Test case 1: Should return expected employees by calling once.
Test case 2: should be OK returning no employee.
Test case 3: should turn 404 error into an empty employee result.
Test case 4: should return expected employees when called multiple times.
Find the spec file.
employee.service.spec.ts
import { HttpClientTestingModule, HttpTestingController } from '@angular/common/http/testing';
import { TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { HttpClient, HttpResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Employee } from './employee';
import { EmployeeService } from './employee.service';
//Testing of EmployeeService
describe('EmployeeService', () => {
let httpClient: HttpClient;
let httpTestingController: HttpTestingController;
let empService: EmployeeService;
beforeEach(() => {
//Configures testing app module
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [HttpClientTestingModule],
providers: [
EmployeeService
]
});
//Instantiates HttpClient, HttpTestingController and EmployeeService
httpClient = TestBed.inject(HttpClient);
httpTestingController = TestBed.inject(HttpTestingController);
empService = TestBed.inject(EmployeeService);
});
afterEach(() => {
httpTestingController.verify(); //Verifies that no requests are outstanding.
});
describe('#getAllEmployees', () => {
let expectedEmps: Employee[];
beforeEach(() => {
//Dummy data to be returned by request.
expectedEmps = [
{ id: 101, name: 'Krishna' },
{ id: 102, name: 'Arjun' },
] as Employee[];
});
//Test case 1
it('should return expected employees by calling once', () => {
empService.getAllEmployees().subscribe(
emps => expect(emps).toEqual(expectedEmps, 'should return expected employees'),
fail
);
const req = httpTestingController.expectOne(empService.empUrl);
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('GET');
req.flush(expectedEmps); //Return expectedEmps
});
//Test case 2
it('should be OK returning no employee', () => {
empService.getAllEmployees().subscribe(
emps => expect(emps.length).toEqual(0, 'should have empty employee array'),
fail
);
const req = httpTestingController.expectOne(empService.empUrl);
req.flush([]); //Return empty data
});
//Test case 3
it('should turn 404 error into an empty employee result', () => {
empService.getAllEmployees().subscribe(
emps => expect(emps.length).toEqual(0, 'should return empty employee array'),
fail
);
const req = httpTestingController.expectOne(empService.empUrl);
const msg = '404 error';
req.flush(msg, { status: 404, statusText: 'Not Found' }); //Return error
});
//Test case 4
it('should return expected employees when called multiple times', () => {
empService.getAllEmployees().subscribe();
empService.getAllEmployees().subscribe(
emps => expect(emps).toEqual(expectedEmps, 'should return expected employees'),
fail
);
const requests = httpTestingController.match(empService.empUrl);
expect(requests.length).toEqual(2, 'calls to getAllEmployees()');
requests[0].flush([]); //Return Empty body for first call
requests[1].flush(expectedEmps); //Return expectedEmps in second call
});
});
});
getAllEmployees(), the mock HttpClient will return data assigned to flush() method as below.
req.flush(expectedEmps);
fail is executed. It throws error with error messages.
3. The
expect() creates an expectation. For example.
expect(emps).toEqual(expectedEmps, 'should return expected employees')
emps should be equal to expectedEmps. If not, then test is fail and the fail method will execute.
9. Run Test Cases
To run the test cases, find the steps.1. Install Angular CLI using link.
2. Download source code using download link given below on this page.
3. Use downloaded src in your Angular CLI application.
4. Run ng test using command prompt. Test result can be seen on command prompt as well as on browser.
5. Find the test output in command prompt.
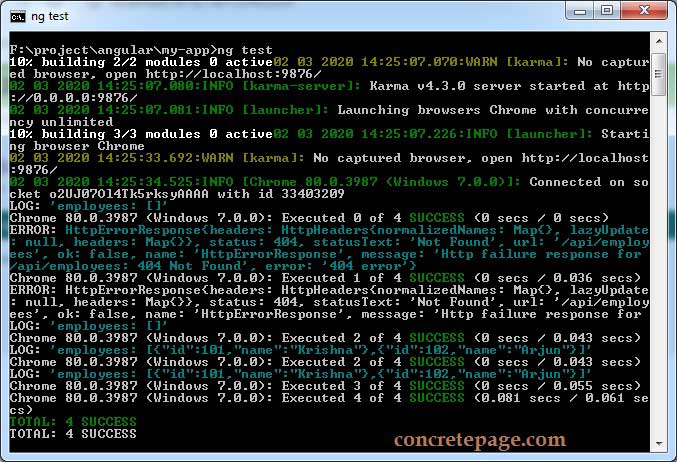
Find the test result in the browser.
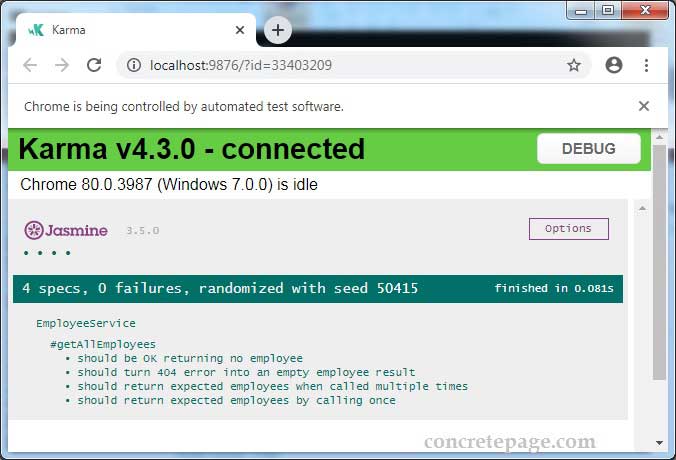
10. References
Angular TestingAngular HttpClient
JASMINE Test


