Angular Test Button Click
August 01, 2020
This page will walk through Angular unit test example for button click. For click event we can use triggerEventHandler method of Angular DebugElement class. We can also call native JavaScript click method of button. On click of button, we call a component method and it is possible that our component method has other dependencies to execute. So to test that method, we should use Jasmine spyOn to create a stub for the component method. To create asynchronous test function, we can use Angular async or fakeAsync method.
Now let us discuss the Angular test button click step-by-step with complete example.
Contents
- 1. Technologies Used
- 2. DebugElement.triggerEventHandler()
- 3. Button Click Test for Property Binding
- 4. Jasmine spyOn()
- 5. Button Click Test to Call Function using
async - 6. Button Click Test to Call Function using
fakeAsync - 7. Complete Test Example
- 8. Run Test Cases
- 9. References
- 10. Download Source Code
1. Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Angular 10.0.0
2. Node.js 12.5.0
3. Jasmine Core 3.5.0
4. Karma 5.0.9
2. DebugElement.triggerEventHandler()
ThetriggerEventHandler can raise any data-bound event by its event name. Find the method syntax from Angular doc.
triggerEventHandler(eventName: string, eventObj: any): void
Find the sample code.
const buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.send-button'));
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
3. Button Click Test for Property Binding
For button click test we have created a component that have three button.person.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-person',
template: `
<button (click)="setName()" class="set-button">Set</button>
<p>{{personName}}</p>
<button (click)="sendData()" class="send-button">Send</button>
<button (click)="editPerson(101)" class="edit-button">Edit</button>
`
})
export class PersonComponent {
personName: string;
setName() {
this.personName = 'Mahesh';
}
sendData() {
console.log('---sendData---');
//Call Service to send data over HTTP
}
editPerson(id: number) {
console.log('---editPerson---', id);
//Call Service to send data over HTTP
}
}
1. On click of Set button, we are calling a function that sets a value to a component property. We will test that button is clicked and value is set to property and bound to HTML.
2. On click of Send button, we are calling a function. We will test that function is called.
3. On click of Edit button, we are calling a function with arguments. We will test that function is called.
Here we will create unit test for case 1 i.e. on click of Set button, we are calling a function that sets a value to a component property.
person.component.spec.ts
import { ComponentFixture, TestBed, async } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { By } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { PersonComponent } from './person.component';
describe('PersonComponent', () => {
let component: PersonComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture<PersonComponent>;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [PersonComponent]
});
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(PersonComponent);
component = fixture.componentInstance;
});
it('should click Set button', async(() => {
fixture.detectChanges();
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.set-button'));
let p = fixture.debugElement.nativeElement.querySelector('p');
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
fixture.detectChanges();
fixture.whenStable().then(() => {
expect(component.personName).toBe('Mahesh');
expect(p.textContent).toBe('Mahesh');
});
}));
});
async is the Angular testing API to create asynchronous test function which will automatically complete when all asynchronous calls within this test function are done.
whenStable: The
whenStable is the method of ComponentFixture. The whenStable gives Promise that resolves when the fixture is stable.
detectChanges: The
detectChanges triggers a change detection cycle for the component.
In the above code to trigger click event, we can also call native element click method with following code changes.
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.nativeElement.querySelector('.set-button');
buttonElement.click();
it('should click Set button', async(() => {
fixture.detectChanges();
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.nativeElement.querySelector('.set-button');
let p = fixture.debugElement.nativeElement.querySelector('p');
buttonElement.click();
fixture.detectChanges();
fixture.whenStable().then(() => {
expect(component.personName).toBe('Mahesh');
expect(p.textContent).toBe('Mahesh');
});
}));
4. Jasmine spyOn()
ThespyOn is a Jasmine API that spies the given function of given object. The spyOn accepts two parameters as following.
spyOn(someObj, 'functionName');
someObj.functionName();
functionName() will not run in real means. Using spyOn for the functions are useful where our functions have dependencies to execute, such as calling HTTP request. We can bypass these dependencies and test our method to be called.
If we want to pass some arguments and return value we can do as following.
spyOn(someObj, 'functionName').withArgs(10, 20, 30).and.returnValue(50); someObj.functionName(10, 20, 30); // returns 50
spyOn as following.
spyOn(someObj, 'functionName').and.callFake(function(){
console.log('functionName called.');
return 'result';
});
5. Button Click Test to Call Function using async
Here we will write a test case for Send button on click of which the sendData() method of component will be called. We will use spyOn for sendData() method so that it should not be called in real but as a stub. Jasmine handles spying on the method and later by calling toHaveBeenCalled() we test if it is called or not on button click. The toHaveBeenCalled() can only be called on spy object. Here we use async and whenStable() function.
it('should click Send button with async', async(() => {
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.send-button'));
spyOn(component, 'sendData');
//Trigger click event after spyOn
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
fixture.whenStable().then(() => {
expect(component.sendData).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
}));
6. Button Click Test to Call Function using fakeAsync
The fakeAsync is the Angular testing API that wraps a test function in a fake asynchronous test zone. The tick() simulates the asynchronous passage of time.
Find the button click test code to call a component method.
it('should click Send button with fakeAsync', fakeAsync(() => {
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.send-button'));
spyOn(component, 'sendData');
//Trigger click event after spyOn
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
tick();
expect(component.sendData).toHaveBeenCalled();
}));
Now we will test Edit button of our component. On click of Edit button, we are calling a function with arguments. We will test that function is called.
it('should click Edit button', fakeAsync(() => {
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.edit-button'));
spyOn(component, 'editPerson');
//Trigger click event after spyOn
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
tick();
expect(component.editPerson).toHaveBeenCalled();
}));
7. Complete Test Example
Find the complete code of our unit test in our demo application.person.component.spec.ts
import { ComponentFixture, TestBed, async, fakeAsync, tick } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { By } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { PersonComponent } from './person.component';
describe('PersonComponent', () => {
let component: PersonComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture<PersonComponent>;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [PersonComponent]
});
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(PersonComponent);
component = fixture.componentInstance;
});
it('should click Set button', async(() => {
fixture.detectChanges();
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.set-button'));
let p = fixture.debugElement.nativeElement.querySelector('p');
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
fixture.detectChanges();
fixture.whenStable().then(() => {
expect(component.personName).toBe('Mahesh');
expect(p.textContent).toBe('Mahesh');
});
}));
it('should click Send button with async', async(() => {
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.send-button'));
spyOn(component, 'sendData');
//Trigger click event after spyOn
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
fixture.whenStable().then(() => {
expect(component.sendData).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
}));
it('should click Send button with fakeAsync', fakeAsync(() => {
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.send-button'));
spyOn(component, 'sendData');
//Trigger click event after spyOn
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
tick();
expect(component.sendData).toHaveBeenCalled();
}));
it('should click Edit button', fakeAsync(() => {
let buttonElement = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.edit-button'));
spyOn(component, 'editPerson');
//Trigger click event after spyOn
buttonElement.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
tick();
expect(component.editPerson).toHaveBeenCalled();
}));
});
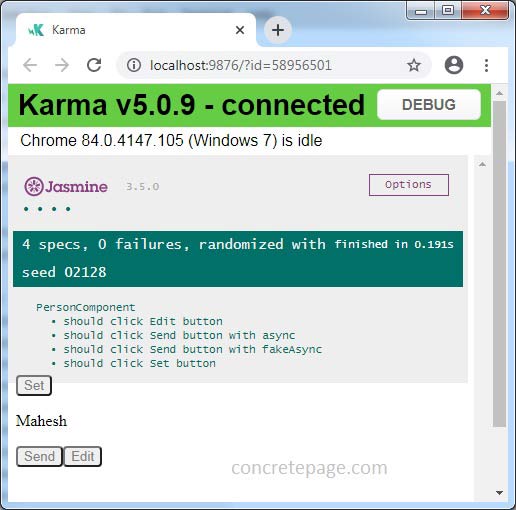
8. Run Test Cases
To run the test cases, find the steps.1. Install Angular CLI using link.
2. Download source code using download link given below on this page.
3. Use downloaded src in your Angular CLI application.
4. Run ng test using command prompt. Test result can be seen on command prompt as well as on browser.
5. A chrome for test result will open automatically or we can also use the URL http://localhost:9876/
Find the test result print screen.
9. References
Basics of testing componentsComponentFixture
Jasmine Spy


