Angular Reactive Forms
July 09, 2019
Angular reactive form is a model-driven form that handles form inputs whose values change over time. Each change to the form state returns new state that maintains the integrity of model between changes. There are two types of Angular form i.e. reactive form and template-driven form. Reactive forms are more scalable, reusable and testable than template-driven form. If forms are playing major role in our application, we should use reactive form. Template-driven form can be used for basic form requirements such as login form. Reactive forms are created in component class whereas template-driven form is created using directive. Reactive forms can be validated using functions whereas template-driven forms are validated using directives. Reactive forms are immutable whereas template-driven forms are mutable. Reactive forms are more predictable with synchronous access whereas the predictability of template-driven form is lesser and asynchronous. To create a reactive form, Angular provides classes such as FormControl, FormGroup, FormArray and FormBuilder etc.
Here on this page we will create a reactive form with validations. Find the complete example step-by-step.
Contents
Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Angular 8.0.3
2. TypeScript 3.4.3
3. Node.js 12.5.0
4. Angular CLI 8.0.6
1. Import ReactiveFormsModule
ReactiveFormsModule provides the required classes and directive to create reactive form.
import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
@NgModule({
imports: [
------
ReactiveFormsModule
],
------
})
export class AppModule { }
2. Create Reactive Form
Find some Angular classes that are used in creating reactive form.FormControl: Tracks the value and validation state of a form control.
FormGroup: Tracks the value and validity state of a group of
FormControl.
FormArray: Tracks the value and validity state of array of
FormControl, FormGroup and FormArray.
FormBuilder: Creates a big reactive form with minimum code in Angular.
FormBuilder has methods as group(), control() and array() that returns FormGroup, FormControl and FormArray respectively.
Let us understand how to use them.
2.1 FormControl
FormControl tracks the value and validation state of a form control. For every form control such as text, checkbox, radio button we need to create an instance of FormControl in our class.
city = new FormControl();
<input [formControl]="city">
[formControl] is FormControlDirective.
To set a default value to our form control, we can pass a default value while instantiating a
FormControl in our class.
city = new FormControl('Noida');
married = new FormControl(true);
value property on the instance of FormControl in our class.
console.log(this.city.value);
FormControl instance will be updated with new value.
Now to set a value to a form control at run time, we need to call setValue() method on the instance of FormControl in our class.
setCityValue() {
this.city.setValue('Varanasi');
}
2.2 FormGroup
FormGroup tracks the value and validity state of a group of FormControl. To use it, create an instance of FormGroup with the instances of FormControl.
userForm = new FormGroup({
name: new FormControl(),
age: new FormControl('20')
});
age form control will be pre-populated with the value 20.
Now we create a
<form> element in our HTML template. The selector of FormGroupDirective is [formGroup]. We will bind FormGroup instance userForm with the selector [formGroup] and FormControl instances are bound to form control using FormControlName directive i.e. formControlName. Find the HTML code.
<form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()"> Name: <input formControlName="name" placeholder="Enter Name"> Age: <input formControlName="age" placeholder="Enter Age"> <button type="submit">Submit</button> </form>
ngSubmit will call our method onFormSubmit. Now create a method that will be called when form is submitted.
onFormSubmit() {
console.log('Name:' + this.userForm.get('name').value);
}
FormGroup provides setValue() and patchValue() and both are used to set values to FormGroup instance at run time. The difference between them is that when we use setValue(), we have to set all form controls in our FormGroup and when we use patchValue() then selected form control can be set. Find the example.
1. Using
setValue()
this.userForm.setValue({name: 'Mahesh', age: '20' });
setValue() otherwise it will throw error.
2. Using
patchValue()
this.userForm.patchValue({name: 'Mahesh'});
patchValue() then it is not necessary to mention all form controls.
Now to get the value of form control named as
name after form submit, we need to write the code as below.
this.userForm.get('name').value
this.userForm.value
reset() method on FormGroup instance.
resetForm() {
this.userForm.reset();
}
2.3 FormArray
FormArray tracks the value and validity state of array of FormControl, FormGroup and FormArray.
The FormArray is used to add and remove form elements at runtime. We can use a FormArray inside a FormGroup as given below.
userForm = new FormGroup({
name: new FormControl(),
users: new FormArray([
new FormControl('Mahesh'),
new FormControl()
])
});
<form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()"> <div> Name: <input formControlName="name" placeholder="Enter Name"> </div> <div formArrayName="users"> <div *ngFor="let user of users.controls; index as i"> <input [formControlName]="i" placeholder="Enter User Name"> <button type="button" (click)="deleteUserField(idx)">Delete</button> </div> </div> <button type="button" (click)="addUserField()">Add More User</button> <button type="submit">Submit</button> </form>
FormArrayName is a directive that syncs a nested FormArray to a DOM element. To add form controls in FormArray at runtime, the instance of FormArray will call push() method that accepts new instance of FormControl and to remove form control we use removeAt() method that accepts index of form control to be removed. Find the code for add and remove methods.
addUserField() {
this.users.push(new FormControl());
}
deleteUserField(index: number) {
this.users.removeAt(index);
}
FormArray as given below.
for(let i = 0; i < this.users.length; i++) {
console.log(this.users.at(i).value);
}
FormArray, we can write code as given below.
this.userForm.value this.userForm.valid
2.4 FormBuilder
FormBuilder creates reactive form with minimum code using FormGroup, FormControl and FormArray. The FormBuilder has following methods.
group(): Creates
FormGroup.
control(): Creates
FormControl.
array(): Creates
FormArray.
Find the sample example to create a form with
FormBuilder using its group() method.
userForm: FormGroup;
constructor(private formBuilder: FormBuilder) { }
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
userName: '',
age: '',
isMarried: false
});
<form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()"> <div> <input formControlName="userName"> </div> <div> <input formControlName="age" type="number"> </div> <div> <input type="checkbox" formControlName="isMarried"> </div> <div> <button>Submit</button> </div> </form>
3. Create Reactive Form with Validations
The constructor ofFormControl accepts initial control state, sync validators and async validators. A FormControl can be instantiated as following.
new FormControl(state, validator?, asyncValidator?)
FormBuilder.
userForm: FormGroup;
constructor(private formBuilder: FormBuilder) { }
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
userName: ['', [Validators.required, Validators.maxLength(15)]],
age: ['', [Validators.required, Validators.min(18)]],
profile: [null, [Validators.required]],
technologies: [null, [Validators.required]],
teamMates: this.formBuilder.array([new FormControl()]),
gender: ['', Validators.required],
isMarried: false,
tc: ['', Validators.requiredTrue]
});
<form> tag and bind our FormGroup instance i.e. userForm using FormGroupDirective with selector formGroup as following.
<form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()"> ------ </form>
3.1 Text Box
In our reactive form, we have two text boxes i.e.userName and age. The form control userName will be validated for required and maxLength. The form control age will be validated for required and min value.
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
userName: ['', [Validators.required, Validators.maxLength(15)]],
age: ['', [Validators.required, Validators.min(18)]],
------
});
userName and age using formControlName directive.
<input formControlName="userName"> <div *ngIf="userName.errors" class="error"> <div *ngIf="userName.errors.required"> Username required. </div> <div *ngIf="userName.errors.maxlength"> Username can be max 15 characters long. </div> </div> <input formControlName="age" type="number"> <div *ngIf="age.errors" class="error"> <div *ngIf="age.errors.required"> Age required. </div> <div *ngIf="age.errors.min"> Minimum age is 18. </div> </div>
userName and age form control in HTML template, we need to create their setter methods in component class.
get userName() {
return this.userForm.get('userName');
}
get age() {
return this.userForm.get('age');
}
userName.errors.required, userName.errors.maxlength for userName form control to display error messages. In the same way, validation errors of age form control can be fetched as age.errors.required and age.errors.min.
3.2 Select Option
Here we will create select option and multiple select option form control in our reactive form.profile is for single select option and technologies is for multiple select option.
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
profile: [null, [Validators.required]],
technologies: [null, [Validators.required]],
------
});
profile and technologies using formControlName directive.
<select formControlName="profile" (change)="onProfileChange()">
<option [ngValue]="null" disabled>Choose your profile</option>
<option *ngFor="let prf of allProfiles" [ngValue]="prf">
{{ prf.prName }}
</option>
</select>
<div *ngIf="profile.errors" class="error">
<div *ngIf="profile.errors.required">
Profile required.
</div>
</div>
<select multiple formControlName="technologies" [compareWith]="compareTech">
<option *ngFor="let tech of allTechnologies" [ngValue]="tech">
{{ tech.techName }}
</option>
</select>
<div *ngIf="technologies.errors" class="error">
<div *ngIf="technologies.errors.required">
Technologies required.
</div>
</div>
profile and technologies form control in HTML template, we need to create their setter methods in component class.
get profile() {
return this.userForm.get('profile');
}
get technologies() {
return this.userForm.get('technologies');
}
profile.errors.required and technologies.errors.required to display error messages.
3.3 Radio Button
Here we will create radio buttons form control in our reactive form withrequired validation.
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
gender: ['', Validators.required],
------
});
gender using formControlName directive.
<input type="radio" value="male" formControlName="gender"> Male <input type="radio" value="female" formControlName="gender"> Female <div *ngIf="gender.errors" class="error"> <div *ngIf="gender.errors.required"> Gender required. </div> </div>
gender form control in HTML template, we need to create its setter method in component class.
get gender() {
return this.userForm.get('gender');
}
gender.errors.required to display error message.
3.4 Checkbox
Here we will create checkbox form control in our reactive form withrequiredTrue validation.
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
tc: ['', Validators.requiredTrue],
------
});
tc using formControlName directive.
<input type="checkbox" formControlName="tc"> <div *ngIf="tc.invalid" class="error"> Accept T & C. </div>
tc form control in HTML template, we need to create its setter method in component class.
get tc() {
return this.userForm.get('tc');
}
tc.invalid to display error message.
4. Reactive Form: Submit and Get Value
To submit the form we need to specify a method name usingngSubmit which will be executed after form submit.
<form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()"> ------ </form>
userName. Our FormGroup instance is userForm. Now fetch value as following.
onFormSubmit() {
console.log(this.userForm.get('userName').value);
}
userName, age, profile, technologies, teamMates, gender, isMarried and tc. Now find the class with same fields names.
user.ts
export class User {
userName: string;
age: number;
teamMates: string[];
gender: string;
isMarried: boolean;
tc: boolean;
profile: Profile = null;
technologies: Technology[];
}
FormGroup instance as following.
onFormSubmit() {
let newUser: User = this.userForm.value;
console.log("User Name: " + user.userName);
}
5. Reactive Form: Set and Patch Value
TheFormGroup methods setValue and patchValue both sets the value in form controls of FormGroup. The setValue sets the value in each and every form control of FormGroup. We cannot omit any form control in setValue but when we want to assign only few form controls of FormGroup then we need to use patchValue. We can pass the object of the class which has same field names as form controls of our FormGroup. Find the sample example of patchValue.
setDefaultValues() {
let user = new User();
user.userName = "Narendra Modi";
user.age = 20;
user.gender = 'male';
this.userForm.patchValue(user);
}
setValue.
this.userForm.setValue(user);
6. Reactive Form Reset
To reset reactive form,FormGroup provides reset() method. We can call reset() method on the instance of FormGroup. Suppose we have following form with a button that will call a component method.
<form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()"> ------ <button type="button" (click)="resetForm(userForm)">Reset</button> </form>
reset() method on the instance of FormGroup.
resetForm(form: FormGroup) {
form.reset();
}
<button type="reset">Reset</button>
7. Complete Example
Find the project structure of our demo application.angular-demo | |--src | | | |--app | | | | | |--domain | | | | | | | |--profile.ts | | | |--technology.ts | | | |--user.ts | | | | | |--services | | | | | | | |--user-service.ts | | | | | |--user-component | | | | | | | |--user.component.ts | | | |--user.component.html | | | |--user.component.css | | | | | |--app.component.ts | | |--app.module.ts | | | |--main.ts | |--index.html | |--styles.css | |--node_modules |--package.json
profile.ts
export class Profile {
constructor(public prId:string, public prName:string) {
}
}
export class Technology {
constructor(public techId:number, public techName:string) {
}
}
import { Profile } from './profile';
import { Technology } from './technology';
export class User {
userName: string;
age: number;
teamMates: string[];
gender: string;
isMarried: boolean;
tc: boolean;
profile: Profile = null;
technologies: Technology[];
}
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Profile } from '../domain/profile';
import { Technology } from '../domain/technology';
import { User } from '../domain/user';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class UserService {
getPofiles(): Profile[] {
let profiles = [
new Profile('dev', 'Developer'),
new Profile('man', 'Manager'),
new Profile('dir', 'Director')
]
return profiles;
}
getTechnologies(): Technology[] {
let technologies = [
new Technology(100, 'Java'),
new Technology(101, 'Angular'),
new Technology(102, 'Hibernate'),
new Technology(103, 'Spring')
]
return technologies;
}
createUser(user: User) {
//Log user data in console
console.log("User Name: " + user.userName);
console.log("User age: " + user.age);
console.log("Profile Id: " + user.profile.prId);
console.log("Profile Name: " + user.profile.prName);
for (let i = 0; i < user.technologies.length; i++) {
console.log("Technology Id: " + user.technologies[i].techId);
console.log("Technology Name: " + user.technologies[i].techName);
}
user.teamMates.forEach(element => console.log("Teammate: " + element));
console.log("Gender: " + user.gender);
console.log("Married: " + user.isMarried);
console.log("T & C Accepted: " + user.tc);
}
}
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormBuilder, FormControl, FormArray, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
import { UserService } from '../services/user-service';
import { Profile } from '../domain/Profile';
import { Technology } from '../domain/technology';
import { User } from '../domain/user';
@Component({
selector: 'app-template',
templateUrl: './user.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./user.component.css']
})
export class UserComponent implements OnInit {
isValidFormSubmitted = null;
allProfiles: Profile[];
allTechnologies: Technology[];
userForm: FormGroup;
constructor(private formBuilder: FormBuilder, private userService: UserService) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.userForm = this.formBuilder.group({
userName: ['', [Validators.required, Validators.maxLength(15)]],
age: ['', [Validators.required, Validators.min(18)]],
profile: [null, [Validators.required]],
technologies: [null, [Validators.required]],
teamMates: this.formBuilder.array([new FormControl()]),
gender: ['', Validators.required],
isMarried: false,
tc: ['', Validators.requiredTrue]
});
this.allProfiles = this.userService.getPofiles();
this.allTechnologies = this.userService.getTechnologies();
}
get userName() {
return this.userForm.get('userName');
}
get age() {
return this.userForm.get('age');
}
get profile() {
return this.userForm.get('profile');
}
get technologies() {
return this.userForm.get('technologies');
}
get teamMates(): FormArray {
return this.userForm.get('teamMates') as FormArray;
}
get gender() {
return this.userForm.get('gender');
}
get tc() {
return this.userForm.get('tc');
}
onFormSubmit() {
this.isValidFormSubmitted = false;
if (this.userForm.invalid) {
return;
}
this.isValidFormSubmitted = true;
let newUser: User = this.userForm.value;
this.userService.createUser(newUser);
this.resetForm(this.userForm);
}
resetForm(form: FormGroup) {
form.reset();
}
setDefaultValues() {
let user = new User();
user.userName = "Narendra Modi";
user.age = 20;
user.gender = 'male';
user.profile = this.allProfiles[2];
user.technologies = [
this.allTechnologies[1],
this.allTechnologies[3]
];
this.userForm.patchValue(user);
}
onProfileChange() {
let profile: Profile = this.profile.value;
console.log('Profile Changed: ' + profile.prName);
}
compareTech(t1: Technology, t2: Technology): boolean {
//console.log(t1.techId + '-' + t2.techId);
return t1 && t2 ? t1.techId === t2.techId : t1 === t2;
}
addUserField() {
this.teamMates.push(new FormControl());
}
deleteUserField(index: number) {
this.teamMates.removeAt(index);
}
}
<h3>User Information</h3>
<p *ngIf="isValidFormSubmitted" class="success">
Form submitted successfully.
</p>
<form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onFormSubmit()">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Name:</td>
<td>
<input formControlName="userName">
<div *ngIf="userName.errors && isValidFormSubmitted != null && !isValidFormSubmitted" class="error">
<div *ngIf="userName.errors.required">
Username required.
</div>
<div *ngIf="userName.errors.maxlength">
Username can be max 15 characters long.
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Age:</td>
<td>
<input formControlName="age" type="number">
<div *ngIf="age.errors && isValidFormSubmitted != null && !isValidFormSubmitted" class="error">
<div *ngIf="age.errors.required">
Age required.
</div>
<div *ngIf="age.errors.min">
Minimum age is 18.
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Select Profile: </td>
<td>
<select formControlName="profile" (change)="onProfileChange()">
<option [ngValue]="null" disabled>Choose your profile</option>
<option *ngFor="let prf of allProfiles" [ngValue]="prf">
{{ prf.prName }}
</option>
</select>
<div *ngIf="profile.errors && isValidFormSubmitted != null && !isValidFormSubmitted" class="error">
<div *ngIf="profile.errors.required">
Profile required.
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Select Technologies: </td>
<td>
<select multiple formControlName="technologies" [compareWith]="compareTech">
<option *ngFor="let tech of allTechnologies" [ngValue]="tech">
{{ tech.techName }}
</option>
</select>
<div *ngIf="technologies.errors && isValidFormSubmitted != null && !isValidFormSubmitted" class="error">
<div *ngIf="technologies.errors.required">
Technologies required.
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Enter Teammates: </td>
<td>
<div formArrayName="teamMates">
<div *ngFor="let teamMate of teamMates.controls; index as i">
<input [formControlName]="i" placeholder="Enter teammate name">
<button type="button" (click)="deleteUserField(i)">Delete</button>
</div>
</div>
<button type="button" (click)="addUserField()">Add More</button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Gender:</td>
<td>
<input type="radio" value="male" formControlName="gender"> Male
<input type="radio" value="female" formControlName="gender"> Female
<div *ngIf="gender.errors && isValidFormSubmitted != null && !isValidFormSubmitted" class="error">
<div *ngIf="gender.errors.required">
Gender required.
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Are you married? </td>
<td>
<input type="checkbox" formControlName="isMarried">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Accept T & C </td>
<td>
<input type="checkbox" formControlName="tc">
<div *ngIf="tc.invalid && isValidFormSubmitted != null && !isValidFormSubmitted" class="error">
Accept T & C.
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<button>Submit</button>
<button type="button" (click)="setDefaultValues()">Set Default</button>
<button type="button" (click)="resetForm(userForm)">Reset</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
.error {
color: red;
}
.success {
color: green;
}
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<app-template></app-template>
`
})
export class AppComponent {
}
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { UserComponent } from './user-component/user.component';
import { UserService } from './services/user-service';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
ReactiveFormsModule
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
UserComponent
],
providers: [
],
bootstrap: [
AppComponent
]
})
export class AppModule { }
8. Run Application
To run the application, find the steps.1. Download source code using download link given below on this page.
2. Use downloaded src in your Angular CLI application. To install Angular CLI, find the link.
3. Run ng serve using command prompt.
4. Access the URL http://localhost:4200
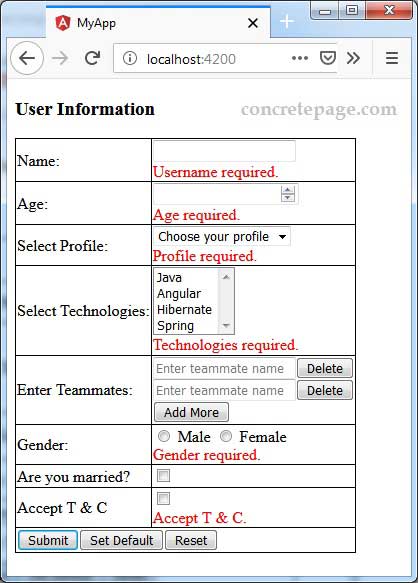
Find the print screen.
References
Reactive FormsAngular FormControl Example
Angular FormGroup Example
Angular FormBuilder Example
Angular Select Option using Reactive Form


