Angular Caching Http Interceptor
January 24, 2024
On this page, I will create a caching interceptor using HttpInterceptor interface in our Angular standalone application.
1. Angular provides
HttpInterceptor interface with intercept() method that is used to intercept HttpRequest and handle them.
2. To create an Interceptor, we need to create a service by implementing
HttpInterceptor interface and override its intercept() method.3. There can be more than one interceptor in our applications and these interceptors run in the given order.
4. Interceptors transform the outgoing request before passing it to the next interceptor in the chain. Interceptor passes the request to the next Interceptor by calling
handle() method of HttpHandler.
Here on this page I will create Http Interceptor to cache the response. The cache Interceptor first checks if the request is already cached or not. If request is not cached then response is generated by running the request URL. If request is cached then we fetch cached response and if it is null then we run the request URL to generate the response and it is also added to cache. We will expire the cache after fixed time. To store the cache I will use
Map in our example. Now find the complete example step-by-step.
Step-1: Create Cache Service
We will create a cache service to get and put response into cache. For caching a response we are usingMap. First of all we will create an abstract class to define caching operation.
cache.ts
import { HttpRequest, HttpResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
export abstract class Cache {
abstract get(req: HttpRequest<any>): HttpResponse<any> | null;
abstract put(req: HttpRequest<any>, res: HttpResponse<any>): void;
}
get() method to fetch response from cache and put() method to put response into cache.
In our example, a cache entry will have following properties.
cache-entry.ts
import { HttpResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
export interface CacheEntry {
url: string;
response: HttpResponse<any>
entryTime: number;
}
export const MAX_CACHE_AGE = 20000; // in milliseconds
response: Response to be cached as
HttpResponse.
entryTime: Time when response is cached. It will help to find out expired cache.
MAX_CACHE_AGE decides the age of cache. After this time, cache will be considered as expired.
Now we will create our service to get and put cache using
Map.
cache-map.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpRequest, HttpResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Cache } from './cache';
import { CacheEntry, MAX_CACHE_AGE } from './cache-entry';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class CacheMapService implements Cache {
cacheMap = new Map<string, CacheEntry>();
get(req: HttpRequest<any>): HttpResponse<any> | null {
const entry = this.cacheMap.get(req.urlWithParams);
if (!entry) {
return null;
}
const isExpired = (Date.now() - entry.entryTime) > MAX_CACHE_AGE;
return isExpired ? null : entry.response;
}
put(req: HttpRequest<any>, res: HttpResponse<any>): void {
const entry: CacheEntry = { url: req.urlWithParams, response: res, entryTime: Date.now() };
this.cacheMap.set(req.urlWithParams, entry);
this.deleteExpiredCache();
}
private deleteExpiredCache() {
this.cacheMap.forEach(entry => {
if ((Date.now() - entry.entryTime) > MAX_CACHE_AGE) {
this.cacheMap.delete(entry.url);
}
})
}
}
1. In
get() method, we are fetching cached response from our Map for a request URL. If the result is undefined, it means there is no cached response for that URL, then we are returning null. If there is cached response for that URL, then first we check if it is expired or not. If cache is expired then we return null. If cache is not expired then return cached response.
2. In
put() method, first we are creating cache entry with request URL, response and entry time. Then we set this cache entry into the Map. We also delete all expired cache.
Step-2: Create Cache Interceptor
To create an Http interceptor we need to create a service that will implementHttpInterceptor interface and implement its intercept() method.
caching-interceptor.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpInterceptor, HttpRequest, HttpResponse, HttpHandler } from '@angular/common/http';
import { of } from 'rxjs';
import { tap } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { CacheMapService } from '../services/cache-map.service';
const CACHABLE_URL = "/api/booksSearch";
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class CachingInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor {
constructor(private cache: CacheMapService) { }
intercept(req: HttpRequest<any>, next: HttpHandler) {
if (!this.isRequestCachable(req)) {
return next.handle(req);
}
const cachedResponse = this.cache.get(req);
if (cachedResponse !== null) {
return of(cachedResponse);
}
return next.handle(req).pipe(
tap(event => {
if (event instanceof HttpResponse) {
this.cache.put(req, event);
}
})
);
}
private isRequestCachable(req: HttpRequest<any>) {
return (req.method === 'GET') && (req.url.indexOf(CACHABLE_URL) > -1);
}
}
method, urlWithParams etc.
HttpHandler: It transforms an
HttpRequest into a stream of HttpEvent. HttpHandler provides handle() method to dispatch request from first interceptor to second and so on.
HttpResponse: It is a full HTTP response. It has getter methods such as
body, headers, status, url etc.
In our cache Interceptor, we are processing following steps.
1. First we will check if request is cachable, if not then we pass request for next processing using
handle() method of HttpHandler.
2. If request is cachable, fetch it from cache and if it is not null then return the response as
Observable.
3. If cached response is null then let the request processed and then cache its response and return it.
Step-3: Configure Interceptors for Standalone Application
In our demo application, I am using Angular standalone application. Suppose we have following interceptors used in our application./app/http-interceptors/index.ts
import { HTTP_INTERCEPTORS } from '@angular/common/http';
import { LoggingInterceptor } from './logging-interceptor';
import { CachingInterceptor } from './caching-interceptor';
export const BOOK_HTTP_INTERCEPTOR_PROVIDERS = [
{ provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: LoggingInterceptor, multi: true },
{ provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: CachingInterceptor, multi: true }
];
app.config.ts
import { ApplicationConfig, importProvidersFrom } from '@angular/core';
import { provideRouter, withComponentInputBinding } from '@angular/router';
import { routes } from './app.routes';
import { provideHttpClient, withInterceptorsFromDi } from '@angular/common/http';
import { InMemoryWebApiModule } from 'angular-in-memory-web-api';
import { TestData } from './test-data';
import { CacheMapService } from './services/cache-map.service';
import { BOOK_HTTP_INTERCEPTOR_PROVIDERS } from './http-interceptors';
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [
provideHttpClient(withInterceptorsFromDi()),
BOOK_HTTP_INTERCEPTOR_PROVIDERS,
{ provide: Cache, useClass: CacheMapService },
provideRouter(routes, withComponentInputBinding()),
importProvidersFrom(InMemoryWebApiModule.forRoot(TestData))
]
};
HttpClient service to be available for injection.
withInterceptorsFromDi() : Includes class based interceptors that implements
HttpInterceptor.
src/main.ts
import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { appConfig } from './app/app.config';
import { AppComponent } from './app/app.component';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent, appConfig)
.catch((err) => console.error(err));
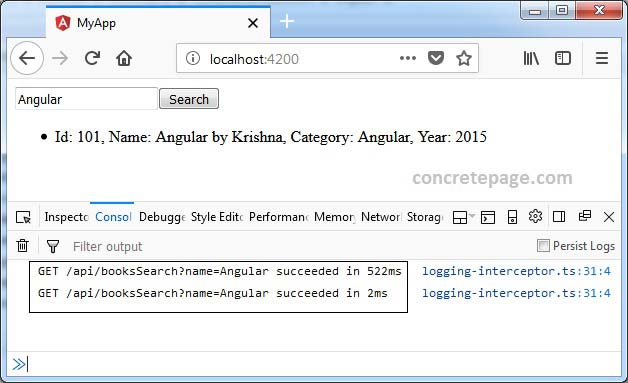
4. Output
Download source code and run the application. Search the book and look into the console log. Click the search button and wait for the output and after this, again click the search button without changing the search keyword.