Angular + Observable Example
January 26, 2024
This page will walk through how to use RxJS Observable in our Angular application. The Observable belongs to RxJS library. To perform asynchronous programming in Angular application, we can use either Observable or Promise. When we send and receive data over HTTP, we need to deal it asynchronously because fetching data over HTTP may take time. The actual HTTP request hits the server only when the Observable instance is subscribed in TypeScript class or we use async pipe in HTML template.
The
Observable is a class of RxJS library. RxJS is ReactiveX library for JavaScript that performs reactive programming. The Observable represents any set of values over any amount of time. The Observable plays most basic role in reactive programming with RxJS operators. Some operators of RxJS library are subscribe, map, mergeMap, switchMap, exhaustMap, debounceTime, of, retry, catchError, throwError etc.
To use RxJS library in Angular programming, we need to ensure that we have installed RxJS. In case we are using Angular CLI, it installs RxJS by default. We can ensure it by checking
package.json. If RxJS is not there in package.json, we can install it as following.
npm install rxjs --save
Observable in our Angular application, we need to import it as following.
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
Observable in our Angular application step-by-step with complete example.
Contents
- 1. Angular HttpClient and Observable
- 2. Observable + Async Pipe + NgFor
- 3. Observable + Async Pipe + NgIf
- 4. Subscribe to Observable
- 5. Observable.pipe()
- 6. Using map()
- 7. Using mergeMap()
- 8. Using switchMap()
- 9. Using of()
- 10. Observable Error Handling
- 11. Run Application
- 12. Reference
- 13. Download Source Code
1. Angular HttpClient and Observable
AngularHttpClient performs HTTP requests for the given URL. HttpClient works with Observable. Find some of the methods of HttpClient.
get(url: string, options: {...}): Observable<any>
post(url: string, body: any | null, options: {...}): Observable<any>
put(url: string, body: any | null, options: {...}): Observable<any>
delete(url: string, options: {...}): Observable<any>
HttpClient returns instance of Observable. When we subscribe to the Observable instance, then actual HTTP operation is performed. The Observable instances can also be executed using Async Pipe. Find the sample code to use HttpClient to perform HTTP GET operation.
getBooksFromStore(): Observable<Book[]> {
return this.http.get<Book[]>(this.bookUrl);
}
HttpClient.get returns Observable<any>. We can specify our required data type in place of any, for example we are returning here Observable<Book[]> .
2. Observable + Async Pipe + NgFor
Angularasync pipe subscribes to Observable and returns its last emitted value. Here we will provide code snippets to use Observable with async pipe using ngFor.
Step-1: We create a method to fetch data over HTTP using Angular
HttpClient in our service as following.
getBooksFromStore(): Observable<Book[]> {
return this.http.get<Book[]>(this.bookUrl);
}
Observable<Book[]>.
Step-2: In our component, we will create a property.
allBooks$: Observable<Book[]>;
Observable variable.
Now we will call the service method and assign value to the
allBooks$ property in our component.
getBooks() {
this.allBooks$ = this.bookService.getBooksFromStore();
}
ngOnInit.
ngOnInit() {
this.getBooks();
}
Observable variable i.e. allBooks$ using async pipe. We need to keep in mind that HTTP hit will take place only when we subscribe our Observable variable. In our HTML template, we subscribe our Observable variable with async pipe.
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let book of allBooks$ | async" >
Id: {{book.id}}, Name: {{book.name}}, Category: {{book.category}}
</li>
</ul>
3. Observable + Async Pipe + NgIf
Here we will provide how to useObservable using async pipe with ngIf. We will fetch data over HTTP and will display it. We will show loading image while data is being fetched over HTTP.
Step-1: We have created a method in service to fetch data over HTTP for the demo.
getFavBookFromStore(id: number): Observable<Book> {
return this.http.get<Book>(this.bookUrl + "/" + id);
}
Observable<Book>.
Step-2: In component we have created a property of
Observable type.
favBook$: Observable<Book>;
favBook$ as following.
getFavBook() {
this.favBook$ = this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(101);
}
ngOnInit for demo.
ngOnInit() {
this.getFavBook();
}
Observable variable favBook$ using async pipe.
<div *ngIf="favBook$ | async as book; else loading">
Id: {{book.id}}, Name: {{book.name}}, Category: {{book.category}}
</div>
<ng-template #loading>
<img src="assets/images/loading.gif">
</ng-template>
book array will be iterated.
4. Subscribe to Observable
subscribe() is a method of Observable class. subscribe is used to invoke Observable to execute HTTP request and to emit the result. If we have an Observable instance that fetches data over an HTTP then actual hit to server takes place only when we subscribe to Observable using subscribe method in TypeScript class or async pipe in HTML template. Here we will discuss subscribe method to subscribe to Observable.
Step-1: We have created a method in service to fetch data over HTTP.
getBooksFromStore(): Observable<Book[]> {
return this.http.get<Book[]>(this.bookUrl);
}
Observable<Book[]>.
Step-2: We will create a component property as following.
softBooks: Book[] = [];
Observable result of getBooksFromStore() as following.
getsoftBooks() {
this.bookService.getBooksFromStore().subscribe(books => this.softBooks = books);
}
ngOnInit.
ngOnInit() {
this.getsoftBooks();
}
softBooks in HTML template using ngFor.
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let book of softBooks" >
Id: {{book.id}}, Name: {{book.name}}, Category: {{book.category}}
</li>
</ul>
5. Observable.pipe()
TheObservable.pipe() pipe is used to combine RxJS operators into a chain. Find the code snippet.
getNumbers(): Observable<number> {
return of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7);
}
calculateNumbers() {
this.getNumbers().pipe(
filter(n => n % 2 === 1),
map(n => n + 10)
)
.subscribe(result => console.log(result));
}
We can see that
filter() and map() operators have been combined into a chain. First filter() operator will execute and then map() operator will execute. In this way, using pipe(), we can chain as many RxJS operators as we want.
6. Using map()
map is an operator of RxJS API. map applies a given function to the value of its source Observable and then returns result as Observable. The map is imported as following.
import { map } from 'rxjs/operators';
map in our Angular application.
getBookName() {
this.favBookName$ = this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(101).pipe(
map(book=> book.name)
);
}
getFavBookFromStore() service method is returning Observable<Book>. Using map we have converted it into Observable<string>. The component property favBookName$ will now only emit book name. getFavBookFromStore() is defined as following.
getFavBookFromStore(id: number): Observable<Book> {
return this.http.get<Book>(this.bookUrl + "/" + id);
}
favBookName$ can be displayed in HTML template as following.
<div *ngIf="favBookName$ | async as bookName">
Name: {{bookName}}
</div>
map with subscribe().
getBookName() {
this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(101).pipe(
map(book=> book.name)
).subscribe(name=> {
console.log(name);
});
}
7. Using mergeMap()
mergeMap is an operator of RxJS API. mergeMap emits Observable based on the given function. If inner functions returns Observable then final output will be the result of inner Observable emitted data. If it gets multiple request before completing one, then mergeMap maps values by combining those multiple inner Observable into one by merging their emissions. mergeMap is imported as following.
import { mergeMap } from 'rxjs/operators';
mergeMap in our Angular application.
getAllFavBooks() {
this.myAllfavBooks$ = this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(101)
.pipe(mergeMap(book => this.bookService.getBooksByCategoryFromStore(book.category)));
}
getFavBookFromStore method then by using this book's category we are fetching all books of same category using getBooksByCategoryFromStore() method. Our service methods are defined as following.
getFavBookFromStore(id: number): Observable<Book> {
return this.http.get<Book>(this.bookUrl + "/" + id);
}
getBooksByCategoryFromStore(category: string): Observable<Book[]> {
return this.http.get<Book[]>(this.bookUrl + "?category=" + category);
}
myAllfavBooks$ can be displayed in HTML template as following.
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let book of myAllfavBooks$ | async" >
Id: {{book.id}}, Name: {{book.name}}, Category: {{book.category}}
</li>
</ul>
subscribe() with mergeMap we can do it as given below.
getAllFavBooks() {
this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(101).pipe(mergeMap(book => {
let category = book.category;
return this.bookService.getBooksByCategoryFromStore(category);
})).subscribe(books => {
this.allFavBooks = books;
});
}
8. Using switchMap()
switchMap is an operator of RxJS API. switchMap returns an Observable that emits data by applying the given function. If we have provided an inner Observable to our switchMap function then the final output will be emitted data by inner Observable. If switchMap receives multiple requests to execute inner Observable before completing the existing one, then it stops the existing execution and starts executing only the latest inner Observable execution request and keeps on doing so. The use case for switchMap could be search functionality where user keeps on changing search keyword before getting result and requires only result for latest search keyword.
The
switchMap is imported in Angular application as following.
import { switchMap } from 'rxjs/operators';
switchMap.
searchSimilarBooks(id: number) {
this.similarBooks$ = this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(id).pipe(
switchMap(book => {
let category = book.category;
return this.bookService.getBooksByCategoryFromStore(category);
}),
catchError(err => of([]))
);
}
getFavBookFromStore() is returning Observable<Book> and on the basis of book category we are fetching all books of same category by using getBooksByCategoryFromStore() that returns Observable<Book[]>. Our final output is the output of inner Observable and hence the final output will be of Observable<Book[]> type. In our BookService these methods are defined as following.
getFavBookFromStore(id: number): Observable<Book> {
return this.http.get<Book>(this.bookUrl + "/" + id);
}
getBooksByCategoryFromStore(category: string): Observable<Book[]> {
return this.http.get<Book[]>(this.bookUrl + "?category=" + category);
}
switchMap with subscribe.
searchSimilarBooks(id: number) {
this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(id).pipe(
switchMap(book => {
let category = book.category;
return this.bookService.getBooksByCategoryFromStore(category);
}),
catch(err => of([]))
).subscribe(books => {
this.similarFavBooks = books;
console.log(books);
});
}
9. Using of()
Theof() is a static method of Observable. The of is used to create a Observable instance using data passed as an argument.
The
of is imported as following.
import { of } from 'rxjs';
const value as following.
const bookDetails: Book[] = [
{ id: 101, name: 'Angular by Krishna', category: 'Angular' },
{ id: 102, name: 'Core Java by Vishnu', category: 'Java' },
{ id: 103, name: 'NgRx by Rama', category: 'Angular' }
];
bookDetails into Observable by calling of(bookDetails) . We can create a method to get this result as following.
getBooksFromStore(): Observable<Book[]> {
return of(bookDetails);
}
10. Observable Error Handling
To handle error inObservable, RxJS provides throwError(), catchError() and retry() operator. The operator throwError() can throw custom error. The catchError() operator catches the error thrown by Observable and then it can either return new Observable instance or can throw custom error using throwError. The method retry just retries executing Observable for the given number of times. To handle error in subscribe method, the second argument of subscribe caches the error. Here we will describe all these error handling in detail.
10.1 Using throwError()
ThethrowError() creates an Observable that immediately emits error. It is used to conditionally throw error from map, mergeMap, switchMap etc. We can import throwError() as following.
import { throwError } from 'rxjs';
throwError in our Angular application.
return this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(101).pipe(
map(book=> {
if(book.name.length < 15) {
return book.name;
} else {
throwError('Length less than 15');
}
}));
getFavBookFromStore returns Observable<Book>.
If we want to call
throwError using Observable, we can call throwError as Observable.throwError().
10.2 Using catchError()
ThecatchError is an RxJS operator. catchError operator catches errors in the Observable to handle it by returning a new Observable or throwing an error. We can import catchError in our Angular application as following.
import { catchError } from 'rxjs/operators';
catchError.
return this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(101).pipe(
map(book=> {
if(book.name.length < 15) {
return book.name;
} else {
throw('Length less than 15');
}
}),
catchError(error => {
console.log(error);
//return of("Default Name");
throwError(error.message || error);
})
);
catchError block, we can return any new value or can throw error.
a. Returning a value: If we want to return a value, we can do it by returning any
Observable instance.
catch(error => {
console.log(error);
return of("Default Name");
});
catch(error => {
console.log(error);
throw(error.message || error);
});
10.3 Error Handling in subscribe()
In thesubscribe method of Observable, second argument is to catch error. We can catch error in subscribe method while subscribing to Observable as following.
this.bookService.getFavBookFromStore(101).pipe(
map(book=> {
if(book.name.length < 15) {
return book.name;
} else {
throwError('Length less than 15');
}
}),
catchError(error => {
console.log(error);
//return of("Default Name");
throw(error.message || error);
})
).subscribe(name=> {
this.bookName = name;
console.log(name);
},
err => {
console.log(err);
}
);
Using HttpErrorResponse with subscribe:
When we have an
Observable instance obtained from HttpClient methods, there could be scenario as following.
a. If backend returns unsuccessful response codes such as 404, 500 etc, then
HttpClient will throw error with backend response code.
b. If something goes wrong to client-side, for example, an exception is thrown by RxJS operators or if network error prevents the request from completing successfully then actual
Error object is thrown by HttpClient.
We can check if error is of
Error type by using HttpErrorResponse and accordingly log the error messages.
HttpErrorResponse can be imported from @angular/common/http library as following.
import { HttpErrorResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
this.bookService.getBooksFromStore().subscribe(books => {
this.softBooks = books
},
(err: HttpErrorResponse) => {
if (err.error instanceof Error) {
console.log('An error occurred:', err.error.message);
} else {
console.log('Backend returned status code: ', err.status);
console.log('Response body:', err.error);
}
}
);
10.4 Using retry()
Theretry() is an RxJS operator. Some errors can be handled by just retrying request such as if errors are transient and unlikely to repeat. For example if we have slow network error and our request could not get success then if request is retried, there are the chances to make request successful
We can retry request automatically by using
retry() operator. It accepts argument as number. Suppose we pass argument as retry(3) then the request will be retried for 3 times. The retry is imported from RxJS as following.
import { retry } from 'rxjs/operators';
retry() operator.
this.bookService.getBooksFromStore().pipe(
retry(3)
).subscribe(books => {
this.softBooks = books;
},
(err: HttpErrorResponse) => {
if (err.error instanceof Error) {
console.log('An error occurred:', err.error.message);
} else {
console.log('Backend returned status code: ', err.status);
console.log('Response body:', err.error);
}
}
);
11. Run Application
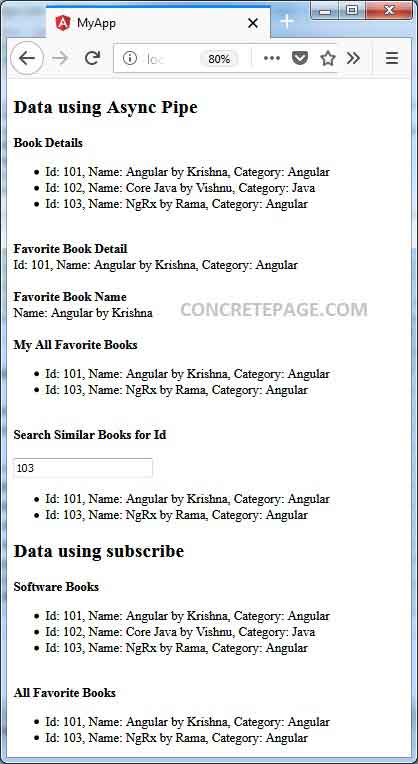
Download source code using download link given below on this page and run it. Find the print-screen of the output.