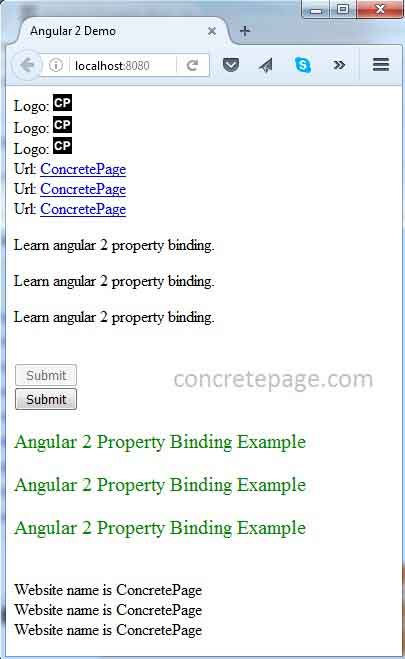
Angular Property Binding Example
February 10, 2024
On this page we will provide Angular property binding example. Property binding is a one-way data binding from data source to view target. Property binding is performed with component property, HTML element and Angular directives. Component property binding is used for communication between parent and child component because using this binding we can send property values from parent to child component. In element property binding the DOM property of HTML element can be assigned with a value of component property. In directive property binding we can assign component property values to Angular directives.
Component property binding is performed as below.
<my-msg prefixMsg= "Website name is " [siteName] = "website.name"> </my-msg>
<a [href]="website.url" [textContent]="website.name"> </a>
<p [ngClass]="'one two'"> Angular 2 Property Binding Example </p>
<script> tag then it will not allow. Angular filters the data before display. Angular calls such type of coding not only a HTML but HTML Plus because it is more powerful. Now find the complete example of Angular property binding step-by-step.
Contents
Property Binding with Diagram
Find the diagram for Angular property binding.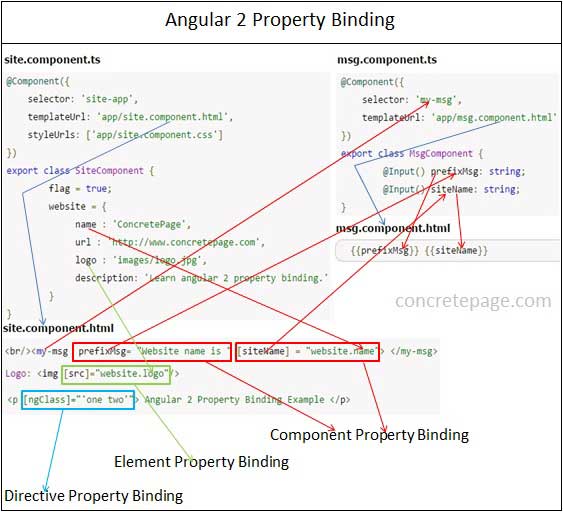
1. Angular provides three types of property binding and these are component property binding, element property binding and directive property binding.
2. Component property binding works within component element to bind parent component property into child component property. In the diagram the arrows and rectangles in red color are displaying the functionality related to component property binding.
3. Element property binding works within HTML element and it binds a component property to a DOM property. In the diagram the arrows and rectangle in green color are displaying the functionality related to element property binding.
4. Directive property binding works within HTML element with angular directives such as
NgClass and NgStyle. In directive property binding a component property or any angular expression is bound to angular directive. In the diagram the arrows and rectangles in light blue color are displaying the functionality related to directive property binding.
5. In the diagram for the component property binding we have two components.
SiteComponent is acting as parent component and MsgComponent is acting as child component. The property website.name from SiteComponent is bound to the property siteName from MsgComponent. So the values of website.name has been copied to siteName. We need to take care that the input property of child component must be decorated with @Input() decorator. The property prefixMsg of MsgComponent has been bound to a constant string using component property binding that is called one-time string initializing.
6. For element property binding demo we are using <img> element. The component property
website.logo is getting bound to DOM property src of <img> element.
7. For directive property binding we are using
NgClass. We have two CSS classes .one and .two . In <p> element we are bounding these CSS classes to NgClass directive using directive property binding.
Property Binding Types and Syntax
Property binding is performed as one-way from data source to view target. In property binding there is source and target. For the example we can define it as [href]="website.url". Here href is a target that is a property of anchor tag and source is a component property i.e website.url.Types of Property Binding
In property binding there is source and target. Property binding is performed as one-way from data source to view target. There are three types of property binding.
1. Element property
2. Directive property
3. Component property
Syntax
Property binding target will use the below syntax.
1. Bracket []
2. bind- prefix
3. Interpolation {{expression}}
We can choose any of the above syntax for property binding that fits to our readability point of view.
Create Component, HTML Template and CSS
Find the component and its HTML template that is being used in our example.site.component.ts
import {Component} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './site.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./site.component.css']
})
export class SiteComponent {
flag = true;
website = {
name : 'ConcretePage',
url : 'http://www.concretepage.com',
logo : '/assets/images/logo.jpg',
description: 'Learn angular 2 property binding.'
}
}
Logo: <img [src]="website.logo"/>
<br/>Logo: <img bind-src="website.logo"/>
<br/>Logo: <img src="{{website.logo}}"/>
<br/>Url: <a [href]="website.url" [textContent]="website.name"> </a>
<br/>Url: <a bind-href="website.url" bind-textContent="website.name"> </a>
<br/>Url: <a href="{{website.url}}" textContent="{{website.name}}"> </a>
<p [textContent]="website.description"> </p>
<p bind-textContent="website.description"> </p>
<p textContent="{{website.description}}"> </p>
<br/><button [disabled]="flag">Submit</button>
<br/><button bind-disabled="!flag">Submit</button>
<p [ngClass]="'one two'"> Angular 2 Property Binding Example </p>
<p bind-ngClass="'one two'"> Angular 2 Property Binding Example </p>
<p ngClass="{{'one two'}}"> Angular 2 Property Binding Example </p>
<br/><my-msg prefixMsg= "Website name is " [siteName] = "website.name"> </my-msg>
<br/><my-msg prefixMsg= "Website name is " bind-siteName = "website.name"> </my-msg>
<br/><my-msg prefixMsg= "Website name is " siteName = "{{website.name}}"> </my-msg>
.one {
color: green;
}
.two {
font-size: 20px;
}
Component Property Binding
We will discuss here component property binding. Using component property binding parent and child component can communicate. The parent component property as source is bound to child component property as target in component property binding. We will understand component property binding step by step.A. In parent component
site.component.ts we have a property as follows.
website = {
name : 'ConcretePage',
url : 'http://www.concretepage.com',
logo : '/assets/images/logo.jpg',
description: 'Learn angular 2 property binding.'
}
website.name property to child component.
Find the child component and its HTML template.
msg.component.ts
import {Component, Input} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'my-msg',
templateUrl: './msg.component.html'
})
export class MsgComponent {
@Input() prefixMsg: string;
@Input() siteName: string;
}
{{prefixMsg}} {{siteName}}
prefixMsg and siteName properties have been decorated with @Input decorator. @Input is responsible to decorate a component property as input property that will be bound with parent component property to accept values from parent.
C. Now for component property binding, in
site.component.html we are creating a tag with my-msg that is selector of child component. Component property binding can be performed in following ways.
1. Using bracket []
<my-msg [siteName] = "website.name"> </my-msg>
<my-msg bind-siteName = "website.name"> </my-msg>
<my-msg siteName = "{{website.name}}"> </my-msg>
D. In this way
website.name property value from site.component.ts has been copied into siteName of msg.component.ts. This is component property binding.
E. One-time string initialization
We can also perform one-time string initialization. In this type of initialization we do not use [ ], bind- or interpolation. But we need to take care that target will accept string only which is fixed and will not change. In the below code snippet
prefixMsg is being used as one-time string initialization.
<my-msg prefixMsg= "Website name is " > </my-msg> <my-msg prefixMsg= "Website name is " [siteName] = "website.name"> </my-msg>
Element Property Binding
Here we will discuss HTML element property binding.1. Using bracket [ ]
Find the property binding in HTML element <img>, <a>, <p> and <button>.
<img [src]="website.logo"/> <a [href]="website.url" [textContent]="website.name"> </a> <p [textContent]="website.description"> </p> <button [disabled]="flag">Submit</button>
website.logo. In the same way href of anchor tag has been assigned with value of website.url and textContent has been assigned with the value of website.name and same in <p> tag. In Angular framework disabled property can be assigned with true and false value which in normal HTML coding it does not work.
2. Using bind-
Find the element property using bind-. We just have to add it as prefix with element properties as follows.
<img bind-src="website.logo"/> <a bind-href="website.url" bind-textContent="website.name"> </a> <p bind-textContent="website.description"> </p> <button bind-disabled="!flag">Submit</button>
3. Using Interpolation
Now find the element property binding using interpolation.
<img src="{{website.logo}}"/>
<a href="{{website.url}}" textContent="{{website.name}}"> </a>
<p textContent="{{website.description}}"> </p>
Directive Property Binding
Property binding can also be achieved for Angular directives. In our example we are usingngClass directive. We are assigning CSS classes. For the example we have two CSS classes i.e. .one and .two.
1. Using bracket [ ]
Find the directive property binding using [ ].
<p [ngClass]="'one two'"> Angular 2 Property Binding Example </p>
2. Using bind-
Find the directive property binding using bind-.
<p bind-ngClass="'one two'"> Angular 2 Property Binding Example </p>
3. Using Interpolation
Find the directive property binding using interpolation.
<p ngClass="{{'one two'}}"> Angular 2 Property Binding Example </p>
Create Module
app.module.ts
import {NgModule} from '@angular/core';
import {BrowserModule} from '@angular/platform-browser';
import {SiteComponent} from './site.component';
import {MsgComponent} from './msg.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [BrowserModule],
declarations: [SiteComponent, MsgComponent],
bootstrap: [SiteComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }