Spring Bean Life Cycle
March 15, 2023
On this page, we will learn Spring bean life cycle with examples.
1. Spring bean life cycle involves initialization and destruction callbacks and Spring bean aware classes.
2. Initialization callback methods execute after dependency injection is completed. Their purposes are to check the values that have been set in bean properties, perform any custom initialization or provide a wrapper on original bean etc. Once the initialization callbacks are completed, bean is ready to be used.
3. When IoC container is about to remove bean, destruction callback methods execute. Their purposes are to release the resources held by bean or to perform any other finalization tasks.
4. When more than one initialization and destructions callback methods have been implemented by bean, then those methods execute in certain order.
Here on this page we will discuss spring bean life cycle step-by-step. We will discuss the order of execution of initialization and destruction callbacks as well as Spring bean aware classes.
Contents
- 1. Bean Life Cycle Diagram
- 2. Initialization Callbacks
- 3. Destruction Callbacks
- 4. Bean Life Cycle Order
- 5. BeanNameAware
- 6. BeanFactoryAware
- 7. BeanPostProcessor
- 8. @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy
- 9. InitializingBean and DisposableBean
- 10. init-method and destroy-method
- 11. Reference
- 12. Download Source Code
1. Bean Life Cycle Diagram
Find the Spring bean life cycle diagram. Here we are also showing the steps involved in Spring bean life cycle.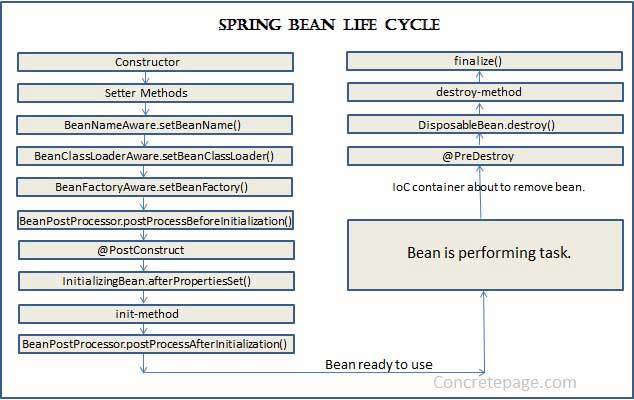
1. Within IoC container, a Spring bean is created using class constructor.
2. Now the dependency injection is performed using setter method.
3. Once the dependency injection is completed,
BeanNameAware.setBeanName() is called. It sets the name of bean in the bean factory that created this bean.
4. Now < code>BeanClassLoaderAware.setBeanClassLoader() is called that supplies the bean class loader to a bean instance.
5. Now < code>BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory() is called that provides the owning factory to a bean instance.
6. Now the IoC container calls
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization on the bean. Using this method a wrapper can be applied on original bean.
7. Now the method annotated with
@PostConstruct is called.
8. After
@PostConstruct, the method InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet() is called.
9. Now the method specified by
init-method attribute of bean in XML configuration is called.
10. And then
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization() is called. It can also be used to apply wrapper on original bean.
11. Now the bean instance is ready to be used. Perform the task using the bean.
12. Now when the
ApplicationContext shuts down such as by using registerShutdownHook() then the method annotated with @PreDestroy is called.
13. After that
DisposableBean.destroy() method is called on the bean.
14. Now the method specified by
destroy-method attribute of bean in XML configuration is called.
15. Before garbage collection,
finalize() method of Object is called.
2. Initialization Callbacks
In the bean life cycle, initialization callbacks are those methods which are called just after the properties of the bean has been set by IoC container. The SpringInitializingBean has a method as afterPropertiesSet() which performs initialization work after the bean properties has been set. Using InitializingBean is not being recommended by Spring because it couples the code. We should use @PostConstruct or method specified by bean attribute init-method in XML which is the same as initMethod attribute of @Bean annotation in JavaConfig. If all the three are used together, they will be called in below order in bean life cycle.
1. First
@PostConstruct will be called.
2. Then
InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet() is called
3. And then method specified by bean
init-method in XML or initMethod of @Bean in JavaConfig.
3. Destruction Callbacks
In bean life cycle, when a bean is destroyed from the IoC container, destruction callback is called. To get the destruction callback, bean should implement SpringDisposableBean interface and the method destroy() will be called. Spring recommends not to use DisposableBean because it couples the code. As destruction callback we should use @PreDestroy annotation or bean attribute destroy-method in XML configuration which is same as destroyMethod attribute of @Bean in JavaConfig. If we use all these callbacks together then they will execute in following order in bean life cycle.
1. First
@PreDestroy will be called.
2. After that
DisposableBean.destroy() will be called.
3. And then method specified by bean
destroy-method in XML configuration is called.
4. Bean Life Cycle Order
Here we will provide a demo in which we will use all initialization and destructions callbacks and bean aware to check their order of execution in bean life cycle. We will use XML configuration.build.gradle
dependencies {
compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:1.3.3.RELEASE'
compile 'javax.inject:javax.inject:1'
}
package com.concretepage;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Book implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean, BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, BeanClassLoaderAware {
private String bookName;
private Book() {
System.out.println("---inside constructor---");
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
System.out.println("---BeanClassLoaderAware.setBeanClassLoader---");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("---BeanNameAware.setBeanName---");
}
public void myPostConstruct() {
System.out.println("---init-method---");
}
@PostConstruct
public void springPostConstruct() {
System.out.println("---@PostConstruct---");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("---BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory---");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("---InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet---");
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
System.out.println("setBookName: Book name has set.");
}
public void myPreDestroy() {
System.out.println("---destroy-method---");
}
@PreDestroy
public void springPreDestroy() {
System.out.println("---@PreDestroy---");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("---DisposableBean.destroy---");
}
@Override
protected void finalize() {
System.out.println("---inside finalize---");
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization");
return bean;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.concretepage"/>
<bean id="book" class="com.concretepage.Book" init-method="myPostConstruct"
destroy-method="myPreDestroy">
<property name="bookName" value="Mahabharat"/>
</bean>
<bean class="com.concretepage.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
Book book = (Book)context.getBean("book");
System.out.println("Book Name:"+ book.getBookName());
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
---inside constructor--- setBookName: Book name has set. ---BeanNameAware.setBeanName--- ---BeanClassLoaderAware.setBeanClassLoader--- ---BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory--- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization ---@PostConstruct--- ---InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet--- ---init-method--- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization Book Name:Mahabharat ---@PreDestroy--- ---DisposableBean.destroy--- ---destroy-method---
5. BeanNameAware
In bean life cycle,BeanNameAware interface is aware of bean name in bean factory. This interface needs to be implemented by the bean and the method setBeanName() of BeanNameAware should be implemented. BeanNameAware.setBeanName() is called just after the dependency injection is completed. Find the sample example.
Book.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
public class Book implements BeanNameAware {
private String bookName;
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("Bean Name:" + name);
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(name = "myBook")
public Book getBean() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookName("Mahabharat");
return book;
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.register(AppConfig.class);
ctx.refresh();
Book book = ctx.getBean(Book.class);
System.out.println("Book Name:"+ book.getBookName());
ctx.close();
}
}
Bean Name:myBook Book Name:Mahabharat
6. BeanFactoryAware
In bean life cycle,BeanFactoryAware interface is implemented by beans when it wants to aware of its owning BeanFactory. We need to override setBeanFactory() method. This method is called just after the dependency injection is completed. Using this method we can change the bean properties value. Find the example.
Book.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
public class Book implements BeanFactoryAware {
private String bookName;
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
Book b = beanFactory.getBean(Book.class);
b.setBookName(getBookName()+"-Updated");
}
}
Book Name:Mahabharat-Updated
7. BeanPostProcessor
TheBeanPostProcessor interface is used for custom modification of newly created bean properties. To use BeanPostProcessor we need to create a class and override its two method postProcessBeforeInitialization() and postProcessAfterInitialization(). In bean life cycle BeanPostProcessor is called before and after initialization callbacks such as InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet(), @PostConstruct and init-method. Here in our example we will use InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet() and this will be called between postProcessBeforeInitialization() and postProcessAfterInitialization() methods of BeanPostProcessor.
MyBeanPostProcessor.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization: Bean Name- " + beanName);
if (bean instanceof Book) {
Book b = (Book)bean;
b.setBookName(b.getBookName()+"-Before");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization: Bean Name- " + beanName);
if (bean instanceof Book) {
Book b = (Book)bean;
b.setBookName(b.getBookName()+"-After");
}
return bean;
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Book implements InitializingBean {
private String bookName;
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
System.out.println("---Inside setBookName---");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("---afterPropertiesSet---");
bookName = bookName + "-Hello";
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.concretepage")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(name = "myBook")
public Book getBean() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookName("Mahabharat");
return book;
}
}
---Inside setBookName--- postProcessBeforeInitialization: Bean Name- myBook ---Inside setBookName--- ---afterPropertiesSet--- postProcessAfterInitialization: Bean Name- myBook ---Inside setBookName--- Book Name:Mahabharat-Before-Hello-After
8. @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy
Here we will discuss the role of JSR-250@PostConstruct and @PreDestroy annotation in Spring bean life cycle. Spring recommends these annotations to use as initialization and destruction callbacks. @PostConstruct annotated method executes just after dependency injection is completed to perform any initialization. It is customary to specify name as init(). @PreDestroy annotated method executes before the bean is being removed from Spring container. It is commonly used to release resources held by bean. It is customary to specify name as destroy(). This method is called on calling of close() method of Spring context. Find the sample example.
Book.java
package com.concretepage;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class Book {
private String bookName;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("inside init()");
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
System.out.println("---Inside setBookName---");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("inside destroy()");
}
}
---Inside setBookName--- inside init() Book Name:Mahabharat inside destroy()
9. InitializingBean and DisposableBean
In bean life cycle,InitializingBean interface is a initialization callback whose method afterPropertiesSet() executes once the dependency injection is completed. This method is used to check if all properties have been initialized or to perform any custom initialization. org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean interface is a destruction callback whose method destroy() executes before bean is going to be removed from Spring container. This method is used to release resources and is called on calling of close() method of Spring context.
Book.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Book implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String bookName;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Inside afterPropertiesSet()");
bookName+= "-Updated";
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
System.out.println("---Inside setBookName---");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Inside dispose()");
}
}
---Inside setBookName--- Inside afterPropertiesSet() Book Name:Mahabharat-Updated Inside dispose()
10. init-method and destroy-method
In Spring bean life cycleinit-method and destroy-method attributes are used to specify initialization and destruction callbacks custom method respectively in XML configuration. The equivalent attributes in JavaConfig are initMethod and destroyMethod respectively in a @Bean annotation. The customary method name for init-method or initMethod is init(). The customary method name for destroy-method or destroyMethod is destroy(). init() is called just after bean properties are set. This method is used to perform any custom initialization or to check if the values are set to the properties. destroy() method is called to release any resources before the Spring container removes the bean. destroy() will be called before bean is removed from Spring container. This method is called on calling of close() method of Spring context. Find the example.
Book.java
package com.concretepage;
public class Book {
private String bookName;
public void init() {
System.out.println("inside init()");
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
System.out.println("---Inside setBookName---");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("inside destroy()");
}
}
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(name = "myBook", initMethod="init", destroyMethod="destroy")
public Book getBean() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookName("Mahabharat");
return book;
}
}
init-method and destroy-method attributes are declared as follows.
<bean id="myBook" class="com.concretepage.Book" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> <property name="bookName" value="Mahabharat"/> </bean>
---Inside setBookName--- inside init() Book Name:Mahabharat inside destroy()


