Spring Boot Getting Started using Maven and Gradle with Eclipse
January 11, 2017
This page will walk through Spring boot getting started using maven and gradle with eclipse. Using Spring boot we can create standalone and production grade spring applications and that will be ready to run. Many spring configurations and JAR dependencies are auto configured. We can start our application using java -jar as well as deploying WAR file. Spring boot applications have following features.
1. Spring boot performs many configurations automatically. So the development is faster.
2. Spring Boot includes support for embedded Tomcat, Jetty, and Undertow servers with default port 8080.
3. Using spring boot we can externalize our configurations so that we can work with the same application code in different environments. We can use properties files, YAML files, environment variables and command-line arguments to externalize configuration.
4. Spring Boot uses Commons Logging for all internal logging, but we can also implement our Logging. By default Logback is used.
5. Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Redis, MongoDB, Neo4j, Elasticsearch, Solr and Cassandra NoSQL technologies.
6. Spring boot auto configures the necessary infrastructure to send and receive messages using JMS.
7. Spring boot provides @EnableAutoConfiguration that allows spring boot to configure spring application based on JAR dependencies that we have added.
8. Spring provides
@SpringBootApplication annotation that is the combination of @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan annotations.
9. Spring boot uses
SpringApplication.run() inside java main method to bootstrap the application.
10. Spring Boot provides a
@SpringBootTest annotation to test spring boot application.
Here on this page we will craete Spring REST application from scratch using spring boot step by step.
Contents
- Step 1: Software Used in the Demo Application
- Step 2: Start Creating Project using Spring Initializer
- Step 3: Configure Eclipse Classpath
- Step 4: Create Application
- Step 5: Run Application using Maven
- Step 6: Run Application using Gradle
- Understanding Maven for Spring Boot
- Understanding Gradle for Spring Boot
- Using @EnableAutoConfiguration Annotation and SpringApplication Class with Main method
- Using @SpringBootApplication Annotation
- Useful Commands for Spring Boot Application
- Some Spring Boot Application Starters
Step 1: Software Used in the Demo Application
We are using following software to run our application.1. Java 8 (Minimum Required Java 7)
2. Maven 3.3.9
3. Gradle 3.3
4. Spring Boot 1.4.3.RELEASE
5. Eclipse Mars
We need to make sure that these software are installed in the system.
Step 2: Start Creating Project using Spring Initializer
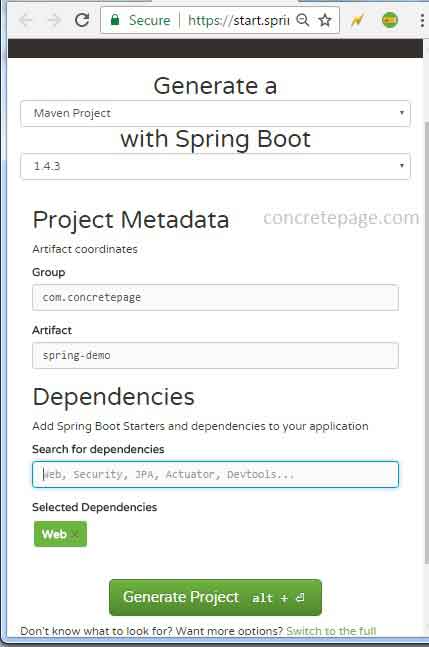
Go to the spring initializer URL https://start.spring.io and here we will select following details.a. First select Maven project or Gradle project. For the example we have selected maven project.
b. Now select the spring boot version. In our example we have selected spring boot version as 1.4.3.
c. We need to specify artifact coordinates i.e. group and artifact name. In our example I have specified project metadata as following.
Group: com.concretepage
Artifact: spring-demo
d. Now select dependencies required by project. If we want to create web project then enter web keyword and we will get drop-down for web and select it. This will provide all required JAR dependencies to develop web project.
e. Now click on Generate Project button. A project will get started to download.
Find the print screen.
Step 3: Configure Eclipse Classpath
First of all we will update eclipse classpath to configure required spring JAR as follows.a. Using command prompt, go to the root directory of the project.
b. Run the command mvn clean eclipse:eclipse
The above command will clean the existing classpath and configure all required JAR dependencies for our web project. If we select Gradle in spring initializer then we need to run following command to configure classpath.
gradle clean eclipse
Step 4: Create Application
Now the time is to start coding and creating our application. In our example we are creating a simple web application. We will create a simple REST project. The application will respond JSON format values of a list. Find the project structure.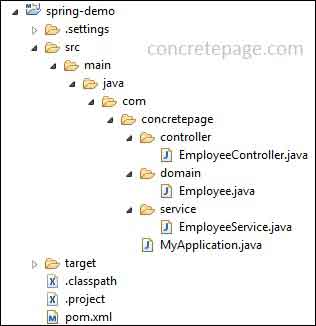
MyApplication.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
EmployeeController.java
package com.concretepage.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.concretepage.domain.Employee;
import com.concretepage.service.EmployeeService;
@RestController
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService service;
@RequestMapping("home")
public List<Employee> showData() {
List<Employee> list = service.getAllEmployee();
return list;
}
}
package com.concretepage.domain;
public class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
private String location;
public Employee(int id, String name, String location) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.location = location;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
}
package com.concretepage.service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.concretepage.domain.Employee;
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
public List<Employee> getAllEmployee() {
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Employee(1, "Mahesh", "Varanasi"));
list.add(new Employee(2, "Ram", "Ayodhya"));
list.add(new Employee(3, "Krishna", "Mathura"));
return list;
}
}
Step 5: Run Application using Maven
Now we will run our example using maven. Find the maven file. This file will be located in the root folder of project.pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.concretepage</groupId> <artifactId>spring-demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>spring-demo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
a. Using command prompt, go to the root directory of the project.
b. Run the command mvn spring-boot:run
The above command will start an embedded tomcat server by spring boot.
Using IDE we can also run our application.
1. Go to the main class
2. Right click and Run As -> Java Application
Now access the URL using browser.
http://localhost:8080/home
We will get following output.
[{"id":1,"name":"Mahesh","location":"Varanasi"},{"id":2,"name":"Ram","location":"Ayodhya"},{"id":3,"name":"Krishna","location":"Mathura"}]
a. Using command prompt, go to the root directory of the project.
b. Run the command mvn clean package
The above command will create two JAR files inside a directory named as target as follows.
1. Executable JAR i.e spring-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
2. Original JAR i.e spring-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.original
Run first JAR that is spring-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar as follows.
java -jar target/spring-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
The above command will execute JAR that will start embedded tomcat server. Now run the URL to access the application.
Step 6: Run Application using Gradle
Now we will use gradle in our application. While creating project structure from spring initializer https://start.spring.io we will select Gradle Project and rest will be the same as using maven project. Click on Generate Project button and a zip file will be downloaded. Import the project into eclipse and create your application. Now set eclipse classpath using following command.gradle clean eclipse
We can change gradle file as per our requirement. We are using following gradle file in our application. This file will be located in the root folder of project.
build.gradle
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '1.4.3.RELEASE'
id 'java'
id 'eclipse'
}
archivesBaseName = 'spring-demo'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")
}
a. Using command prompt, go to the root directory of the project.
b. Run the command gradle bootRun
The above command will start an embedded tomcat server by spring boot. Now access the URL using browser.
http://localhost:8080/home
To run the application with archive file, we will do as follows.
a. Using command prompt, go to the root directory of the project.
b. Run the command gradle clean build
The above command will create two JAR files inside a directory named as build/libs as follows.
1. Executable JAR i.e spring-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
2. Original JAR i.e spring-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.original
Run first JAR that is spring-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar as follows.
java -jar build/libs/spring-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
The above command will execute JAR that will start embedded tomcat server. Now run the URL to access the application.
Understanding Maven for Spring Boot
Here we will understand ourpom.xml. Spring provides many boot starters for different purposes. When we create a spring application then we have to configure all related JAR with proper versions. Sometimes these tasks are tedious. Here comes the role of spring boot starter. If we want to create web application then we can simply use spring boot starter for web and that will configure all related JAR. Let us understand spring boot starter management.
A. Spring Boot Starter Parent
Spring boot provides starters that resolve the required JAR dependencies. One of which is spring-boot-starter-parent. Now look into the
pom.xml. In parent section we have used following code snippet.
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
1. spring-boot-starter-parent provides dependency management. It keeps the list of dependencies it supports. When using spring-boot-starter-parent with a base version then other spring boot starters configured in pom.xml need not to specify versions. If version specified then the default will be overridden.
2. spring-boot-starter-parent provides useful maven defaults. Using command
mvn dependency:tree
We get the tree representation of project dependencies. Suppose we have configured other spring boot starters also and now we want to know all JAR dependencies used by the project then we can run the command mvn dependency:tree and it will print all JAR names used by the project.
B. Spring Boot Starter Web
As we have created web application, so we have added spring boot starter for web. Find the code snippet from
pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
pom.xml, spring automatically understands that we are creating spring web application and accordingly spring boot configures the required JAR.
C. Spring Boot Maven Plugin to Create Executable JAR
Spring boot provides spring-boot-maven-plugin that is used to create executable JAR of the application. We will configure it as follows.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
1. mvn clean package : Creates executable and original JAR both.
2. mvn spring-boot:run : Starts the tomcat server to run application in exploded form.
Understanding Gradle for Spring Boot
Now we will discuss gradle used in our web application. Look into thebuild.gradle file. There is no spring boot starter parent. We are directly using spring boot starter web. Let us understand build.gradle step by step.
A. Spring Boot Starter Parent
There is no spring boot starter parent in gradle. But we can use command to get dependency tree.
gradle dependencies
The above command gives the list of direct and transitive dependencies.
B. Spring Boot Starter Web
As per application requirement, we configure spring boot starter. We have created a web application, so we need to configure spring-boot-starter-web. We have configured it as follows.
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '1.4.3.RELEASE'
C. Spring Boot Gradle Plugin to Create Executable JAR
spring-boot-gradle-plugin is available in gradle. We need not to configure it separately. Like maven, we can create executable JAR using gradle. spring-boot-gradle-plugin provides the following command functionality.
1. gradle clean build : Create executable and original JAR.
2. gradle bootRun : Starts the tomcat server to run application in exploded form.
Using @EnableAutoConfiguration Annotation and SpringApplication Class with Main method
To run spring boot application we need to create a class with main method and annotated with@EnableAutoConfiguration as follows.
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
SpringApplication: It bootstraps a spring application by calling
SpringApplication.run().
When we run main method we will get logs as follows.
. ____ _ __ _ _ /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \ ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \ \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) ) ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / / =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/ :: Spring Boot :: (v1.4.3.RELEASE) 2017-01-11 18:27:52.323 INFO 2208 --- [ main] com.concretepage.MyApplication : Starting MyApplication on Renu-PC with PID 2208 (F:\arvind\PROJECT\mars\spring-boot\spring-demo\build\classes\main started by Renu in F:\arvind\PROJECT\mars\spring-boot\spring-demo) 2017-01-11 18:27:52.328 INFO 2208 --- [ main] com.concretepage.MyApplication: No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default
Using @SpringBootApplication Annotation
In developing spring web application, we need to use spring annotations such as@Configuration and @ComponentScan. Mostly we use these annotations with @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation at main class while creating boot application. In this case Main class should be located at the parent package as follows.
src/main/java -
|
-- MyApplication.java
-- controller
-- domain
-- service
@SpringBootApplication annotation that is the combination of @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan annotations. So we can use MyApplication.java in following manner.
1. Using
@SpringBootApplication
MyApplication.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
2. Using
@Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan annotations.
MyApplication.java
package com.concretepage;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
Useful Commands for Spring Boot Application
Here we are consolidating the commands used by the spring boot application.1. For Maven
mvn dependency:tree: Prints tree of JAR dependencies.
mvn clean eclipse:eclipse: Creates
.classpath
mvn clean package: Creates JAR/WAR for the application.
mvn spring-boot:run: Starts tomcat to run application in exploded form.
2. For Gradle
gradle dependencies: Prints list of direct and transitive dependencies.
gradle clean eclipse: Creates
.classpath
gradle clean build: Creates JAR/WAR for the application.
gradle bootRun: Starts tomcat to run application in exploded form.
3. For Java
a. Run Executable JAR.
java -jar <JAR-NAME>
java -Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:server=y,transport=dt_socket,address=8000,suspend=n \ -jar <JAR-NAME>
Some Spring Boot Application Starters
Find some frequently used spring boot application starters.spring-boot-starter-web : Used in Web, REST and Spring MVC applications.
spring-boot-starter-security : Used in spring security application.
spring-boot-starter-web-services : Used in Spring Web Services.
spring-boot-starter-mail : Used for Java Mail Support in spring framework.
spring-boot-starter-test : Used in Spring Framework Test application.
spring-boot-starter-jdbc : Used in JDBC integration with Spring Framework.
spring-boot-starter-validation : Used in Java Bean Validation with Hibernate Validator.
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf : Used in Thymeleaf integration with Spring Framework.
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa : Used in Spring Data JPA with Hibernate.
spring-boot-starter-freemarker : Used in FreeMarker integration with Spring Framework.
I am done now. Happy Spring Boot learning!


